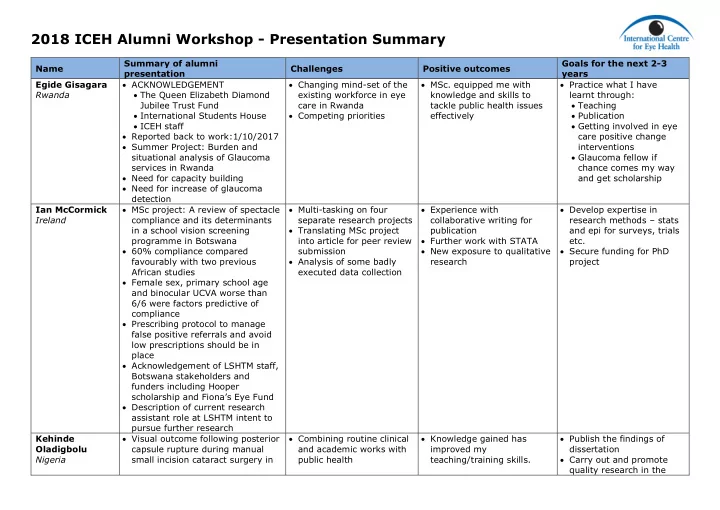

2018 ICEH Alumni Workshop - Presentation Summary Summary of alumni Goals for the next 2-3 Name Challenges Positive outcomes presentation years Egide Gisagara ACKNOWLEDGEMENT Changing mind-set of the MSc. equipped me with Practice what I have Rwanda The Queen Elizabeth Diamond existing workforce in eye knowledge and skills to learnt through: Jubilee Trust Fund care in Rwanda tackle public health issues Teaching International Students House Competing priorities effectively Publication ICEH staff Getting involved in eye Reported back to work:1/10/2017 care positive change Summer Project: Burden and interventions situational analysis of Glaucoma Glaucoma fellow if services in Rwanda chance comes my way Need for capacity building and get scholarship Need for increase of glaucoma detection Ian McCormick MSc project: A review of spectacle Multi-tasking on four Experience with Develop expertise in Ireland compliance and its determinants separate research projects collaborative writing for research methods – stats in a school vision screening Translating MSc project publication and epi for surveys, trials programme in Botswana into article for peer review Further work with STATA etc. 60% compliance compared submission New exposure to qualitative Secure funding for PhD favourably with two previous Analysis of some badly research project African studies executed data collection Female sex, primary school age and binocular UCVA worse than 6/6 were factors predictive of compliance Prescribing protocol to manage false positive referrals and avoid low prescriptions should be in place Acknowledgement of LSHTM staff, Botswana stakeholders and funders including Hooper scholarship and Fiona’s Eye Fund Description of current research assistant role at LSHTM intent to pursue further research Kehinde Visual outcome following posterior Combining routine clinical Knowledge gained has Publish the findings of Oladigbolu capsule rupture during manual and academic works with improved my dissertation Nigeria small incision cataract surgery in public health teaching/training skills. Carry out and promote quality research in the
2018 ICEH Alumni Workshop - Presentation Summary Kaduna, Nigeria - a case control Getting support from Research and management university/hospital where study. stakeholders for rural eye skills for enhanced I work Methods: Analytical, case care services performance - concluded Partner with stakeholders controlled, hospital-based study. Scarcity and difficulty supervision of 2 to establish sustainable Result: Participants with posterior accessing research grants ophthalmology residents’ rural eye care capsular rupture (PCR) and >60 dissertations for the final programmes years of age were 7.0 and 1.4 fellowship award. Involve in advocacy for times respectively, more likely to Partnership with quality eye care have poor visual outcome (<6/18) stakeholders in promoting compared to others. eye health education and Acknowledgement of CSSS, BCPB, services – ABU campus FM ICEH lecturers and management and rural health authorities. of LSHTM. Made new friends and developed wider network with people from other parts of the world. Robert Ewusi- Acknowledgement to BCPB, CSSS, Combining clinical work Networking with colleague Planning to do a public Wilson Lecturers, ICEH staff and public health work and staff of ICEH health project to improve Ghana Summer Project: Benefits to NHS Gained new knowledge and cataract surgical services partners from the VISION 2020 skills to do research and uptake and a school LINKS programme. plan for public health screening programme 6 UK NHs partners were included programmes Do more research and in the study look into doing a PhD Teams were made up of 8 ophthalmologists, 2 optometrists, 3 orthoptists and 2 registered nurses. Teams visited four African countries namely Zambia, Malawi, Tanzania, and The Gambia. More than half of them noted that they have had significant or slight improvement in the 6 dimensions namely communication, personal development, equality and diversity, service improvement, project management and developing leadership skills.
2018 ICEH Alumni Workshop - Presentation Summary Shalinder Acknowledgement to BCPB, CSSS, Putting knowledge and Gained the knowledge and Complete residency Sabherwal lecturers, ICEH staff skills into practice skills to implement eye care programme India Reported back to work programme from the MSc Involve in public health Summer Project: Evaluation Networking with colleague approach, opportunity affirming eye care services in and staff of ICEH gets to my way Jigawa State North-Western Summer project: presence Publish, do more research Nigeria. of HS support to PEC and look into doing PhD. Need for training, supportive supervision and supply for basic PEC. Lila Puri Acknowledgement Human resource as it in Research methodology Involve in 5-year corneal Nepal Lieutenant-Colonel Henry remote area training to residents and infection project – LSHTM Kirkpatrick Scholarship Government, new ophthalmologists. and Lahan Eye Hospital Supervisor- Matthew Burton structure DR proposal to Lions PEEK for School health Fellow colleagues Finding time to pursue International which is programme ICEH research amongst busy approved- 200,000 USD Combine public health for LSHTM clinical/administrative Fellowship curriculum eye care with clinical LSHTM Trust Fund responsibilities development ophthalmology Summer project: Microbial Balancing clinical work in Eye care center Strengthen research and Keratitis in South East Nepal: hospital and public health establishment- 2 community activities Determinants of poor outcome RAAB involvement – Strengthen training and strategies to improve the involved in planning programme clinical and outcome Drafting eye care road map community related Aim: To determine factors in province 2 Involve in strategic associated with a poor outcome Planning of CBR in one planning from Microbial Keratitis (MK) in district as pilot project South East Nepal and make School eye health recommendations for community programme and hospital-based interventions Patient satisfaction survey to improve the outcome. at the hospital MK was most frequently seen in Surgical audit to improve the young and productive age the surgical quality group Clinical Quality audit to most people were involved in improve the clinical services either farming or household work Evaluation of services at 2 activities. eye hospitals as a team The most common predisposing member of evaluation team factor was ocular trauma Delay in presentation to the hospital was common findings
2018 ICEH Alumni Workshop - Presentation Summary Patient lack of accessibility to eye care service followed by lack of awareness about the disease, unavailability of eye care service, cost, visit to various places for the initial consultations and late referral, lack of awareness about eye hospital, lack of family support and faith on traditional healer were main barriers for early uptake of existing corneal services by patients. approximately three- fourth of the total patients had visited places like local medical shop, government health center and traditional healers Most of the patients 86(49%) were using antibiotic eye drops bought mostly from local medical store.38 (22%) patients were using steroid eye drops and 22(13%) were using TEMs. fungal keratitis (48%)was more common than bacterial keratitis (22%) From the 2016 data analysis, we found that 35% were blind in the affected eye and 42% had poor outcome. In the prospective study, 60% were blind in the affected eye at presentation, 57% had poor outcome at the end of 3 weeks follow up. age, trauma (with vegetative matter), use of steroid and TEMs and delayed presentation were significant factors for the poor visual outcome as found in the
Recommend
More recommend