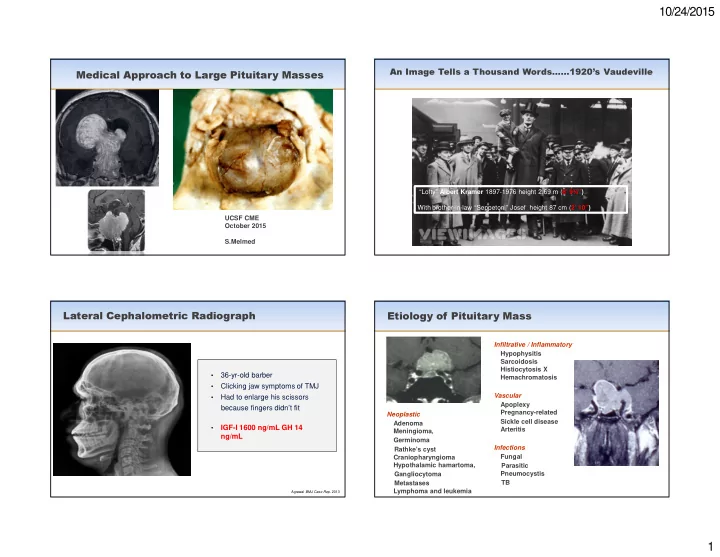

10/24/2015 An Image Tells a Thousand Words……1920’s Vaudeville Medical Approach to Large Pituitary Masses “Lofty” Albert Kramer 1897-1976 height 2.69 m ( 8’ 9¾”) With brother-in-law “Seppetoni” Josef height 87 cm ( 2’ 10”) UCSF CME October 2015 S.Melmed Lateral Cephalometric Radiograph Etiology of Pituitary Mass Infiltrative / Inflammatory Hypophysitis Sarcoidosis Histiocytosis X • 36-yr-old barber Hemachromatosis • Clicking jaw symptoms of TMJ Vascular • Had to enlarge his scissors Apoplexy because fingers didn’t fit Neoplastic Pregnancy-related Sickle cell disease Adenoma • IGF-I 1600 ng/mL GH 14 Arteritis Meningioma , ng/mL Germinoma Infections Rathke’s cyst Craniopharyngioma Fungal Hypothalamic hamartoma, Parasitic Pneumocystis Gangliocytoma TB Metastases Lymphoma and leukemia Agrawal BMJ Case Rep . 2013 1
10/24/2015 Image Challenge What is the most likely diagnosis in this 32-year-old man? A. Craniopharyngioma B. Cushing disease C. Meningioma D. Prolactinoma E. Rathke cleft cyst Prolactinoma is the most common cause of a pituitary adenoma. This large tumor regressed substantially following cabergoline treatment . IGF-1 1150 ng/ml Male Macroprolactinomas Giant pituitary adenoma PRL 103 ng/mL PRL on dilution: 13,000 ng/ml Stalk Compression? PRL Capture Antibody Signal Antibody Cabergoline-induced shrinkage HOOK EFFECT Ahmed NEJM 2010 Fleseriu J Neurooncol 2006 Anwuzia-Iwegbu BMJ 2013 2
10/24/2015 Prolactinoma: Cabergoline-induced Bromocriptine-induced brainstem angulation pneumocephalus detected by brain CT with invasive prolactinoma CT shows bony destruction of clivus and skull base Lou JCEM 2013 Machicado JCEM 2012 Hypo/hypergonadism ? Giant adenomas PITUICYTOMA Thyroid transcription factor 1 Sagittal Left Right ovary ovary Right ovary Sphenoid sinus Suprasellar extension Newnham NEJM 2008 Amenorrhea, Abdominal Pain, and Weight Gain Coronal FSH-oma E2 23,501 pmol/l LH <0.1 IU/l FSH 27 IU/l Suprasellar vessel encroachment Van Wijk NEJM 2011 Cappabianca Acta Neurochir , 2014 3
10/24/2015 Non-functioning Adenomas: Atypical Pituitary Adenomas Recurrence-free Survival Invasion of neighboring structures • rapid growth • recurrence • diameter >4 cm • resistance to medical therapy • extracranial metastasis (carcinoma) ACTH WHO 2004 Aggressive,invasive ,pleomorphic increased mitotic activity, Ki-67 >3% Mayson , J Neurooncol , 2014 p53 immunoreactivity p53 Ki-67 Losa, J Neurosurg , 2008 Zada J Neurosurg 2011 Silent Corticotroph Adenoma 69 yr old man with acute food poisoning � In good health when eating breakfast at restaurant Nonfunctioning � Stomach cramps, vomiting, bloody diarrhea, Large/Invasive � Severe headache Cytologically Atypical acute bacterial enterocolitis Plurihormonal � Late p.m.: Diplopia Right ptosis Non-reactive pupils 3 rd , 4 th , 6 th nerve palsies Apoplexy PAS ACTH POMC 4
10/24/2015 Hypophysitis with stalk thickening Hypophysitis with stalk thickening Sagittal T1 post contrast Coronal T1 post-contrast M.Maya M.Maya Hypophysitis Hypophysitis PRL TSH Injections : CTLA-4 blocking AB Control Monocytes GH Anti-CTL4 ACTH CD45 FSH F4/80 S-100 Sci Trans Med 6(230):1-11 , 2014 Sci Trans Med 6(230):1-11 , 2014 5
10/24/2015 Hypophysitis Lessons learned……… Significance: All cancer patients receiving CTLA-4 blockers should be screened for pituitary dysfunction and hormone replacement initiated. Survival Pre-Rx Rx Rx Post-Rx 100 80 Percent survival + Hypophysitis, p=0.05 Combination with PD-1 blockade may be an added risk factor. 60 40 Hypophysitis may be a positive survival predictor No Hypophysitis 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 Months after treatment initiation Hypophysitis positively predicts metastatic melanoma survival J Clin Endocrinol Metab 99:4078, 2014 Obesity : Hypothalamic tumor Giant craniopharyngioma MRI T2 : hyperintense lesion All 3 cranial fossae Extending as low as C2 anterior to the brainstem. Müller Horm Res 2008 Garg Ped Neurosurg 2013 6
10/24/2015 Intermittent Facial Flushing and Diarrhea Aggressive parasellar mass Adamantinomatous Craniopharyngioma Containing Teeth Mc Cormack NEJM 2014 Beaty N Engl J Med 2014. Octreoscan: Chronic acromegaly Octreoscan: Pituitary Carcinoma 38-year-old female Post-GTT GH 27 ng/mL IGF-1 498 ng/mL MRI S/P transsphenoidal surgery 5 years prior MRI nl 60 50 GH (ng/mL) 40 30 *A:V gradient 1:7 20 10 Octreoscan 0 –30d –7d 3 h 9 h 18 h 40 h Surgery * Melmed, NEJM 322, 1990 Greenman JCEM 1996 7
10/24/2015 Non-secreting Pituitary Mass Pituitary Imaging……………… Lawson JCEM 2008 Differential diagnosis by MRI and clinical features P ancreas P ituitary Dynamic pituitary reserve testing Non-functioning Other sellar mass adenoma Exclude aneurysm Micro adenoma Macro adenoma Low risk of Surgery visual loss Histologic diagnosis Surgery Observe P arathyroid May require disease- Trophic hormone Follow-up: MRI MRI MRI specific Trophic testing and therapy hormone testing replacement and replacement Melmed & Jameson Harrisons Internal Medicine 2015 Aggressive GH-secreting tumor ………………………. 50 * TumorA/V 45 40 GH GRADIENT * SERUM GH (ng/ml) 35 34/368 30 25 20 15 10 Galactorrhea 5 Elevated GH and IGF1 0 Small pituitary gland -72 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 24 48 72 144 hours Ectopic GH Melmed NEJM 1985 8
10/24/2015 Reserves 9
Recommend
More recommend