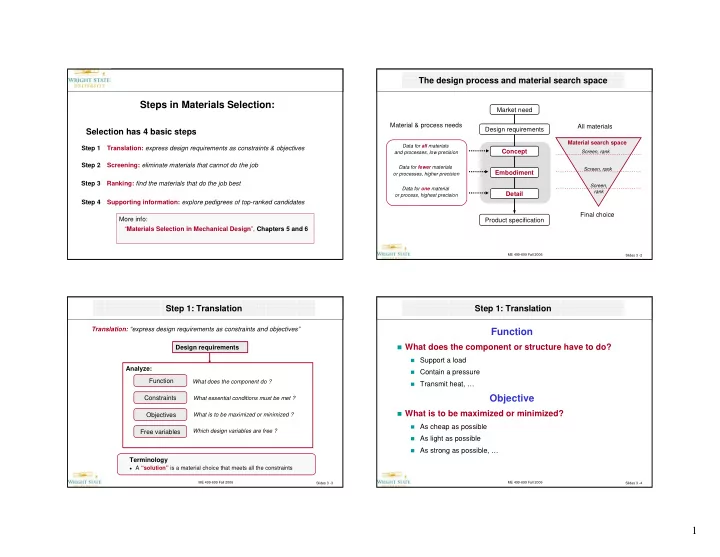

The design process and material search space Steps in Materials Selection: Market need Material & process needs All materials Design requirements Selection has 4 basic steps Material search space Data for all materials Step 1 Translation: express design requirements as constraints & objectives Concept Screen, rank and processes, low precision Step 2 Screening: eliminate materials that cannot do the job Data for fewer materials Screen, rank Embodiment or processes, higher precision Step 3 Ranking: find the materials that do the job best Screen, Data for one material rank Detail or process, highest precision Step 4 Supporting information: explore pedigrees of top-ranked candidates Final choice More info: Product specification “ Materials Selection in Mechanical Design ”, Chapters 5 and 6 ME 499-699 Fall 2006 Slides 3 -2 Step 1: Translation Step 1: Translation Translation: “express design requirements as constraints and objectives” Function � What does the component or structure have to do? Design requirements � Support a load Analyze: � Contain a pressure Function What does the component do ? � Transmit heat, … Objective Constraints What essential conditions must be met ? � What is to be maximized or minimized? Objectives What is to be maximized or minimized ? � As cheap as possible Free variables Which design variables are free ? � As light as possible � As strong as possible, … Terminology � A “solution” is a material choice that meets all the constraints ME 499-699 Fall 2006 ME 499-699 Fall 2006 Slides 3 -3 Slides 3 -4 1
Step 1: Translation Step 1: Translation Constraints Free Variables � What essential conditions must be met? � Which design variables are free? � Component must be of a certain length � These variables are under our control to � Component must carry a certain load change in order for the component to perform � Component must operate above a certain temperature,… the function, satisfy the objectives, without � Hard Constraints (non-negotiable) violating the constraints � Component MUST meet the specification � The materials choice (one we will always have!) � The beam must support the weight of a 300 lb person � The cross sectional area � Soft Constraints (negotiable) � The cross sectional shape … � Component MAY meet the specification - often aesthetic or cost related e.g. beam should cost less than $50 � If a design can’t meet the soft constraint no one dies ME 499-699 Fall 2006 ME 499-699 Fall 2006 Slides 3 -5 Slides 3 -6 Step 2: Screening Screening Graph Stage – Single property � Design requirements can be qualitative or yes/no 100 � Material must be transparent � Design requirements are often quantitative � Material must be able to operate above 1000ºC 10 Price (USD/kg) � Material must be less dense than water ( ρ < 1000 kg/m 3 ) � Material must have a Young’s modulus > 100 GPa 1 � We can use Property charts to find subset of materials that satisfy screening criteria � Find a stiff (E>100 GPa), cheap material (<$0.50/kg) for 0.1 building and highway construction MaterialUniverse:\Ceramics and glasses MaterialUniverse:\Hybrids: composites, foams, natural materials MaterialUniverse:\Metals and alloys MaterialUniverse:\Polymers and elastomers Material ME 499-699 Fall 2006 ME 499-699 Fall 2006 Slides 3 -7 Slides 3 -8 2
Screening Graph Stage – Single property Screening Graph Stage – Two properties Low cost and high stiffness materials for construction Low carbon steel Limestone 1e11 Cement Concrete Marble 1e11 1e10 Young's modulus (Pa) 1e10 Sandstone Young's modulus (Pa) 1e9 1e9 1e8 1e8 1e7 1e7 1e6 1e6 MaterialUniverse:\Ceramics and glasses MaterialUniverse:\Hybrids: composites, foams, natural materials MaterialUniverse:\Metals and alloys MaterialUniverse:\Polymers and elastomers Material 0.1 1 10 100 Price (USD/kg) ME 499-699 Fall 2006 ME 499-699 Fall 2006 Slides 3 -9 Slides 3 -10 Screening Graph Stage Material for a Heat Sink T s >1000ºC and λ <10W/m.K Need a material to make a heat sink for a power 7 of 94 electronics application. The material must not Materials 1000 interfere with the functioning of the electronic Maximum service temperature (°C) component and must not allow the temperature to 500 rise above 200ºC. 200 Selection for this application is demonstrated using the “Limit” stage of the CES Edupack 100 Software 50 0.1 1 10 100 Thermal conductivity (W/m.K) ME 499-699 Fall 2006 ME 499-699 Fall 2006 Slides 3 -11 Slides 3 -12 3
Material for a Heat Sink Material for a Heat Sink Function Heat sink Translation: “Express the requirement in terms of properties” Translation Constraints Screening: “Eliminate materials that can’t do the job” Retain materials with: • operate at 200 o C 1. Max service temp > 200º C • be electrical insulator 2. “Good insulator”, or R > 10 20 μ ohm.cm Example: heat sink for • conduct heat well 3. “Good T-conductor” or T-conduct. λ > 100 W/m.K power electronics 4. Density < 3 Mg/m 3 • not heavy Level 1 Level 2 Free variable Choice of material and process ME 499-699 Fall 2006 ME 499-699 Fall 2006 Slides 3 -13 Slides 3 -14 Screening using a LIMIT STAGE Screening using GRAPH STAGE Max service temperature (K) WC Toolbar Browse Select Search Print Search web � Screening using Steel bar-charts Copper Alumina CFRP Materials, Level 1 200 0 C PEEK Glass A limit stage PP GFRP Aluminum PTFE Zinc Fibreboard Mechanical attributes Minimum Maximum New Lead Density Mg/m 3 Metals Polymers Ceramics Composites Young’s modulus GPa R > 10 20 μΩ .cm 1000 Elastic limit MPa Ceramics � Graph stage Metals Thermal attributes � Screening using Thermal conductivity (W/m.s) Max. service temp. C 200 100 property charts λ > 100 W/m.K � Limit stage T-expansion 10 -6 /K T-conductivity 100 W/m.K � Tree stage 10 Electrical attributes Polymers & b Composites elastomers Good insulator 1 Poor insulator Poor conductor Good conductor 0.1 Foams 0.01 10 10 1 10 20 10 30 Electrical resistivity ( μΩ .cm) ME 499-699 Fall 2006 ME 499-699 Fall 2006 Slides 3 -15 Slides 3 -16 4
Screening using a TREE STAGE The main points • The four steps of selection: Toolbar Browse Select Search Print Search web 1. Translation , giving constraints and objectives These are often enough ! 2. Screening , using constraints Select what? Materials, Level 1 3. Ranking , using objectives 4. Supporting information for prime candidates New A tree stage • Translation of design requirements into a material prescription: analyse � Graph stage the function of the component, Cast the constraints must meet, � Limit stage Join Deform the objective of the design, Mold Process Shape � Tree stage the free variables of the problem Composite Surface Powder • CES allows Prototype screening using limit stages, graph stages and tree stages ME 499-699 Fall 2006 ME 499-699 Fall 2006 Slides 3 -17 Slides 3 -18 Homework: Select a new material for a CD case Translation: “express design requirements as constraints and objectives” CD cases are made of polystyrene (PS). They crack and scratch the disks. Find a better material. Design requirements Translation Function CD enclosure � Contain CD Strength > PS Toughness > PS � Protect without scratching Constraints Transparency Smoothness � Internal label visible Recyclable � Eco-friendly Objectives Minimize cost � Cheap Choice of material Free variable and process ME 499-699 Fall 2006 Slides 3 -19 5
Recommend
More recommend