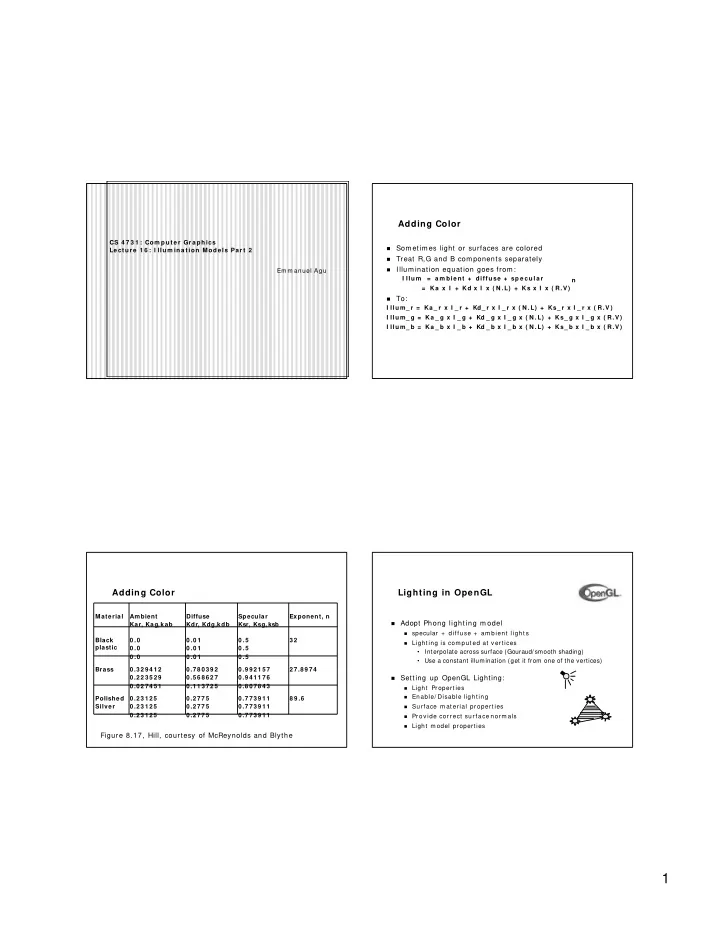

Adding Color CS 4 7 3 1 : Com put e r Gr a phics � Som etim es light or surfaces are colored Le ct ur e 1 6 : I llum ina t ion M ode ls Pa r t 2 � Treat R,G and B com ponents separately � I llum ination equation goes from : Em m anuel Agu I llu m = a m bie nt + diffuse + sp e cu la r n = Ka x I + Kd x I x ( N .L) + Ks x I x ( R.V ) � To: I llu m_ r = Ka _ r x I _ r + Kd_ r x I _ r x ( N .L) + Ks_ r x I _ r x ( R.V ) I llu m_ g = Ka _ g x I _ g + Kd _ g x I _ g x ( N .L) + Ks_ g x I _ g x ( R.V ) I llu m_ b = Ka _ b x I _ b + Kd _ b x I _ b x ( N .L) + Ks_ b x I _ b x ( R.V ) Adding Color Lighting in OpenGL Material Ambient Diffuse Specular Exponent, n � Adopt Phong light ing m odel Kar, Kag, kab Kdr, Kdg,kdb Ksr, Ksg, ksb � specular + diffuse + am bient light s Black 0 .0 0 .0 1 0 .5 3 2 � Light ing is com put ed at vert ices plastic 0 .0 0 .0 1 0 .5 • Interpolate across surface (Gouraud/smooth shading) 0 .0 0 .0 1 0 .5 • Use a constant illumination (get it from one of the vertices) Brass 0.329412 0.780392 0.992157 27.8974 0.223529 0.568627 0.941176 Setting up OpenGL Lighting: � 0.027451 0.113725 0.807843 � Light Properties � Enable/ Disable light ing Polished 0.23125 0.2775 0.773911 8 9 .6 Silver 0.23125 0.2775 0.773911 � Surface m at erial propert ies 0.23125 0.2775 0.773911 � Provide correct surface norm als � Light m odel properties Figure 8.17, Hill, courtesy of McReynolds and Blythe 1
Light Properties Property Exam ple � Properties: � Define colors and position a light � Colors / Posit ion and t ype / at t enuat ion glLight fv( light , pr ope r t y, va lue ) GLfloat light_ambient[ ] = { 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0} ; colors GLfloat light_diffuse[ ] = { 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0} ; 3 2 1 GLfloat light_specular[ ] = { 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0} ; Position GLfloat light_position[ ] = { 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0} ; (1) constant: specify which light you want to set the property What if I set E.g: GL_LI GHT0, GL_LI GHT1, GL_LI GHT2 … you can glLightfv(GL_LIGHT0, GL_AMBIENT, light_ambient); Posit ion t o create multiple lights (OpenGL allows at least 8 lights) glLightfv(GL_LIGHT0, GL_DIFFUSE, light_diffuse); ( 0,0,1,0) ? (2) constant: specify which light property you want to set the value glLightfv(GL_LIGHT0, GL_SPECULAR, light_specular); E.g: GL_AMBI ENT, GL_DI FFUSE, GL_SPECULAR, GL_POSI TI ON glLightfv(GL_LIGHT0, GL_POSITION, light_position); ( check t he r ed book for m or e) (3) The value you want to set to the property Types of lights Turning on the lights � OpenGL supports two types of lights � Turn on the power (for all the lights) � Local light ( point light ) � glEnable( GL_LI GHTI NG) ; � I nfinit e light ( direct ional light ) � glDisable ( GL_LI GHTI NG) ; Determ ined by the light positions you provide � � w = 0: infinit e light source ( fast er) Flip each light’s switch � � w ! = 0: point light – posit ion = ( x/ w , y/ w , z/ w ) � glEnable( GL_LI GHT n ) ( n = 0,1,2,…) GLfloat light_position[ ] = { x,y,z,w} ; glLightfv(GL_LIGHT0, GL_POSITION, light_position); 2
Controlling light position Material Properties � Modelview m atrix affects a light’s position � The color and surface properties of a m aterial (dull, � Two options: shiny, etc) � Option a: � How m uch the surface reflects the incident lights � Treat light like vert ex (am bient/ diffuse/ specular reflecetion coefficients) � Do pushMatrix, t ranslat e, rot at e, .. glLight fv position , glMaterialfv(face, property, value) popm atrix � Then call gluLookat � Light m oves independent ly of cam era Face: m at erial propert y for which face ( e.g. GL_FRONT, GL_BACK, � Option b: GL_FRONT_AND_BACK) � Load ident it y m at rix in m odelview m atrix Propert y: what m at erial propert y you want t o set ( e.g. GL_AMBI ENT, � Call glLight fv t hen call gluLookat GL_DI FFUSE,GL_SPECULAR, GL_SHI NI NESS, GL_EMI SSI ON, et c) Value: t he value you can t o assign t o t he pr oper t y � Light appears at t he eye ( like a m iner’s lam p) Material Exam ple Global light properties � Define am bient/ diffuse/ specular reflection and shininess glLightModelfv(property, value) � Enable two sided lighting � GLfloat m at_amb_diff[ ] = { 1.0, 0.5, 0.8, 1.0} ; � propert y = GL_LI GHT_MODEL_TWO_SI DE refl. coeff. GLfloat m at_specular[ ] = { 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0} ; � value = GL_TRUE ( GL_FALSE if you don’t want t wo sided GLfloat shininess[ ] = { 5.0} ; (range: dull 0 – very shiny 128) lighting) � Global am bient color glMaterialfv(GL_FRONT_AND_BACK, GL_AMBIENT_AND_DIFFUSE, � Propert y = GL_LI GHT_MODEL_AMBI ENT m at_am b_diff); � Value = ( red, green, blue, 1.0) ; glMaterialfv(GL_FRONT, GL_SPECULAR, mat_speacular); � Check the red book for others glMaterialfv(GL_FRONT, GL_SHININESS, shininess); 3
Surface Norm als Lighting revisit � Where is lighting performed in the graphics pipeline? � Correct norm als are essential for correct lighting � Associate a norm al to each vertex v1, m 1 glBegin(… ) glNorm al3f( x,y,z) m odeling and per vert ex proj ect ion glVertex3f(x,y,z) viewing lighting … v3, m 3 v2, m 2 glEnd() viewport interpolate Rast erizat ion clipping vert ex colors m apping texturing � The norm als you provide need to have a unit length shading � You can use glEnable ( GL_ N ORM ALI ZE) t o hav e OpenGL norm alize all t he norm als Display Polygon shading m odel Flat shading � Flat shading - com pute lighting once and assign the � Only use one vertex norm aland m aterial property to color to the whole (m esh) polygon com pute the color for the polygon Benefit: fast to com pute � Used when: � � Polygon is sm all enough � Light source is far away ( why?) � Eye is very far away ( why?) OpenGL com m and: glShadeModel(GL_FLAT) � 4
Mach Band Effect Sm ooth shading Fix the m ach band effect – rem ove edge discontinuity � � Flat shading suffers from “m ach band effect” Com pute lighting for m ore points on each face � � Mach band effect – hum an eyes accentuate the discontinuity at the boundary perceived intensity Fla t sha ding Sm oot h sha ding Side view of a polygonal surface Sm ooth shading Gouraud Shading Two popular m ethods: � The sm ooth shading algorithm used in OpenGL � � Gouraud shading ( used by OpenGL) g lSh a d e M od e l( GL_ SM OOTH ) � Phong shading ( bet t er specular highlight , not in OpenGL) � Lighting is calculated for each of the polygon vertices � Colors are interpolated for interior pixels 5
Gouraud Shading Gouraud Shading � Per- vertex lighting calculation Com pute vertex illum ination (color) before the � � Norm al is needed for each vertex projection transform ation � Per- vertex norm al can be com puted by averaging the � Shade interior pixels: color interpolation (norm als are adjust face norm als not needed) C1 n n 2 n 1 for all scanlines Ca = lerp(C1, C2) Cb = lerp(C1, C3) n 4 n 3 n = ( n1 + n2 + n3 + n4) / 4.0 C3 C2 * lerp: linear int erpolat ion Lerp( Ca, Cb) Gouraud Shading Gouraud Shading Problem Lighting in the polygon interior can be inaccurate � � Linear interpolation x = a / (a+ b) * v1 + b/ (a+ b) * v2 a b x v1 v2 � I nterpolate triangle color: use y distance to interpolate the two end points in the scanline, and use x distance to interpolate interior pixel colors 6
Phong Shading Phong Shading � Norm al interpolation I nstead of interpolation, we calculate lighting for each � n1 pixel inside the polygon (per pixel lighting) � Need norm als for all the pixels – not provided by user nb = lerp(n1, n3) na = lerp(n1, n2) � Phong shading algorithm interpolates the norm als and com pute lighting during rasterization ( need t o m ap t he lerp(na, nb) norm al back t o w orld or eye space t hough) n2 n3 � Slow – not supported by OpenGL and m ost graphics hardware References � Hill, chapter 8 7
Recommend
More recommend