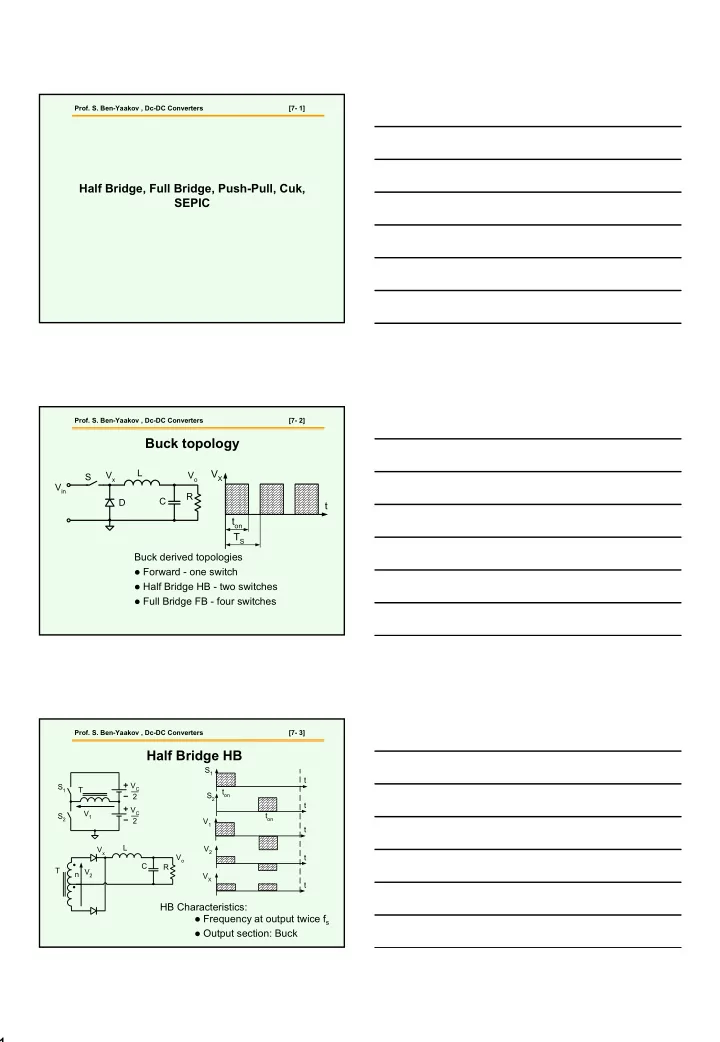

Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , Dc-DC Converters [7- 1] Half Bridge, Full Bridge, Push-Pull, Cuk, SEPIC Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , Dc-DC Converters [7- 2] Buck topology L V X V x V o S V in R C D t t on T S Buck derived topologies � Forward - one switch � Half Bridge HB - two switches � Full Bridge FB - four switches Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , Dc-DC Converters [7- 3] Half Bridge HB S 1 t V C S 1 T t on S 2 2 t V C V 1 S 2 t on 2 V 1 t L V x V 2 V o t C R T n V 2 V X t HB Characteristics: � Frequency at output twice f s � Output section: Buck 1
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , Dc-DC Converters [7- 4] Full Bridge FB L V x V C V o S 1 S 3 C R T T C n V 2 1 S 2 S 4 S 1 t S 2 t T S S 3 t S 4 t Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , Dc-DC Converters [7- 5] Reset of Forward, HB, FB � Forward - auxiliary winding � HB,FB - Natural L V x Example HB V C V o C R C 1 S 1 T n V 2 T C 2 V 1 S 2 V C V T S � C 1 , C 2 capacitor divider 1 2 2 t on t T S V C t on − 2 2 Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , Dc-DC Converters [7- 6] Push-Pull 2
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , Dc-DC Converters [7- 7] Forward, HB, FB, PP Switch Utilization I L ripple for same L Important consideration: V s (off), I s (on) ∆ � Forward: I Assumption: ∆ I � Same input and output power � HB, FB, PP: 2 � Same input voltage I S I FW FORWARD t off t on t V S + D V 1 on C D off t Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , Dc-DC Converters [7- 8] I S I HB =2I FW Waveforms t off t on t HB V S V C t I S I FB =I FW t off t on t FB V S V C t Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , Dc-DC Converters [7- 9] Stresses I S V FW 1 1 + Don Doff HB 2 1 PP 1 2 FB 1 1 � Power conversion capability: FW<HB<FB 3
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , Dc-DC Converters [7- 10] Topology selection Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , Dc-DC Converters [7- 11] Cuk Converter L 1 C 1 L 2 V out � Voltage V in R D C 2 V C1 V 2 V 1 of C 1 ≈ constant S ON OFF L 2 L 1 L 2 L 1 V out V out V in V in R R C 2 C 2 C 1 C 1 = = − ⋅ V V V V D (buck) o c 1 on 1 o = − − ⋅ V ( V V ) D = V V o in o on 2 in V D = − V V V = − o on c 1 in o V D in off Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , Dc-DC Converters [7- 12] Cuk with isolation L 2 L 1 C 1a C 1b V out V in C 2 R V 2 D S 1:n � Any polarity � Any voltage ratio V D = ± o on n V D in off 4
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , Dc-DC Converters [7- 13] Cuk advnatages and disadvantages Advantages � Continuos input and output currents � Single switch � Step-up and step-down Disadvantages � Two inductors � Extra capacitor (of high rms current) � Difficult to stabilize V + V � High voltage on switch in out Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , Dc-DC Converters [7- 14] SEPIC Converter L 1 C 1 D V x V out V in C 2 S L 2 R ON OFF L 1 C 1 L 1 C 1 V x V x D V in V in C 2 C 2 S S L 2 L 2 R R V = 0 = ⋅ − ⋅ = V V D V D 0 L 1 x o off in on V = 0 V D L 2 = o on V D V = V C 1 in in off Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , Dc-DC Converters [7- 15] Auxiliary output 5
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , Dc-DC Converters [7- 16] Topologies Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , Dc-DC Converters [7- 17] Topologies Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , Dc-DC Converters [7- 18] HB waveforms 6
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , Dc-DC Converters [7- 19] VOLTAGE REGULATION MODULE (VRM) � Synchronous rectifier 7
Recommend
More recommend