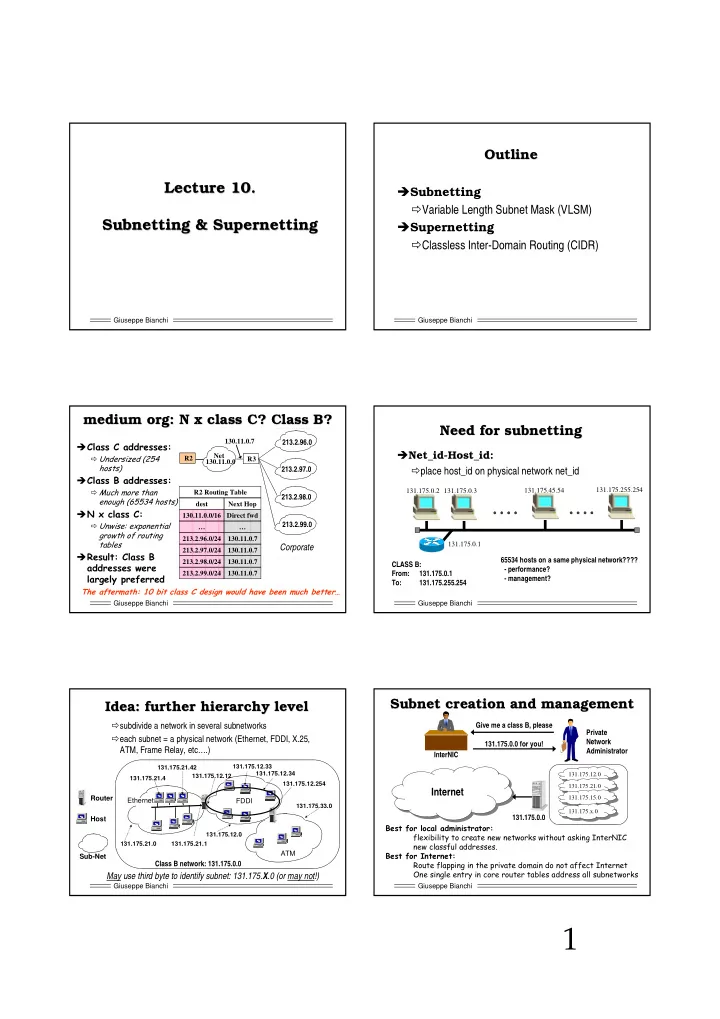

Outline Outline Lecture 10. Lecture 10. � Subnetting � Variable Length Subnet Mask (VLSM) Subnetting & & Supernetting Supernetting Subnetting � Supernetting � Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) Giuseppe Bianchi Giuseppe Bianchi medium org: N x class C? Class B? medium org: N x class C? Class B? Need for subnetting subnetting Need for 130.11.0.7 213.2.96.0 � ������������������ � Net_id-Host_id: Net � ���������������� R2 R3 130.11.0.0 ������ � place host_id on physical network net_id 213.2.97.0 � ������������������ � ��������������� 131.175.255.254 R2 Routing Table 131.175.0.2 131.175.0.3 131.175.45.54 213.2.98.0 �������������������� dest Next Hop � ������������ 130.11.0.0/16 Direct fwd � �������������������� 213.2.99.0 … … ������������������ 213.2.96.0/24 130.11.0.7 �� ��� 131.175.0.1 Corporate 213.2.97.0/24 130.11.0.7 � ���������������� 213.2.98.0/24 130.11.0.7 65534 hosts on a same physical network???? ��������������� CLASS B: - performance? 213.2.99.0/24 130.11.0.7 From: 131.175.0.1 ����������������� - management? To: 131.175.255.254 ���������������������������������������������������������������� � Giuseppe Bianchi Giuseppe Bianchi Subnet creation and management Subnet creation and management Idea: further hierarchy level Idea: further hierarchy level � subdivide a network in several subnetworks Give me a class B, please Private � each subnet = a physical network (Ethernet, FDDI, X.25, Network 131.175.0.0 for you! ATM, Frame Relay, etc….) Administrator InterNIC 131.175.12.33 131.175.21.42 131.175.12.34 131.175.12.0 131.175.12.12 131.175.12.0 131.175.21.4 131.175.12.254 131.175.21.0 131.175.21.0 Internet Router 131.175.15.0 Ethernet FDDI 131.175.15.0 131.175.33.0 131.175.x.0 131.175.x.0 131.175.0.0 Host ������������������������������ 131.175.12.0 ����� ����!���������������������"������������"����#����$#% 131.175.21.0 131.175.21.1 ������������ ���������& ���������!��������� ATM Sub-Net '������������������������(�������������������������#������� Class B network: 131.175.0.0 )��������������!������������������ ������������������ ������"� May use third byte to identify subnet: 131.175. X .0 (or may not!) Giuseppe Bianchi Giuseppe Bianchi 1
Subnet Address Subnet Address & & Mask Mask Subnetting Subnetting � "����!#��������� Class B address example Class B address example �$%&���&%&�' ��������&��������&��������&�������� � ��������( ������)����)� network prefix *$$&*$$&�&� (network address) ��������&��������&��������&�������� � +������,��) � *����������������������������"+�*���������� !�������������� 1 0 NET ID (14bit) HOST ID (16 bit) � ,��������������� ������!�������"-����������!��� � -�����������������������������$������������.�� Extended network prefix � �� �������"�.�/�0 ��������&��������&��������&�������� (subnet address) � /prefix-length notation � �� �������"�.����&���&��1&2� � (dot decimal notation) ��������&��������&��������&�������� 1 0 NET ID (14bit) SUBNET ID (n bit) HOST ID (16-n bit) � 0�3&022&2&2�.����4�� � 0�3&022&1&2�.����������������"��������������4��5�� ���4��� � ,���(������ �����!��0�3&022&1&2/�0 Giuseppe Bianchi Giuseppe Bianchi Remember: subnetting Remember: subnetting is arbitrary! is arbitrary! Typical class B subnetting subnetting Example: subnetting Example: subnetting Class C 193.1.1.0 Address Class C 193.1.1.0 Address Typical class B Base net 11000001.00000001.00000001.00000000 193.1.1.0/24 � Class B address = /16 network prefix � network address = 131.175.0.0 Class C 1 1 0 NET ID (21bit) HOST ID (8 bit) /24 prefix � natural mask = 255.255.0.0 Subnetted Subnet Host id � Subnetted with /24 network prefix 255.255.255.224 1 1 0 NET ID (21bit) (3 bit) (5bit) /27prefix 1 0 NET ID (14bit) SUBNET ID (8 bit) HOST ID (8 bit) 11000001.00000001.00000001. 000 00000 193.1.1.0/27 Subnet # 0 11000001.00000001.00000001. 001 00000 193.1.1.32/27 Subnet # 1 � 255.255.255.0 subnet mask 193.1.1.64/27 11000001.00000001.00000001. 010 00000 Subnet # 2 11000001.00000001.00000001. 011 00000 193.1.1.96/27 Subnet # 3 � subnet ID = third number in dotted notation 11000001.00000001.00000001. 100 00000 193.1.1.128/27 Subnet # 4 193.1.1.160/27 Subnet # 5 11000001.00000001.00000001. 101 00000 � 131.175. 21 .0 11000001.00000001.00000001. 110 00000 193.1.1.192/27 Subnet # 6 No technical reasons to use /24 subnets, but convenient for humans 11000001.00000001.00000001. 111 00000 193.1.1.224/27 Subnet # 7 (subnet boundary clearly visible in dotted notation) Remember: maximum 30(2 5 -2) hosts attachable to each subnet Giuseppe Bianchi Giuseppe Bianchi Example: route 193.205.102.36 Example: route 193.205.102.36 193 205 102 36 Possible Possible netmask netmask values values 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 Class C address; 128 16 8 4 2 1 64 32 Outside private domain routed with mask 255.255.255.0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 = 128 network host 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 = 192 193 205 102 36 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 = 224 Inside private domain, administrator has set netmask 255.255.255.248 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 = 240 255 255 255 248 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 = 248 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 = 252 Hence, route to subnet address and then to host id, computed as: 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 = 254 network subnet host 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 = 255 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 193.205.102.32 /29 4 Giuseppe Bianchi Giuseppe Bianchi 2
Recommend
More recommend