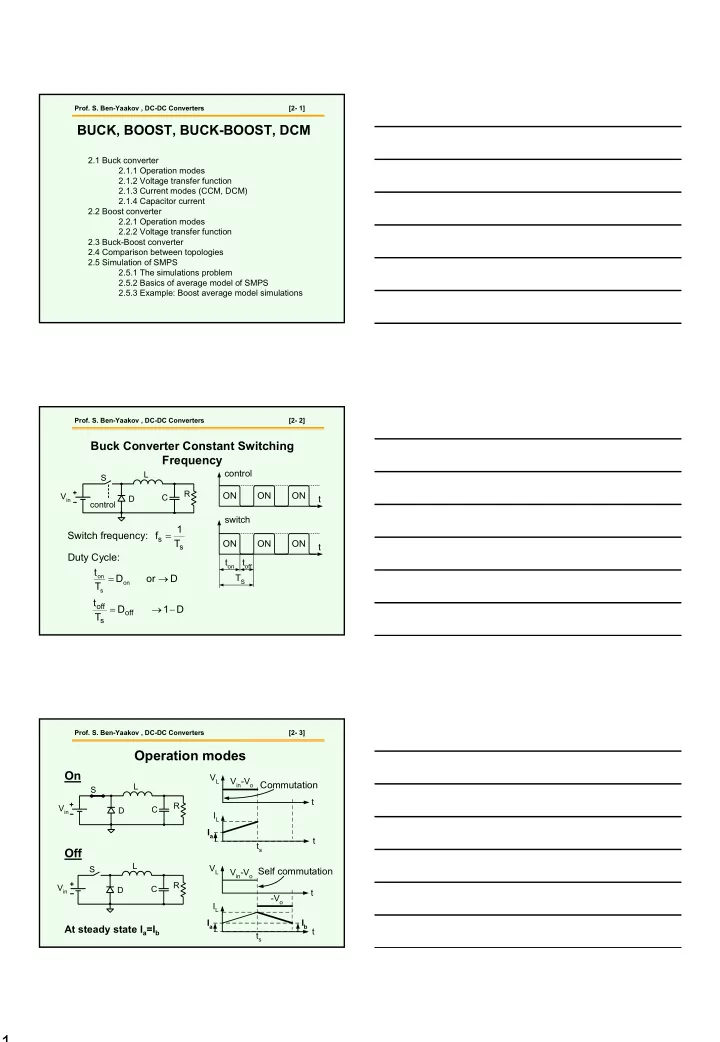

Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [2- 1] BUCK, BOOST, BUCK-BOOST, DCM 2.1 Buck converter 2.1.1 Operation modes 2.1.2 Voltage transfer function 2.1.3 Current modes (CCM, DCM) 2.1.4 Capacitor current 2.2 Boost converter 2.2.1 Operation modes 2.2.2 Voltage transfer function 2.3 Buck-Boost converter 2.4 Comparison between topologies 2.5 Simulation of SMPS 2.5.1 The simulations problem 2.5.2 Basics of average model of SMPS 2.5.3 Example: Boost average model simulations Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [2- 2] Buck Converter Constant Switching Frequency control L S R V in ON ON ON C D t control switch 1 f = Switch frequency: s T ON ON ON t s Duty Cycle: t on t off t on = D or → D T S on T s t off = → − D 1 D off T s Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [2- 3] Operation modes On V L V in -V o Commutation L S t R V in C D I L I a t t s Off L V L S Self commutation V in -V o R V in D C t -V o I L I a I b t At steady state I a =I b t s 1
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [2- 4] Buck t on In this case S t off R V in C D Inductor current waveform at steady state I L V in − V V o o − L L ∆ I t t on t off Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [2- 5] Voltage transfer function The ∆ I method in − V V I L o V o Right triangle L − Left triangle V L o t ∆ = ⋅ I − V V off ∆ = in o ⋅ L I t ∆ I on L t t on t off − V V V = in o t o t on off L L V t t o = on = on = D Independent of L ! on + V t t T in on off s Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [2- 6] Voltage transfer function The average voltage method V L t on V o S V in -V o t off t off R + V in V L C t D - t on -V o T s At steady state, over one switching cycle: V L = 0 ; S = ( V − V ) ⋅ t ; + in o on = − o ⋅ S ( V ) t ; − off V + = ⇒ o = S S 0 D + − on V in 2
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [2- 7] Load Change with Fixed D I L L V o S R V in D C control t t on t off T s How will I L change if R is getting smaller? Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [2- 8] Load Change I L V in − V V o o − L L R 1 < < R R R R 2 1 2 3 R 3 t t on t off T s CCM - Continues Conductor Current Mode DCM - Discontinues Conductor Current Mode Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [2- 9] Discontinuous Inductor Current Mode (DCM) R 4 >R 3 I L L V x V o S R 3 V in R 4 R D C control t t off t on T s t' off � Different voltage transfer ratio ≠ D on � Higher ripple current 3
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [2- 10] Voltage transfer function (DCM) I L The ∆ I method I pk − V V V = = ′ I in o t o t pk on off L L − ( V V ) D D = in out on t t ' t on off V off out T s − 1 1 V V = ⋅ + I in o T T ( D D ) AV on S on off T 2 L S − − 1 V V V V I = T ⋅ D ( 1 + ) in o in o AV on on 2 L V o − 2 = 2 V R ( V V ) D T V 2 LV AV = I o in o on S in o R V R D 2 T 8 L = + − o on s 1 1 2 V 4 L R D T in on s Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [2- 11] Boundary of CCM and DCM I L L min in − V V V o o − L L 2 L I av t t on t off T s � For CCM L > L min V V D R D = = = = o t I 2 I L o off off � In Buck off pk av min L 2 I f 2 f min av s s Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [2- 12] Example A BUCK converter has a following characteristics: V o = = = Output voltage: Output current: 5 V I I 10 A out av V in = f s = Input voltage: Frequency: 10 V 100 kHz Current mode: CCM Find: L min V CCM = = → = − = o D 0 . 5 D 1 D 0 . 5 on off on V in ⋅ V D 5 0 . 5 = = = µ L o off 1 . 2 H min ⋅ ⋅ 5 2 I f 2 10 10 av s 4
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [2- 13] Capacitor current L S V o I L R I av V in C I L I C D I R control t I R I av DC � Assumption: V 0 has small ripple t I C Capacitor current AC = − I I I t C L R Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [2- 14] BOOST Step-Up L D V X V o V in S R C � V o > V in Why ?? Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [2- 15] Operation modes Boost V L ON V L =V in V in L t V o I L V in R C I a t t s V L OFF V L =V in -V o V in L V o t V in -V o I L V in R C I a I b t t s 5
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [2- 16] Voltage transfer function The average voltage method L V x D V X V o V o V in S R C t t off T S = − = = V 0 ; V V 0 ; V V ; L in x in x V = V ; in in V t = = V o off V D ; x o off T s V 1 = → = V V D o in o off V D in off Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [2- 17] Voltage transfer function The ∆ I method L D V X V o o − I L V in V V − in L L V in S R C ∆ I − V V V t ⋅ = ⋅ in t o in t on off L L t on t off T s ⋅ + = ⋅ V ( t t ) V t in on off o off V = 1 o V D in off Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [2- 18] BUCK-BOOST Step-Up Step-Down V X D S V o V in C R L � Find V o /V in Hint: Average of V x ? 6
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [2- 19] Comparison between basic topologies CCM L D V o V o S L V in C V in C S D R R Basic Cell V o L D S D V in C R L S Switched inductor b L a c Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [2- 20] Input and Output Currents Source current Load current I in I o Buck t t I in I o Boost t t I in I o Buck Boost t t Continues current -> Low ripple component Discontinues current -> High ripple component Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [2- 21] The simulation problem Switched Assembly V o V + in − V D e Modulator Control 7
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [2- 22] The simulation problem Switched Assembly V o V + in − V D e Modulator Control •The problematic part : Switched Assembly • Rest of the circuit continuous - SPICE compatible • Only possible simulation : Time domain (cycle-by-cycle) -Transient • The objective : translate the Switched Assembly into an equivalent circuit which is SPICE compatible Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [2- 23] Average Simulation of PWM Converters T L V L V b on d a d c out out I I I I b L L C + + I R R − − Load b Load C C V V I f f in in C c b Buck Boost T V b d c on out I I V + b C R in − − L I Load C L f a Buck − Boost Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [2- 24] The Switched Inductor Model L T L b b a a on T DCM T off c c T on - switch conduction time T off - diode conduction time T DCM - no current time (in DCM) 8
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [2- 25] The Switched Inductor Model (SIM) (CCM) The concept of average signals I b b T L I on a a I c c T off I I a a t I I b b t I I c c t Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [2- 26] The SIM Objective : To replace the switched part by a continuous network I b b T I L on a a I c c T off ⇓ I b b I a ? a I c c Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [2- 27] Average current I T I = L on = I I D b b T b L on T L I on a S a I c T T c ON = off D on T = S I I a L I I b I Similarly : L I I T b = L off = I I D c L off T T ON S T S 9
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [2- 28] Toward a continuous model I = I ⋅ D b b L on = a I I a L = ⋅ I I D c c L off ⇓ G a , G b ,C c - current b I G dependent sources b b G G ≡ I I a a a L a ≡ ⋅ G I D b L on I G G ≡ I ⋅ D c c c c L off Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [2- 29] Average inductor current Deriving I L d I dI V V L = L ⇒ L = L dt L dt L V I I L L L I L V V L t I L V L Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [2- 30] Average inductor current V ( ) L V a , b V ( a , b ) b L a c V ( a , c ) ( ) V a , c T T on off T s ⋅ + ⋅ V ( a , b ) T V ( a , c ) T = on off = V L T S = ⋅ + ⋅ V ( a , b ) D V ( a , c ) D on off 10
Recommend
More recommend