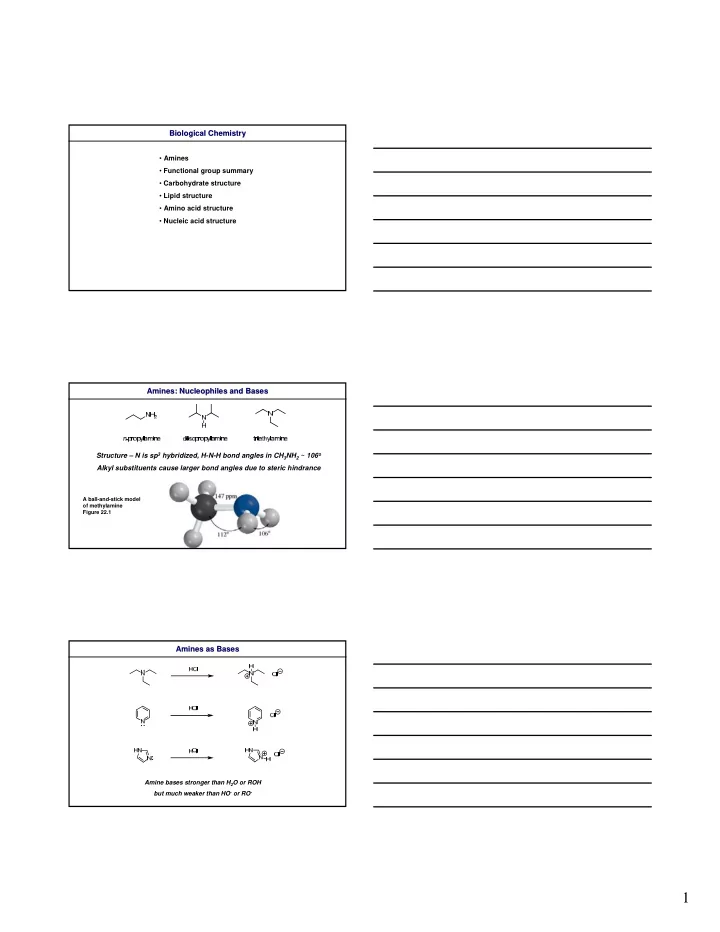

Biological Chemistry Biological Chemistry • Amines • Functional group summary • Carbohydrate structure • Lipid structure • Amino acid structure • Nucleic acid structure Amines: Nucleophiles Amines: Nucleophiles and Bases and Bases Structure – N is sp 3 hybridized, H-N-H bond angles in CH 3 NH 2 ~ 106 o Alkyl substituents cause larger bond angles due to steric hindrance A ball-and-stick model of methylamine Figure 22.1 Amines as Bases Amines as Bases Amine bases stronger than H 2 O or ROH but much weaker than HO - or RO - 1
Amine- Amine -containing Natural Products containing Natural Products O HO N N N H O O H H OH O HO HO N quinine codeine morphine H 2 N N H 2 HO N N H cadaverine HO N OH N H 2 H 2 N nicotine epinephrine putrescine Amino Acids Amino Acids – – Building Blocks for Proteins Building Blocks for Proteins Functional Group Summary Functional Group Summary 2
Functional Group Summary Functional Group Summary OH Br alkane alcohol halide alkene (no F.G.) non-polar (water insoluble) non-polar (grease, fats) polar (water soluble) non-polar (water insoluble) tetrahedral tetrahedral tetrahedral trigonal O NH alkyne aromatic aldehyde/ketone imine polar (water soluble) non-polar (water insoluble) non-polar (water insoluble) polar (water soluble) linear flat trigonal trigonal Functional Group Summary Functional Group Summary Functional Group Summary Functional Group Summary NH 2 O HO OH H 3 CO OCH 3 OH amine hydrate acetal carboxylic acid polar (water soluble) non-polar (water insoluble) polar (water soluble) polar (water soluble) tetrahedral tetrahedral tetrahedral trigonal O O O O O OCH 3 NH 2 Cl O carboxylic ester carboxylic amide acyl halide acid anhydride polar (water-solube) polar (water soluble) non-polar (reacts w/water) non-polar (reacts w/water) trigonal trigonal trigonal trigonal 3
Carbohydrate Structure Carbohydrate Structure Furanose Pyranose forms forms All present in solution, free sugars can interconvert Carbohydrate Structure Carbohydrate Structure D-glucose D-galactose D-glucosamine D-GlcNAc L-Fucose D-ManAcA D-Ribose 2-Deoxy-D-ribose Carbohydrate Structure - - Mutarotation Mutarotation Carbohydrate Structure • dissolve dextrose in water, measure [ α ] D : +112.2 • dissolve β -D-glucopyranose in water, measure [ α ] D : +18.7 • allow either to equilibrate, measure [ α ] D : +52.5 4
Carbohydrate Structure Carbohydrate Structure - - Glycosides Glycosides • Free sugar + alcohol + acid gives a glycoside • Glycosides are no longer free sugars and do not mutarotate Carbohydrate Structure Carbohydrate Structure – – Glycosides; Disaccharides Glycosides; Disaccharides Note: 2 amino acids give 4 peptides; 2 hexoses can give >20 possible reducing disaccharides Carbohydrate Structure – – Glycosides; Oligosaccharides Glycosides; Oligosaccharides Carbohydrate Structure Blood antigens H (type O) A (type A) B (type B) 5
Carbohydrate Structure Carbohydrate Structure – – Biological Recognition Biological Recognition Molecular recognition • multiple functional groups • multiple contact points • more complex alphabet than peptides Important Functions • cell-cell adhesion • antibody recognition • viral and bacterial adhesion Carbohydrate Structure Carbohydrate Structure – – Glycosides; Vaccines Glycosides; Vaccines Danishefsky et. al. Sloan-Kettering/Columbia – Synthetic vaccine against 3 types of cancer Lipid Structure Lipid Structure An unsaturated fat (triglyceride) A saturated fat (triglyceride) 6
Lipid Biosynthesis Lipid Biosynthesis Acetyl coenzyme A can serve as a 2-carbon nucleophile or electrophile as needed Lipid Biosynthesis Lipid Biosynthesis carbon chain extended by 2, can go up to C16, C18, C20 iteratively Lipid Structures Lipid Structures 7
Lipid Structures – Lipid Structures – Prostaglandins Prostaglandins Terpene Biosynthesis Terpene Biosynthesis OH Vitamin A -Carotone OPP (-H+) OPP OPP dimethylallyl isopentyl Geranyl pyrophosphate pyrophosphate pyrophosphate Biosynthetic Pathways Biosynthetic Pathways 8
Transfer of Information in Protein Expression Transfer of Information in Protein Expression mRNA Protein transcription translation Double-stranded DNA Amino Acids and Nucleic Acids Amino Acids and Nucleic Acids X-ray crystal structure of peanut lectin bound to C-lactose (Kishi et. al.) Amino Acids- - Structures Structures Amino Acids 9
Amino Acids and Peptide Linkages Amino Acids and Peptide Linkages Amino Acids and Peptide Linkages Amino Acids and Peptide Linkages polypeptide Amino Acids and Peptide Linkages Amino Acids and Peptide Linkages Organic Chem Biochemistry Structural Biology 10
o and 4 o Structure Amino Acids and Proteins Amino Acids and Proteins – – 3 3 o and 4 o Structure Ribbons and coils represent amino acid sequences in α -helical or β -sheet arrangements Protein Function, e.g. Catalysis (Enzymes) Protein Function, e.g. Catalysis (Enzymes) Cyanogenic β -Glucosidase from White Clover OH O HO O HO OH CN glycosidase OH HO O HO OH HO CN OH Structure 1995 , 3 , 951-960 Transfer of Information in Protein Expression Transfer of Information in Protein Expression mRNA Protein transcription translation Double-stranded DNA 11
Nucleic Acid Structure – Nucleic Acid Structure – Genetic Alphabet Genetic Alphabet Nucleic Acid Structure – Nucleic Acid Structure – DNA Alphabet DNA Alphabet O NH 2 NH N HO N O HO N O O O OH H OH H thymidine cytidine NH 2 O N N N NH HO N HO N N N NH 2 O O OH H OH H adenosine guanosine Nucleic Acid Structure – – RNA Alphabet RNA Alphabet Nucleic Acid Structure O NH 2 NH N HO N O HO N O O O OH H OH H uridine cytidine NH 2 O N N N NH HO N HO N N N NH 2 O O OH H OH H adenosine guanosine 12
Nucleic Acid Structure – Nucleic Acid Structure – Phosphate Derivatives Phosphate Derivatives Nucleic Acid Structure – Nucleic Acid Structure – RNA and DNA Polymers RNA and DNA Polymers RNA and DNA Polymers – – Hydrogen Hydrogen- -bonding Interactions bonding Interactions RNA and DNA Polymers 2 H bonds hold A and T together 3 H bonds hold G and C together 13
RNA and DNA Polymers – RNA and DNA Polymers – Information Storage Information Storage Biological Communication and Construction Biological Communication and Construction biosynthesis Organic material Biological Systems Chem 3719/3720 3719/3720 – – Introduction to Organic Chemistry Introduction to Organic Chemistry Chem H C H H H 1800 – Organic Chemistry : the chemistry of natural products based on carbon 2008 – Organic Chemistry : “molecular engineering” 14
Recommend
More recommend