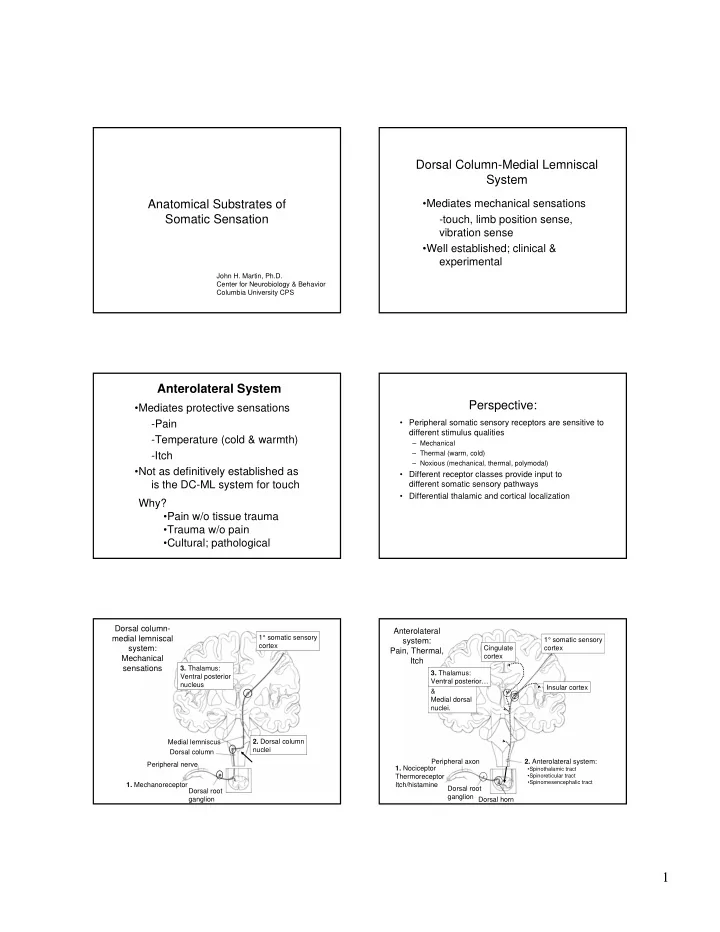

Dorsal Column-Medial Lemniscal System Anatomical Substrates of •Mediates mechanical sensations Somatic Sensation -touch, limb position sense, vibration sense •Well established; clinical & experimental John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center for Neurobiology & Behavior Columbia University CPS Anterolateral System Perspective: •Mediates protective sensations -Pain • Peripheral somatic sensory receptors are sensitive to different stimulus qualities -Temperature (cold & warmth) – Mechanical – Thermal (warm, cold) -Itch – Noxious (mechanical, thermal, polymodal) •Not as definitively established as • Different receptor classes provide input to is the DC-ML system for touch different somatic sensory pathways • Differential thalamic and cortical localization Why? •Pain w/o tissue trauma •Trauma w/o pain •Cultural; pathological Dorsal column- Anterolateral medial lemniscal 1° somatic sensory system: 1° somatic sensory cortex system: Cingulate cortex Pain, Thermal, cortex Mechanical Itch sensations 3. Thalamus: 3. Thalamus: Ventral posterior Ventral posterior… nucleus Insular cortex & Medial dorsal nuclei. 2. Dorsal column Medial lemniscus nuclei Dorsal column Peripheral axon 2. Anterolateral system: Peripheral nerve 1. Nociceptor •Spinothalamic tract Thermoreceptor •Spinoreticular tract •Spinomesencephalic tract 1. Mechanoreceptor Itch/histamine Dorsal root Dorsal root ganglion ganglion Dorsal horn 1
Rapidly adapting Slowly adapting Nociceptors, Mechano- thermoreceptors, & itch receptors receptor are receptive bare nerve endings fields Meissner's Merkel Mechanoreceptors are encapsulated Bare nerve ending Merkel’s receptor Meissner’s Pacinian Pacinian Ruffini corpuscle corpuscle NTA 5-3 PNS 22-3 Dermatomes Fiber Histogram: Fiber Histogram: Sensory Sensory axon axon innervating the skin innervating a muscle IV (C) IV (C) III (A- δ ) I (A- α ) III (A- δ ) II (A- β ) II (A- β ) Area of skin innervated by all sensory fibers w/in single dorsal root NTA 5-4 Dermatomes Dorsal Skin column Dorsal root overlap ganglion Lateral column “Anterolateral” column Ventral column Dorsal root Dermatome facts: Peripheral nerve Spinal Dorsal horn Pain dermatomes nerve Intermediate zone overlap < touch Dorsal Ventral horn Dermatomal root boundaries Ventral root Ventral vary root NTA 5-5 2
Lamina 5 NTA 5-6 NTA 5-6 Spinal Hemisection Syringomyelia Site of lesion Ipsilateral loss of touch … Contralateral loss of pain … • Bilateral loss of pain (2-3 segments caudal to injury) & thermal senses • Preservation of mechanosensations Mechanoreceptor Nociceptor NTA 5-9 NTA 5-10 Dorsal column- Somatotopy of spinal paths Anterolateral medial lemniscal system system Postcentral Postcentral gyrus / Insular/ gyrus / 1° SScx Cingulate cortex Dorsal Also: column •Reticular formation •Superior colliculus nuclei Internal Pain, (mesencephalon) arcuate thermal, Mechano… fibers itch Dorsal Spinal NTA 5-1 horn NTA 5-7 commissure 3
1° Somatic Sensory Cortex Cortical Pain Representations Output Systems VP lateral Thalamus Cortex Behavior VP medial Emotional/salience/ Medial dorsal Anterior cingulate valence Ventral med. Post. Mid-insular Limbic (VM po) cortex cortex Mechanosensation Behavioral Amygdala Autonomic Ventral posterior 1° SS ??Localization/ (VPL/VPM) Cortex Discrimination Summary • Early morphological specialization of DRG neurons sets stage for separate mechanosensory and pain/temp/itch systems • Different ascending pathways to distinct subcortical and cortical sites • Single thalamic mechanosensory nucleus and 1° ctx • Multiple thalamic pain nuclei and cortical areas • Parietal lobe projections may play role in stimulus localization, esp. for touch • Cortical pain representations closely tied to emotions 4
Recommend
More recommend