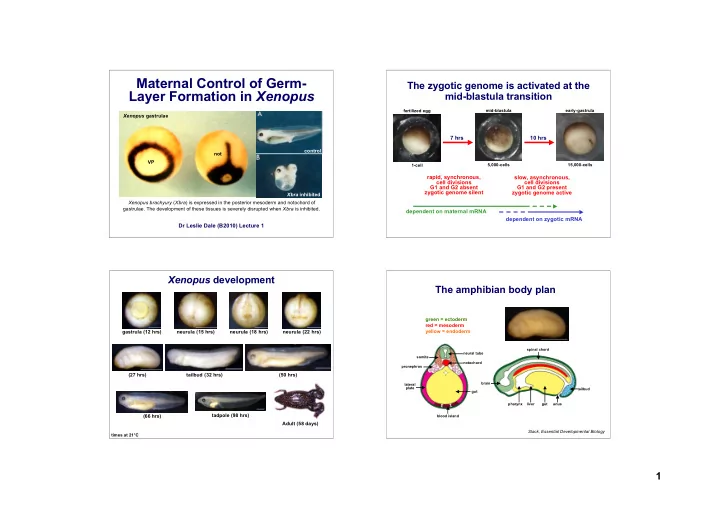

Maternal Control of Germ- The zygotic genome is activated at the Layer Formation in Xenopus mid-blastula transition fertilized egg mid-blastula early-gastrula Xenopus gastrulae 7 hrs 10 hrs control not VP 5,000-cells 15,000-cells 1-cell rapid, synchronous, slow, asynchronous, cell divisions cell divisions G1 and G2 absent G1 and G2 present zygotic genome silent zygotic genome active Xbra inhibited Xenopus brachyury ( Xbra ) is expressed in the posterior mesoderm and notochord of gastrulae. The development of these tissues is severely disrupted when Xbra is inhibited. dependent on maternal mRNA dependent on zygotic mRNA Dr Leslie Dale (B2010) Lecture 1 Xenopus development The amphibian body plan green = ectoderm red = mesoderm gastrula (12 hrs) neurula (15 hrs) neurula (18 hrs) neurula (22 hrs) yellow = endoderm spinal chord neural tube somite notochord pronephros (27 hrs) tailbud (32 hrs) (50 hrs) brain lateral plate tailbud gut pharynx liver gut anus tadpole (98 hrs) (66 hrs) blood island Adult (58 days) Slack, Essential Developmental Biology times at 21°C 1
Fate mapping amphibian embryos Animal-vegetal polarity in Xenopus oocytes Pigmentation Nucleus/Yolk mRNA animal gv vegetal YP VegT Animal-vegetal polarity is established during oogenesis. The animal hemisphere is darkly pigmented and contains the germinal vesicle (gv), the female haploid Fate maps tell us what cells will become at a later stage of development and are an important nucleus. The vegetal hemisphere is lightly pigmented and contains the largest yolk tool for embryologists. The fate map above was generated by laballing small populations of platelets (YP). A small number of maternal mRNAs are localized to the vegetal cells at the early gastrula stage and looking where they were located after the completion of hemisphere during oogenesis, including Vg1 , VegT and Wnt11. The egg is radially neurulation. It is important to note that the fate map does not tell you that cells are already symmetric around this axis. committed to forming these tissues. Specification map of early gastrula Animal-vegetal polarity in Xenopus oocytes Animal Pigmentation Nucleus/Yolk mRNA animal Slack, Essential Developmental Biology Epidermis gv Notoc hord Blood, Mesothelium vegetal YP Endoderm VegT Vegetal Animal-vegetal polarity is established during oogenesis. The animal hemisphere is Xenopus embryos are packed full of yolk, which provides all their nutritional needs until the darkly pigmented and contains the germinal vesicle (gv), the female haploid tadpole can feed for itself. This allows us to isolate fragments of the embryo and culture them in nucleus. The vegetal hemisphere is lightly pigmented and contains the largest yolk neutral media that do not affect their development. In this way we can find out how cells are platelets (YP). A small number of maternal mRNAs are localized to the vegetal specified at a particular stage of development. Above (right) is a specification map that applies to hemisphere during oogenesis, including Vg1 , VegT and Wnt11. The egg is both blastulae and early gastrulae. Note how the future nervous system forms epidermis in this radially symmetric around this axis. assay, demonstrating that it is not yet specified. 2
Antisense oligonucleotides deplete VegT is Sufficient for Endoderm and maternal mRNA Mesoderm Formation RNaseH Oligonucleotides (about 20-25 deoxy nucleotides in length) can be injected into VegT Xenopus oocytes where they hybridize to Control: 5’ 3’ the target mRNA. Hybridized mRNA is then 3’ 5’ epidermis degraded by the enzyme RNase H. Injected oocytes, marked with a vital dye, 5’ 3’ are transferred into a surrogate female, RNA degraded VegT inj: who lays them with a jelly coat that is epidermis required for fertilization. The dye allows mesoderm endoderm injected eggs to be detected from amongst the more numerous uninjected eggs. Slack, Essential Developmental Biology Xenopus eggs were injected in the animal hemisphere with VegT mRNA and animal caps isolated from blastulae. Control caps only form epidermis, while VegT injected caps also form endoderm and mesoderm. This demonstrates that VegT is sufficient for the formation of both of these germ layers. Slack, Essential Developmental Biology Depletion of Depletion of maternal VegT disrupts maternal VegT mesoderm and endoderm formation disrupts normal development Injection of low (L) concentrations of oligonucleotide generates embryos with no endoderm but nearly normal mesoderm. Injection of high (H) concentrations of oligonucleotide generates normal maternal VegT VegT depleted embryos with no endoderm and fate Map mRNA fate map practically no mesoderm. VegT mRNA is localized to the prospective endoderm, yet both endoderm and mesoderm are disrupted in VegT Zhang et al., Cell 94: 515-524 (1998) depleted embryos! Kofron et al., Development 126: 5759-5770 (1999) Xanthos et al., Development 128: 167-180 (2001) 3
Polarity in Xenopus embryos VegT is a T-box transcription factor early-gastrula fertilized egg T-box genes are a large family of T-box DNA Binding Regulatory transcriptional regulators unified by AP Domain Domain a conserved DNA binding domain. Named after the murine T-gene (now known as brachyury ), which dbl VP dbl was first identified as a mutation with a short, blunted tail. They also Transcription contain a C-terminal regulatory domain required for the formation of VegT target gene active transcriptional complexes The newly laid egg has clearly animal-vegetal polarity (AP-VP), which was established during oogenesis. However, it is radially symmetric around this axis. Ten hours after fertilization a darkly pigmented arc appears in the future dorsal Target genes for VegT, expressed in vegetal hemisphere of blastulae: quadrant of the vegetal hemisphere, the dorsal blastopore lip (dbl). The dorsal Transcription Factors: bix1 , bix2 , bix3 , bix4 , mix1 , mix2 , sox17 mesoderm (notochord) and ectoderm (nervous system) form above this lip while Signalling Molecules: xnr1 , xnr2 , xnr4 , xnr5 , xnr6 , derrière ventral tissues form on the opposite side. How did this dorsal-ventral axis form? Dorsal determinants move from the vegetal Cortical rotation breaks radial symmetry pole towards the dorsal marginal zone dorsal cytoplasm - pre cortical rotation vegetal cytoplasm - post cortical rotation SEP normal embryo dorsal cytoplasm - post cortical rotation vegetal cytoplasm - pre cortical rotation inject cytoplasm twinned embryo Dorsal determinants: Wolpert, Principles of Development animal animal + = Disheveled (Dsh) + GSK3 Binding Protein (GBP) vegetal vegetal The meridian of maximal rotation passes through animal pole and SEP. It defines the plane of first cleavage, the dorsal-ventral axis and the left-right axis cortical rotation 4
Cortical rotation and microtubules (MT) UV-irradiating the vegetal pole disrupts MT and ventralizes Xenopus embryos before cortical rotation random after cortical rotaion polarized Weaver & Kimelman, Development131, 3491-3499 (2004) Slack, Essential Developmental Biology MT form in “shear zone” between cortex and deep cytoplasm in the vegetal hemisphere, UV-light blocks MT formation, during cortical rotation, when vegetal pole is with the sperm centrosome at the minus-end organizing centre. Dsh & GBP couple to the Irradiated 25-30 mins after fertilization, causing loss of dorsal tissues. kinesin light chain (KLC) and move along the MT, from minus to plus end, using the Embryos form an epidermal bag containing excess blood and kinesin heavy chain (KHC) motor. Movement (60-90º) is greater than the angle of rotation (30º). MT depolymerizes towards end of first cell cycle releasing Dsh & GBP. mesothelium, and undifferentiated endoderm Dsh and GBP are components of the Wnt dorsalizes Xenopus embryos canonical Wnt signalling pathway Wnt Frizzled Frizzled Dsh GBP casein kinase 1 ∝ Axin CKI ∝ CKI ∝ Dsh APC Axin P glycogen APC ß synthase P adenomatous kinase 3 polyposis GSK3 GBP ß coli GSK3 ß proteosome degradation ß P Lithium ß-catenin ß P ß Wnts that activate the canonical pathway (e.g. Wnt1 & Wnt8) hyperdorsalize Groucho embryos when expressed everywhere. Transcription Localized expression rescues UV TCF-3 TCF TCF ß G irradiated embryos and induces a second siamois, twin, xnr3 dorsal axis, if expressed ventrally. Wnts G mimick the dorsal determinant. Ventral Dorsal Slack, Essential Developmental Biology 5
Recommend
More recommend