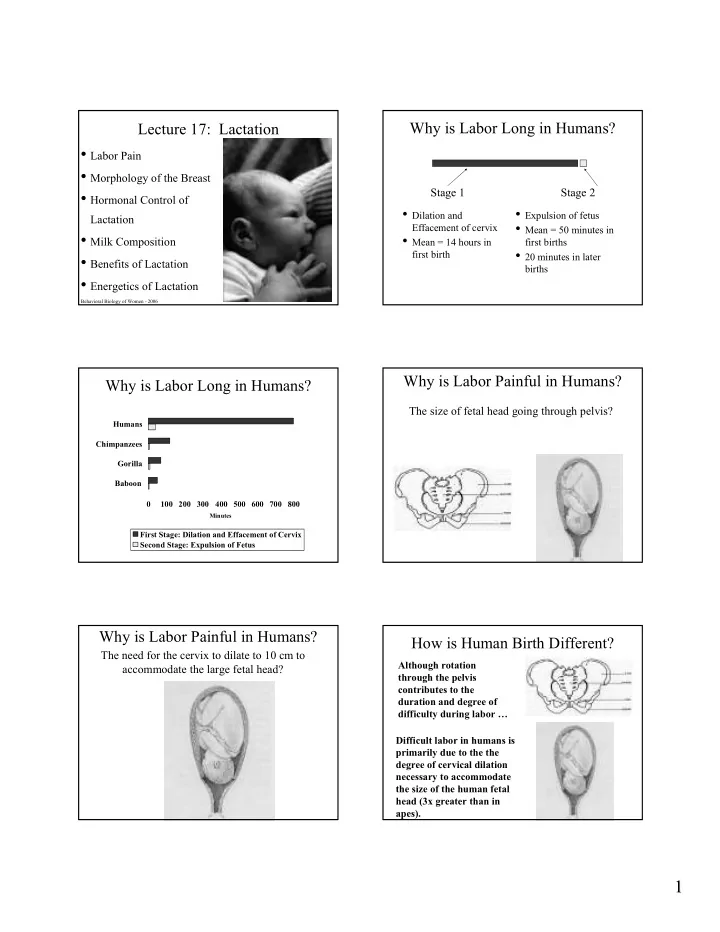

Why�is�Labor�Long�in�Humans? Why�is�Labor�Long�in�Humans? Lecture�17:��Lactation� Lecture�17:��Lactation� • Labor�Pain • Labor�Pain • Morphology�of�the�Breast • Morphology�of�the�Breast Stage�1 Stage�2 • Hormonal�Control�of� • Hormonal�Control�of� • Dilation�and� • • Expulsion�of�fetus • Dilation�and� Expulsion�of�fetus Lactation Lactation • Mean�=�50�minutes�in� • Effacement�of�cervix Effacement�of�cervix Mean�=�50�minutes�in� • Milk�Composition • • Mean�=�14�hours�in� • Milk�Composition Mean�=�14�hours�in� first�births first�births • 20�minutes�in�later� • first�birth first�birth 20�minutes�in�later� • Benefits�of�Lactation • Benefits�of�Lactation births births • Energetics�of�Lactation • Energetics�of�Lactation Behavioral�Biology�of�Women�" 2006 Why�is�Labor�Painful�in�Humans? Why�is�Labor�Painful�in�Humans? Why�is�Labor�Long�in�Humans? Why�is�Labor�Long�in�Humans? The�size�of�fetal�head�going�through�pelvis?�� ������ ����������� ������� ������ � ��� ��� ��� ��� ��� ��� ��� ��� ������� ������ ��!�"�#����������$�%&&�'�������&����(�) �'��$� ��!�"�%)���������&������ Why�is�Labor�Painful�in�Humans? Why�is�Labor�Painful�in�Humans? How�is�Human�Birth�Different? How�is�Human�Birth�Different? The�need�for�the�cervix�to�dilate�to�10�cm�to� *�����!����������� *�����!����������� accommodate�the�large�fetal�head? �����!���������(��� �����!���������(��� '������������������ '������������������ $����������$�$�!�����&� $����������$�$�!�����&� $�&&�'���+�$����!�������, , $�&&�'���+�$����!������� #�&&�'����������������������� #�&&�'����������������������� ��������+�$�������������� ��������+�$�������������� $�!�����&�'��(�'���$�������� $�!�����&�'��(�'���$�������� ��'�����+�����''����$���� ��'�����+�����''����$���� ����������&�����������&����� ����������&�����������&����� ���$�-�)�!��������������� ���$�-�)�!��������������� ����./ ����./ 1 1
Why�is�Labor�Painful�in�Humans? Labor�Pain Why�is�Labor�Painful�in�Humans? Labor�Pain • Why�does�relaxation� • • Humans�spend�significantly�more�time�in� • Why�does�relaxation� Humans�spend�significantly�more�time�in� help? help? the�later�stages�of�dilation�when�pain�is� the�later�stages�of�dilation�when�pain�is� • Autonomic�nervous� • Autonomic�nervous� greatest. greatest. system system • Apes�probably�experience�relatively�little� • > Parasympathetic� Parasympathetic� Apes�probably�experience�relatively�little� > (relaxation) (relaxation) pain�during�labor�because�they�have� pain�during�labor�because�they�have� > Sympathetic�(fight�or� Sympathetic�(fight�or� > relatively�little�dilation relatively�little�dilation flight�response) flight�response) Birth�Support�(doula� doula�effect) effect) Birth�Support�( Assisted�Birth�in�Humans Assisted�Birth�in�Humans • Birth�is�routinely�performed�with�assistance�in� • �������� ����������� Birth�is�routinely�performed�with�assistance�in� �� humans. humans. �� • • Emotional�support�to�the�mother Emotional�support�to�the�mother �� • Mechanical�assistance Mechanical�assistance • �� �� �� �� � 1������� 2����(������ �������� 3)+��'�� 4��!����& 4���� 0� Sosa,�et�al.�(1980) Sosa,�et�al.�(1980) Assisted�Birth�in�Humans Assisted�Birth�in�Humans • • Birth�is�routinely�performed�with� Birth�is�routinely�performed�with� assistance�in�humans. assistance�in�humans. • Emotional�support�to�the�mother • Emotional�support�to�the�mother • Mechanical�assistance Mechanical�assistance • > May�be�particularly�important� May�be�particularly�important� > for�breech�births�(2�" for�breech�births�(2� " 4%�of� 4%�of� births) births) (Gregory�et�al.�1999) 2 2
Morphology�of�the�Breast Morphology�of�the�Breast 3 3
Breast�Changes�during�Pregnancy Breast�Changes�during�Pregnancy Breast�Development Breast�Development ( (mammogenesis mammogenesis) ) • Estrogen�causes�growth�of�ducts�and� • Estrogen�causes�growth�of�ducts�and� proliferation�of�alveoli proliferation�of�alveoli Breast�Changes�during�Pregnancy Breast�Changes�during�Pregnancy Breast�Changes�during�Pregnancy Breast�Changes�during�Pregnancy • Estrogen�causes�growth�of�ducts�and� • • Prolactin • Estrogen�causes�growth�of�ducts�and� Prolactin, , cortisol� cortisol�and�growth�hormone�turn� and�growth�hormone�turn� proliferation�of�alveoli proliferation�of�alveoli breast�cells�into: breast�cells�into: • Progesterone�causes�the�alveolar�milk� • Progesterone�causes�the�alveolar�milk� > Secretory�cells�that�make�milk > Secretory�cells�that�make�milk glands�to�mature glands�to�mature > Muscle�cells�that�will�squeeze�milk�down� Muscle�cells�that�will�squeeze�milk�down� > through�ducts through�ducts Morphology�of�Alveolus Morphology�of�Alveolus Morphology�of�Alveolus Morphology�of�Alveolus • Site�of�milk�synthesis • Site�of�milk�synthesis • Site�of�milk�synthesis • Site�of�milk�synthesis • Contained�with�a�capsule�of�basement�membrane�which� • Contained�with�a�capsule�of�basement�membrane�which� contains�contractile� contains�contractile�myoepithelial� myoepithelial�cells. cells. 4 4
Stages�of�Breast�Milk�Production Stages�of�Breast�Milk�Production Stages�of�Breast�Milk�Production Stages�of�Breast�Milk�Production • Mammogenesis • • Lactogenesis • Mammogenesis:�establishment�of�glandular� :�establishment�of�glandular� Lactogenesis:�establishment�of�actively� :�establishment�of�actively� morphology�capable�of�producing�large� morphology�capable�of�producing�large� secreting�mammary�gland secreting�mammary�gland quantities�of�milk quantities�of�milk Mammogenesis Lactogenesis (complete�at�4�mths) (Begins�at�Parturition) Stages�of�Breast�Milk�Production� Stages�of�Breast�Milk�Production� Hormones�of�Lactation Hormones�of�Lactation • Galactopoiesis • Galactopoiesis:��maintenance�of�milk�secretion :��maintenance�of�milk�secretion Galactopoiesis Prolactin�&�Milk�Production Prolactin�&�Milk�Production Prolactin�&� Prolactin�&� ��������������������� ��������������� ������ Milk� Milk� • Nipple�stimulation • Nipple�stimulation Production Production • • Nipple� Nipple� stimulation stimulation • • Hypothalamus� Hypothalamus� stops�producing� stops�producing� prolactin" prolactin " inhibiting�factor� inhibiting�factor� (dopamine) (dopamine) 5 5
Recommend
More recommend