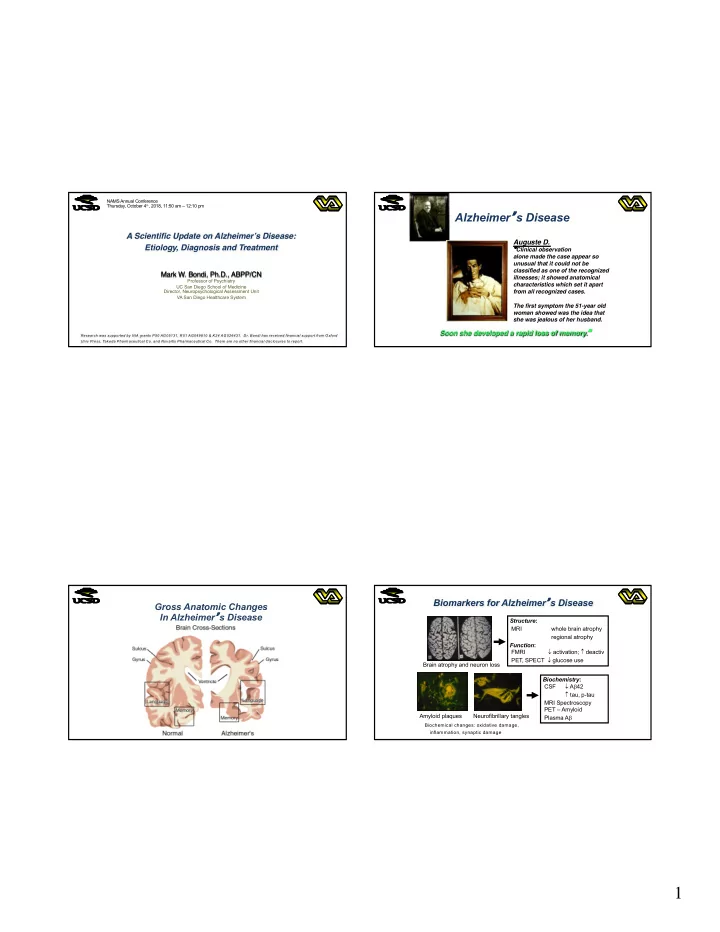

NAMS Annual Conference Thursday, October 4 th , 2018, 11:50 am – 12:10 pm Alzheimer � s Disease A Scientific Update on Alzheimer’s Disease: Auguste D. Etiology, Diagnosis and Treatment � Clinical observation alone made the case appear so unusual that it could not be classified as one of the recognized Mark W. Bondi, Ph.D., ABPP/CN illnesses; it showed anatomical Professor of Psychiatry characteristics which set it apart UC San Diego School of Medicine Director, Neuropsychological Assessment Unit from all recognized cases. VA San Diego Healthcare System The first symptom the 51-year old woman showed was the idea that she was jealous of her husband. Soon she developed a rapid loss of memory. � Research was supported by NIA grants P50 AG05131, R01 AG049810 & K24 AG026431. Dr. Bondi has received financial support from Oxford Univ Press, Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. and Novartis Pharmaceutical Co. There are no other financial disclosures to report. Biomarkers for Alzheimer � s Disease Gross Anatomic Changes In Alzheimer � s Disease Structure : MRI whole brain atrophy regional atrophy Function : ¯ activation; deactiv FMRI PET, SPECT ¯ glucose use Brain atrophy and neuron loss Biochemistry : CSF ¯ A b 42 tau, p-tau MRI Spectroscopy PET – Amyloid Amyloid plaques Neurofibrillary tangles Plasma A b Biochemical changes: oxidative damage, inflammation, synaptic damage 1
MCI Criteria Two Contrasting Theories of Incorporating Biomarkers Alzheimer’s Disease Pathogenesis Amyloid Cascade Model Braak’s Continuum Model Table 3 MCI criteria incorporating biomarkers Biomarker probability A b Neuronal injury Diagnostic category of AD etiology (PET or CSF) (tau, FDG, sMRI) MCI–core clinical criteria Uninformative Conflicting/indeterminant/untested Conflicting/indeterminant/untested MCI due to AD—intermediate likelihood Intermediate Positive Untested Untested Positive MCI due to AD—high likelihood Highest Positive Positive MCI—unlikely due to AD Lowest Negative Negative Abbreviations:AD,Alzheimer’sdisease;A b ,amyloidbetapeptide;PET,positronemissiontomography;CSF,cerebrospinalfluid;FDG,fluorodeoxyglucose; sMRI, structural magnetic resonance imaging. Albert et al. (2011). Alz & Dem . Proposed Staging Framework of the Cascade Preclinical Alzheimer’s Disease Of Events in Preclinical Alzheimer’s Disease Criteria Incorporating Biomarkers Jack et al. (2010). Lancet Neurol. Sperling et al. (2011). Alz & Dem. 2
Anti-Amyloid Trial in Mild to Moderate AD Salloway, Sperling et al. (2014). New Engl J Med. 3
Breitner (2015). Neurology. Neuropathologic Hallmarks Of AD: Cognitive Abilities Affected by AD Evolution of Neurofibrillary Changes Neurofibrillary changes Ø Learning and Memory limited to entorhinal and Stages I / II transentorhinal (TE) regions (pre AD) Severe involvement of TE regions; moderate changes Ø Language and Semantic Memory in hippocampus; Stages III / IV mild changes in some Ø Executive Functions / Attention (early AD) cortical association areas Cortical association areas severely involved; Stages V / VI only primary sensory Ø Visuospatial / Constructional Ability (clinical AD) and motor areas spared Braak & Braak. (1991). Acta Neuropathol. 4
Continuum of AD Tau Pathology: Locus Coeruleus From Brainstem to Cortex “…the pathologic process associated with sporadic AD commences with intraneuritic formation of pretangle material in the lower brainstem rather than in the transentorhinal region…” Braak et al. (2011). J Neuropath Exp Neurol. Stages of AD-Associated Tau Pathology Braak & Del Tredici (2015). Brain. Braak et al. (2011). J Neuropath Exp Neurol. Shafiei et al. (2017). Front Aging Neurosci. 5
The Two-Hit Vascular Hypothesis The Two-Hit Vascular Hypothesis For Alzheimer’s Disease ���������������� ���������������� ������������������������� ������������������������� ������������������������������ ������������������������������ Vascular ������� ������� Biomarker ��������������� ��������� ��������������� ��������� Methods ��������������� ��������������� �������������� �������������� �������� β � �������� β � �������� β � �������� β � ����������������� ��������� ���������� ����������������������� ����������������� ��������� ���������� ����������������������� ������� ������� Current AD �������� β � ����� �������� β � ����� Biomarker Methods ������������������������������� ������������������������������� ����������������� ����������������� ����������������� ����������������� �������� �������� Zlokovic (2011). Nat Rev Neurosci. Zlokovic (2011). Nat Rev Neurosci. ����������������������������� ����������������������������� �� �������������������� ��������� ���������� ������� ��������� �������� ���� ���������� ��� ��������� ���� The Two-Hit Vascular Hypothesis ��� Concluding Comments For Alzheimer’s Disease �� ��������������� ����� ���� ���������� The work aimed at characterizing markers of brainstem tau ��������� ��������� �������� pathology or vascular pathology represents a shift away from the �������� �������� strictures of the amyloid cascade model and may advance our ����������� understanding of AD pathogenesis. ���������� �������� ���������� ���� If successful, it will drive a number of fundamental shifts in ������ biomarker strategies, drug discovery and therapeutics. ��� �������� β � ������� ��������� ����� ��� ����������� ���������� ������ ���� ��� Zlokovic (2011). Nat Rev Neurosci. ����������������������������� 6
Recommend
More recommend