Wireless Link Capacity under Shadowing and Fading Tigran Tonoyan, - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Wireless Link Capacity under Shadowing and Fading Tigran Tonoyan, Postdoc at ICE-TCS, School of Computer Science, Reykjavik University (with Magns M. Halldrsson) Spatial
Wireless Link Capacity under Shadowing and Fading Tigran ¡Tonoyan, ¡Postdoc ¡at ¡ ICE-‑TCS, ¡School ¡of ¡Computer ¡Science, ¡Reykjavik ¡University ¡ (with ¡Magnús ¡M. ¡Halldórsson) ¡
Spatial Reuse Ques%on ¡ How ¡much ¡spaIal ¡reuse ¡can ¡be ¡achieved ¡in ¡a ¡(single ¡channel) ¡wireless ¡network? ¡ ¡ How ¡to ¡find ¡large ¡sets ¡of ¡successfully ¡coexisIng ¡links? ¡
Spatial Reuse Ques%on ¡ How ¡much ¡spaIal ¡reuse ¡can ¡be ¡achieved ¡in ¡a ¡(single ¡channel) ¡wireless ¡network? ¡ ¡ How ¡to ¡find ¡large ¡sets ¡of ¡successfully ¡coexisIng ¡links? ¡ Signal Reception: Basic Model 1 [Interference] ¡< ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡[Signal] ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡[Interference] ¡= ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡[Interference] j ¡ ! ! j
Spatial Reuse Ques%on ¡ How ¡much ¡spaIal ¡reuse ¡can ¡be ¡achieved ¡in ¡a ¡(single ¡channel) ¡wireless ¡network? ¡ ¡ How ¡to ¡find ¡large ¡sets ¡of ¡successfully ¡coexisIng ¡links? ¡ Signal Reception: Basic Model 1 [Interference] ¡< ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡[Signal] ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡[Interference] ¡= ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡[Interference] j ¡ ! ! j ? ¡
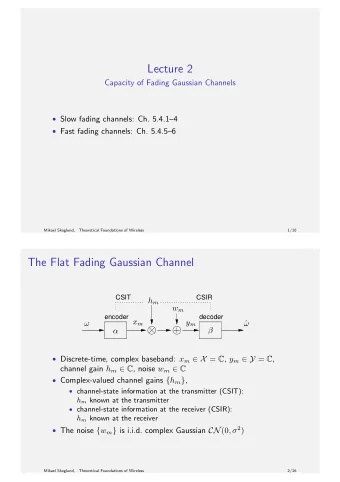
Signal Propagation SpaIal ¡Aspect: ¡Shadowing ¡ Temporal ¡Fading ¡ Geometric: ¡Average ¡Path ¡Loss ¡ P/[distance] α ¡ AXenuaIon ¡by ¡large ¡obstacles ¡ MulIpath ¡effects, ¡ Moving ¡obstacles ¡
Signal Propagation: Stochastic Models Geometric: ¡Average ¡Path ¡Loss ¡ SpaIal ¡Aspect: ¡Shadowing ¡ Temporal ¡Fading ¡ G = P We ¡concentrate ¡on ¡Rayleigh ¡fading: ¡ Signal ¡of ¡link ¡ i : ¡ S i Signal ¡and ¡interference ¡drawn ¡from ¡ ! i ! ¡ a ¡(parameterized) ¡distribuIon ¡ D : ¡ ¡ ¡ G = P Interference ¡by ¡link ¡ j : ¡ I ji D ~ D ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡exponenIal, ¡such ¡that ¡ S i , I ji D , I ji ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡such ¡that ¡ S i ! d ji D !!"#$!!! E I ji ! # D ! # G !!"#$!!! E I ji ! # D D G [ ] = S i E S i $ = I ji E S i $ = S i $ = I ji " " " Example: ¡Lognormal ¡shadowing ¡ Other ¡examples: ¡Rice, ¡Nakagami; ¡ Technically ¡more ¡challenging ¡
Signal Propagation: Stochastic Models Geometric: ¡Average ¡Path ¡Loss ¡ SpaIal ¡Aspect: ¡Shadowing ¡ Temporal ¡Fading ¡ G = P We ¡concentrate ¡on ¡Rayleigh ¡fading: ¡ Signal ¡of ¡link ¡ i : ¡ S i Signal ¡and ¡interference ¡drawn ¡from ¡ ! i ! ¡ a ¡(parameterized) ¡distribuIon ¡ D : ¡ ¡ ¡ G = P Interference ¡by ¡link ¡ j : ¡ I ji D ~ D ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡exponenIal, ¡such ¡that ¡ S i , I ji D , I ji ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡such ¡that ¡ S i ! d ji D !!"#$!!! E I ji ! # D ! # G !!"#$!!! E I ji ! # D D G [ ] = S i E S i $ = I ji E S i $ = S i $ = I ji " " " Example: ¡Lognormal ¡shadowing ¡ Other ¡examples: ¡Rice, ¡Nakagami; ¡ Technically ¡more ¡challenging ¡ What ¡do ¡ ¡ Max ¡#links ¡ E[Max ¡#links] ¡ Max ¡E[#links 1 ] ¡ we ¡want? ¡ 1 under ¡some ¡Tx ¡policies ¡
Results (Mobihoc’17, on arxiv 1706.05269) • Rayleigh ¡(temporal) ¡fading ¡can ¡only ¡change ¡the ¡picture ¡up ¡to ¡constant ¡factors ¡ (under ¡any ¡shadowing) ¡ • Shadowing ¡can ¡significantly ¡increase ¡(but ¡never ¡decrease) ¡the ¡soluIon ¡size ¡ • We ¡present ¡an ¡algorithm ¡for ¡compuIng ¡such ¡soluIons ¡(under ¡shadowing) ¡ ¡ QuesIon: ¡most ¡of ¡the ¡above ¡holds ¡under ¡the ¡assumpIon ¡of ¡sufficient ¡ independence ¡between ¡the ¡distribuIons; ¡ ¡ how ¡to ¡introduce ¡dependencies, ¡s.t. ¡ 1. the ¡resulIng ¡model ¡makes ¡sense, ¡ 2. is ¡algorithmically ¡tractable? ¡
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.