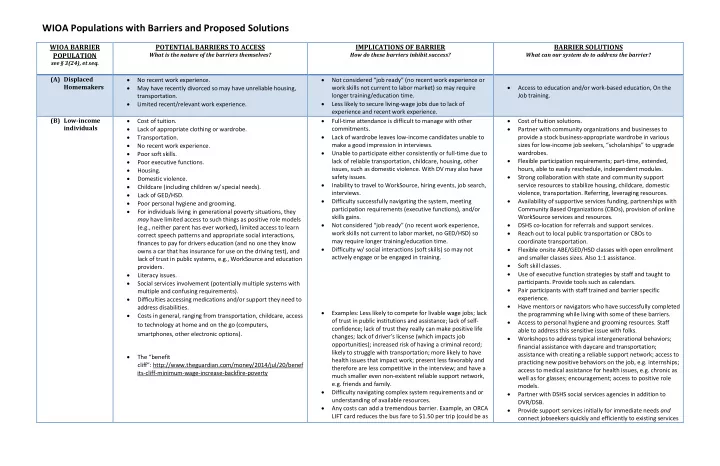

WIOA Populations with Barriers and Proposed Solutions WIOA BARRIER POTENTIAL BARRIERS TO ACCESS IMPLICATIONS OF BARRIER BARRIER SOLUTIONS What is the nature of the barriers themselves? How do these barriers inhibit success? What can our system do to address the barrier? POPULATION see § 3(24), et seq. (A) Displaced • • No recent work experience. Not considered “job ready” (no recent work experience or Homemakers • • May have recently divorced so may have unreliable housing, work skills not current to labor market) so may require Access to education and/or work-based education, On the longer training/education time. Job training. transportation. • • Less likely to secure living-wage jobs due to lack of Limited recent/relevant work experience. experience and recent work experience. • • • (B) Low-income Cost of tuition. Full-time attendance is difficult to manage with other Cost of tuition solutions. individuals • • Lack of appropriate clothing or wardrobe. commitments. Partner with community organizations and businesses to • • Transportation. Lack of wardrobe leaves low-income candidates unable to provide a stock business-appropriate wardrobe in various • make a good impression in interviews. sizes for low-income job seekers, “scholarships” to upgrade No recent work experience. • • Unable to participate either consistently or full-time due to wardrobes. Poor soft skills. • • lack of reliable transportation, childcare, housing, other Flexible participation requirements; part-time, extended, Poor executive functions. • issues, such as domestic violence. With DV may also have hours, able to easily reschedule, independent modules. Housing. • safety issues. • Strong collaboration with state and community support Domestic violence. • Inability to travel to WorkSource, hiring events, job search, service resources to stabilize housing, childcare, domestic • Childcare (including children w/ special needs). interviews. violence, transportation. Referring, leveraging resources. • Lack of GED/HSD. • • Difficulty successfully navigating the system, meeting Availability of supportive services funding, partnerships with • Poor personal hygiene and grooming. participation requirements (executive functions), and/or Community Based Organizations (CBOs), provision of online • For individuals living in generational poverty situations, they skills gains. WorkSource services and resources. may have limited access to such things as positive role models • • Not considered “job ready” (no recent work experience, DSHS co-location for referrals and support services. (e.g., neither parent has ever worked), limited access to learn • work skills not current to labor market, no GED/HSD) so Reach out to local public transportation or CBOs to correct speech patterns and appropriate social interactions, may require longer training/education time. coordinate transportation. finances to pay for drivers education (and no one they know • • Difficulty w/ social interactions (soft skills) so may not Flexible onsite ABE/GED/HSD classes with open enrollment owns a car that has insurance for use on the driving test), and actively engage or be engaged in training. and smaller classes sizes. Also 1:1 assistance. lack of trust in public systems, e.g., WorkSource and education • Soft skill classes. providers. • • Use of executive function strategies by staff and taught to Literacy issues. • participants. Provide tools such as calendars. Social services involvement (potentially multiple systems with • Pair participants with staff trained and barrier specific multiple and confusing requirements). • experience. Difficulties accessing medications and/or support they need to • Have mentors or navigators who have successfully completed address disabilities. • Examples: Less likely to compete for livable wage jobs; lack • the programming while living with some of these barriers. Costs in general, ranging from transportation, childcare, access of trust in public institutions and assistance; lack of self- • Access to personal hygiene and grooming resources. Staff to technology at home and on the go (computers, confidence; lack of trust they really can make positive life able to address this sensitive issue with folks. smartphones, other electronic options). changes; lack of driver’s license (which impacts job • Workshops to address typical intergenerational behaviors; opportunities); increased risk of having a criminal record; financial assistance with daycare and transportation; likely to struggle with transportation; more likely to have assistance with creating a reliable support network; access to • The “benefit health issues that impact work; present less favorably and practicing new positive behaviors on the job, e.g. internships; cliff”: http://www.theguardian.com/money/2014/jul/20/benef therefore are less competitive in the interview; and have a access to medical assistance for health issues, e.g. chronic as its-cliff-minimum-wage-increase-backfire-poverty much smaller even non-existent reliable support network, well as for glasses; encouragement; access to positive role e.g. friends and family. models. • Difficulty navigating complex system requirements and or • Partner with DSHS social services agencies in addition to understanding of available resources. DVR/DSB. • Any costs can add a tremendous barrier. Example, an ORCA • Provide support services initially for immediate needs and LIFT card reduces the bus fare to $1.50 per trip (could be as connect jobseekers quickly and efficiently to existing services
Recommend
More recommend