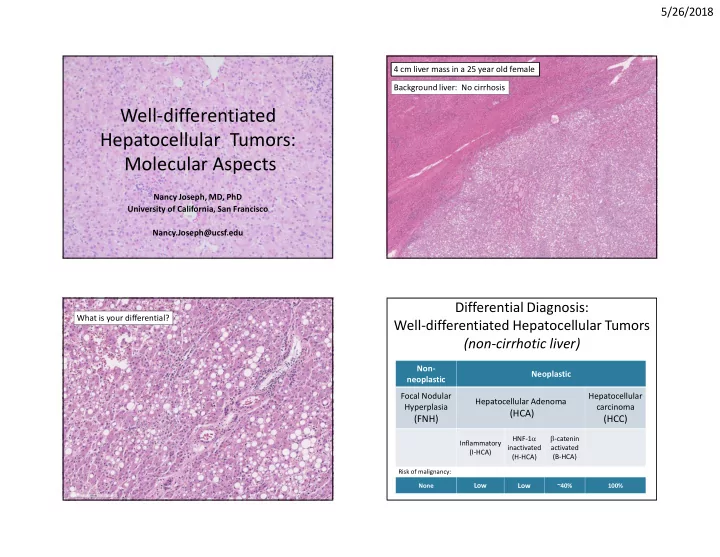

5/26/2018 4 cm liver mass in a 25 year old female Background liver: No cirrhosis Well-differentiated Hepatocellular Tumors: Molecular Aspects Nancy Joseph, MD, PhD University of California, San Francisco Nancy.Joseph@ucsf.edu Differential Diagnosis: What is your differential? Well-differentiated Hepatocellular Tumors (non-cirrhotic liver) Non- Neoplastic neoplastic Focal Nodular Hepatocellular Hepatocellular Adenoma Hyperplasia carcinoma (HCA) (FNH) (HCC) HNF-1 a b -catenin Inflammatory inactivated activated (I-HCA) (H-HCA) (B-HCA) Risk of malignancy: None Low Low ~40% 100% 1
5/26/2018 Management of benign lesions Management of benign lesions No follow up or No follow up or FNH FNH treatment necessary treatment necessary Annual surveillance <5 cm HCA >5 cm Resection b -catenin activated FNH Focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH) • 30-50 year old women • Solitary • Asymptomatic • Well-circumscribed • Central fibrous scar 2
5/26/2018 Useful Immunohistochemistry in FNH: FNH Glutamine synthetase (GS) • Enzyme involved in nitrogen metabolism expressed in centrizonal hepatocytes Normal liver FNH Diagnostic challenge in FNH: Focal nodular hyperplasia: Small biopsy Molecular Aspects H&E Glutamine synthetase (GS) • No recurrent copy number alterations or mutations identified – Multiple prior studies have examined molecular feautures of FNH – Capture based next generation sequencing (500 cancer genes) – Gene expression profiles show overexpression of the b -catenin pathway without gene mutation • Non-clonal, non-neoplastic • No metastasis of FNH have ever been reported Rebouissou et al. Hepatology 2008 (49) 3
5/26/2018 Inflammatory HCA: Classification of Hepatocellular Tumors Clinical features Non- • ~40-50% of all HCA Neoplastic neoplastic • Female gender Focal Nodular Hepatocellular Hepatocellular Adenoma • Associated with obesity and metabolic Hyperplasia carcinoma (HCA) (FNH) (HCC) syndrome – steatosis or steatohepatitis can be present in the HNF-1 a b -catenin Inflammatory inactivated activated non-neoplastic liver (I-HCA) (H-HCA) (B-HCA) Risk of malignancy: None Low Low 40% 100% Inflammatory HCA Reticulin-Inflammatory HCA 4
5/26/2018 Inflammatory HCA Diagnostic challenge: Histologic overlap with Inflammatory HCA Inflammatory Histologic features FNH HCA Nodular architecture 85% 7% Fibrous bands 90% 26% Ductular reaction 83% 43% Inflammation 48% 60% Sinusoidal dilatation 18% 83% Joseph/Kakar, Mod Pathol 2014 (27) Useful Immunohistochemisty in I-HCA Genetic alterations in Inflammatory HCA IL6ST C Reactive Protein (CRP) Serum amyloid A (SAA) Pilati et al. Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews 2015; 26:499-506 5
5/26/2018 HNF1- a inactivated HCA: Genetic alterations in Inflammatory HCA Clinical features • Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1a • ~30-40% of HCA • Female gender • Can have multiple tumors/adenomatosis Pilati et al. Cancer Cell 2014 HNF1- a inactivated HCA Useful Immunohistochemistry in H-HCA: Loss of liver fatty acid binding protein (LFABP) 6
5/26/2018 Diagnostic challenge in H-HCA: Genetic alterations HNF1- a inactivated HCA Differentiating from HCC • LFABP staining can be lost in HCC • Reticulin often lost in fatty areas Pilati et al. Cancer Cell 2014 b -catenin activated HCA b -catenin activated HCA (B-HCA): Clinical Features H&E Reticulin • Male gender (40%) • Age > 50 years • Androgen use • Usually a solitary lesion • Glycogen storage diseases ~40% of cases show cytologic or architectural atypia • Risk for HCC 7
5/26/2018 b -catenin activated HCA (B-HCA): b -HCA Diagnostic Challenge: Useful immunohistochemistry Glutamine Synthetase staining can be difficult to interpret b -catenin (nuclear) Diffuse homogeneous GS Diffuse heterogeneous GS Patchy GS Glutamine Synthetase (GS) 90-100% cells 50%-90% cells < 50% b -catenin activated Hale/Kakar, Mod Pathol 2016 b -HCA Molecular Profile: β-catenin activated HCA: Comparison of cases with and without Genetic Alterations cytoarchitectural atypia WNT/ b- catenin signaling pathway b -HCA – APC/AXIN/GSK3 are negative regulators of this pathway p value No Atypia Atypia – GLUL (Glutamine Synthetase) is a (n=5) (n=6) downstream gene that is upregulated with b- catenin Copy Number Alterations 1/5 (20%) 3/6 (50%) 0.35 activation – Frequent Copy Number Changes (similar to those seen in HCC) ≥ 1 additional pathogenic 2/5 (40%) 3/6 (50%) 0.43 molecular alteration Zucman-Rossi, Hepatol 2006 Bioulac-Sage, Hepatol 2007 Joseph/Kakar, Unpublished data Evason/Kakar, Hum Pathol 2013 8
5/26/2018 b -HCA Molecular Profile: Well-differentiated HCC with diffuse GS Comparison to Well-diff HCC with diffuse GS Glutamine synthetase H&E Reticulin b -HCA Well-diff HCC p-value (n=11) (n=7) 8/11 (73%) 5/7 (72%) <0.68 WNT pathway mutations 0/11 (0%) 3/7 (43%) 0.04 TERT promoter mutation ≥ 1 additional pathogenic 5/11 (45%) 6/7 (86%) 0.10 molecular alteration Joseph/Kakar, Unpublished data Frequency of copy number changes in HCA Classification of Hepatocellular Tumors p Non- Neoplastic neoplastic Focal Nodular Hepatocellular Hepatocellular Adenoma Hyperplasia carcinoma (HCA) (FNH) (HCC) HNF-1 a b -catenin Inflammatory inactivated activated (I-HCA) (H-HCA) (B-HCA) Risk of malignancy: Low None Low 40% 100% Pilati et al. Cancer Cell 2014 9
5/26/2018 4 cm liver mass in a 25 year old female Classification of Hepatocellular Tumors Non- Neoplastic neoplastic Focal Nodular Hepatocellular Hepatocellular Hyperplasia Adenoma Atypical carcinoma (FNH) (HCA) (HCC) HNF-1 a b -catenin Inflammatory inactivated activated (I-HCA) (H-HCA) (B-HCA) Risk of malignancy: Low Low None 40% 100% Case #2 – 30 M with liver mass 4 cm liver mass in a 25 year old woman Case #2 – 30 M with liver mass Case #1 – 4 cm mass in a 25 year old woman Any other stains? Liver fatty acid binding protein (LFABP) CRP SAA 10
5/26/2018 4 cm liver mass in a 25 year old woman Case #2 – 30 M with liver mass Case #1 – 4 cm mass in a 25 year old woman Any other stains? Glutamine synthetase Reticulin Genetic alterations in 250 HCA Final diagnosis: Atypical hepatocellular neoplasm; see comment. • Other terminologies – Hepatocellular neoplasm with uncertain malignant potential – Well-differentiated hepatocellular neoplasm with atypical or borderline features – Inflammatory adenoma with b -catenin activation Pilati et al. Cancer Cell 2014 11
5/26/2018 Take home points • Use a panel for well-differentiated lesions – Glutamine Synthetase (and b-catenin) – Reticulin – CRP or SAA – LFABP • Important to identify b -catenin activation • Glutamine synthetase stain is much more sensitive than b -catenin stain, but can be challenging to interpret in some cases • CTNNB1 sequencing Nault et al. J Hepatology 2017 Nault et al. J Hepatology 2017 Nault et al. J Hepatology 2017 12
5/26/2018 34 year old woman, liver nodule biopsied 34 year old woman, died of drug abuse, liver nodule biopsied LFABP Glutamine synthetase Reticulin H&E Diagnosis? HNF1a inactivated adenoma? b -catenin activated adenoma? HCC? 13
5/26/2018 34 year old woman, died of drug abuse, liver nodule biopsied Arginase HMB-45 UCSF GI-Liver Pathology Angiomyolipoma • Perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa) • Variable admixure of spindled cells, adipose, and thick-walled vessels • Most commonly seen in the kidney • Associated with Tuberous Sclerosis (germline and somatic) • Hepatic AML are usually sporadic – 5-15% are syndromic • Hepatic AML commonly show predominant epithelioid component 14
Recommend
More recommend