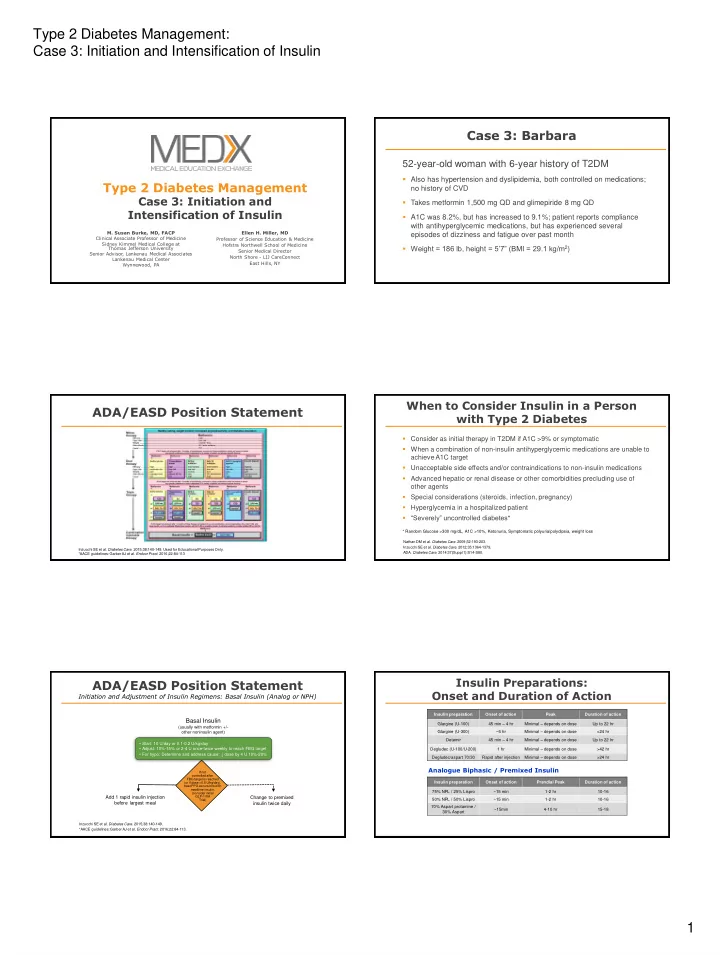

Type 2 Diabetes Management: Case 3: Initiation and Intensification of Insulin Case 3: Barbara 52-year-old woman with 6-year history of T2DM Also has hypertension and dyslipidemia, both controlled on medications; Type 2 Diabetes Management no history of CVD Case 3: Initiation and Takes metformin 1,500 mg QD and glimepiride 8 mg QD Intensification of Insulin A1C was 8.2%, but has increased to 9.1%; patient reports compliance with antihyperglycemic medications, but has experienced several M. Susan Burke, MD, FACP Ellen H. Miller, MD episodes of dizziness and fatigue over past month Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine Professor of Science Education & Medicine Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Hofstra Northwell School of Medicine Weight = 186 lb, height = 5’7” (BMI = 29.1 kg/m 2 ) Thomas Jefferson University Senior Medical Director Senior Advisor , Lankenau Medical Associates North Shore - LIJ CareConnect Lankenau Medical Center East Hills, NY Wynnewood, PA When to Consider Insulin in a Person ADA/EASD Position Statement with Type 2 Diabetes Consider as initial therapy in T2DM if A1C >9% or symptomatic When a combination of non-insulin antihyperglycemic medications are unable to achieve A1C target Unacceptable side effects and/or contraindications to non-insulin medications Advanced hepatic or renal disease or other comorbidities precluding use of other agents Special considerations (steroids, infection, pregnancy) Hyperglycemia in a hospitalized patient “Severely” uncontrolled diabetes* * Random Glucose >300 mg/dL, A1C >10%, Ketonuria, Symptomatic polyuria/polydipsia, weight loss Nathan DM et al. Diabetes Care . 2009;32:193-203. Inzucchi SE et al. Diabetes Care. 2012;35:1364-1379. Inzucchi SE et al. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:140-149. Used for Educational Purposes Only. ADA. Diabetes Care. 2014:37(Suppl 1):S14-S80. *AACE guidelines: Garber AJ et al. Endocr Pract. 2016;22:84-113 Insulin Preparations: ADA/EASD Position Statement Onset and Duration of Action Initiation and Adjustment of Insulin Regimens: Basal Insulin (Analog or NPH) Insulin preparation Onset of action Peak Duration of action Basal Insulin Glargine (U-100) 45 min – 4 hr Minimal – depends on dose Up to 22 hr (usually with metformin +/- other noninsulin agent) Glargine (U-300) ~6 hr Minimal – depends on dose >24 hr Detemir 45 min – 4 hr Minimal – depends on dose Up to 22 hr • Start: 10 U/day or 0.1-0.2 U/kg/day • Adjust: 10%-15% or 2-4 U once-twice weekly to reach FBG target Degludec (U-100/U-200) 1 hr Minimal – depends on dose >42 hr • For hypo: Determine and address cause; ↓ dose by 4 U 10%-20% Minimal – depends on dose Degludec/aspart 70/30 Rapid after injection >24 hr Analogue Biphasic / Premixed Insulin If not controlled after FBG target is reached (or if dose >0.5 U/kg/day), Insulin preparation Onset of action Prandial Peak Duration of action treat PPG excursions with mealtime insulin, 75% NPL / 25% Lispro ~15 min 1-2 hr 10-16 (consider initial Add 1 rapid insulin injection GLP-1 RA Change to premixed 50% NPL / 50% Lispro ~15 min 1-2 hr 10-16 Trial) before largest meal insulin twice daily 70% Aspart protamine / ~15min 4-10 hr 15-18 30% Aspart Inzucchi SE et al. Diabetes Care. 2015;38:140-149. *AACE guidelines: Garber AJ et al. Endocr Pract. 2016;22:84-113. 1
Type 2 Diabetes Management: Case 3: Initiation and Intensification of Insulin Time-Action Profiles of Human Insulins Long-acting Insulins and Insulin Analogs Inhaled insulin Intermediate-acting insulin: NPH Aspart, Glulisine, Lispro Long-acting insulin: Regular Insulin Detemir, Glargine NPH Plasma insulin levels Glargine U-300 Degludec U-100 or U-200 Detemir (basal) Glargine (basal) 4 8 16 24 Time after SC injection (hours) 2 4 6 8 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 0 10 Time Course of Action (Hour) Rosenstock J et al. eds. Textbook of Type 2 Diabetes . 2003:131-154. Plank J et al. Diabetes Care . 2005;28:1107-1112. Rave K et al. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:1077-1082; Afrezza (insulin human). Prescribing information. Available at: Adapted from Hirsch I . N Engl J Med . 2005;352:174-183. http://products.sanofi.us/afrezza/afrezza.html. Insulin Glargine U-300 Insulin Degludec Once-daily long-acting basal insulin New-generation ultra-long-acting basal insulin analog FDA approved 09/25/2015 FDA approved 02/25/2015 Meta-analysis of treat-to-target trials (2,899 people randomized to insulin degludec and Trials comparing glargine U-300 with glargine U-100 1,431 randomized to insulin glargine) Lower hypoglycemia * in T2DM RR = 0.83 [95% CI: 0.74; 0.94] Similar rates of glucose control and HbA1C reduction 86% reduction in insulin-naive patients Lower nocturnal hypoglycemia** in T2DM RR: 0.68 [95% CI: 0.57; 0.82] Lower rates of nocturnal and severe hypoglycemia with U-300 Lower hypoglycemia rate in elderly U-300 has longer duration of action compared with U-100 Improved treatment satisfaction and quality of life FLEX Study: time of daily dosing can be varied without compromising glycemic U-300 has flatter pharmacokinetic profile compared with U-100 control with A1C reduction comparable to fixed time glargine * Plasma glucose <3.1 mmol/L, irrespective of symptoms, or if the hypoglycemia was severe – requiring assistance from a third party); ** Nocturnal hypoglycemia was defined as occurring between 00:00 and 05:59. Riddle MC et al. Diabetes Care. 2014;37:2755-2762; Yki-Järvinen H et al. Diabetes Care. 2014;7:3235-3243; Bolli GB et al. Diabetes Obes Metab . Evans M, McEwan P. J Comp Eff Res. 2015:1-8. [Epub ahead of print]. Ratner R et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013;15:175-184. 2015;17:386-394. Meneghini L et al. Diabetes Care. 2013;36:858-864. Ultra-long Basal Insulins: Insulin Glargine Place in Therapy Follow-on (Biosimilar) Agent FDA approved first follow-on insulin glargine agent in Patients needing less fluctuation of insulin levels December 2015 Includes those with: Also referred to as biosimilar Nocturnal hypoglycemia Long-acting alternative form of currently available Renal impairment, elderly insulin glargine with the same protein sequence and similar glucose-lowering Variable schedules/lifestyle: shift workers, college students Injected once daily, subcutaneously using a prefilled pen formulation Complaints of variability of fasting glucose levels May be priced competitively Adherence issues: can dose within 8 hours if dose was missed Availability for use in US: late 2016 FDA news release, 12-16-15. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm477734.htm. 2
Recommend
More recommend