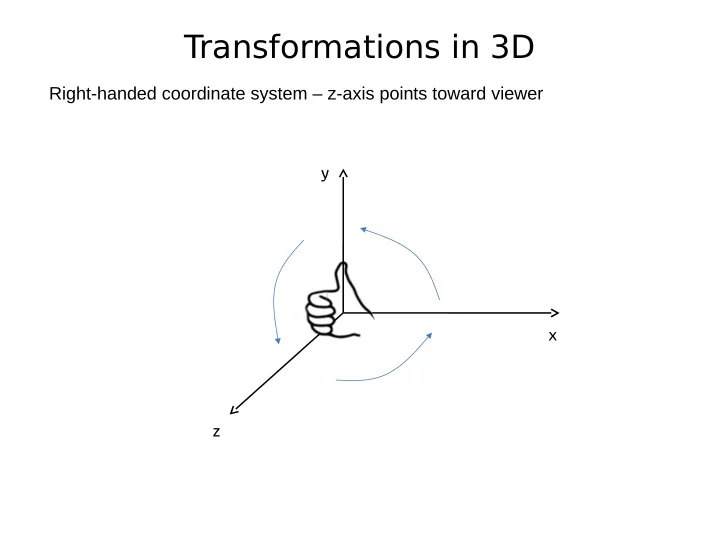

Transformations in 3D Right-handed coordinate system – z-axis points toward viewer y x z
Translation in 3D What are the coordinates of P after translating by d=(dx,dy,dz) x' = ? y' = ? P'(x',y', z') z' = ? P(x,y,z)
Translation in 3D What are the coordinates of P after translating by d=(dx,dy,dz) x' = x + dx = 1*x + 0*y + 0*z + 1*dx y' = y + dy = 0*x + 1*y + 0*z + 1*dy P'(x',y', z') z' = z + dz = 0*x + 0*y + 1*z + 1*dz P(x,y,z) in matrix form 1 0 0 dx x x' = 0 1 0 dy y y' * z z' 0 0 1 dz 1 1 0 0 0 1
Scaling in 3D What are the coordinates of P after scaling by sx,sy,sz x' = ? y' = ? P'(x',y',z') z' = ? P(x,y,z)
Scaling in 3D What are the coordinates of P after scaling by sx,sy,sz x' = sx * dx = sx*x + 0*y + 0*z y' = sy * dy = 0*x + sy*y + 0*z P'(x',y',z') z' = sz * dz = 0*x + 0*y + sz*z P(x,y,z) in matrix form sx 0 0 0 x x' = 0 sy 0 0 y y' * z z' 0 0 sz 0 1 1 0 0 0 1
Rotation in 3D around Z-axis P'(x',y',z') Rotating in a plane parallel to the XY-plane r Same as rotating in 2D P(x,y,z) r keep the Z -coordinate the same a P'(x',y',z') r P(x,y,z) r a
Rotation in 3D around Z-axis P'(x',y',z') Rotating in a plane parallel to the XY-plane r Same as rotating in 2D P(x,y,z) r keep the Z -coordinate the same a Same matrix with extra row, column 0 0 cos α -sin α x x' = y y' sin α cos α 0 0 P'(x',y',z') * z z' r 0 0 1 0 1 1 P(x,y,z) r a 0 0 0 1
Rotation in 3D around Y-axis Rotating in a plane parallel to the XY -plane Same as rotating in 2D P'(x',y',z') keep the Y -coordinate the same a P(x,y,z) P'(x',y',z') a P(x,y,z)
Rotation in 3D around Y-axis Rotating in a plane parallel to the XY -plane Same as rotating in 2D P'(x',y',z') keep the Y -coordinate the same a P(x,y,z) 0 0 cos α sin α x x' P'(x',y',z') = y y' 0 1 0 0 * z z' a 0 0 -sin α cos α 1 1 P(x,y,z) 0 0 0 1
Rotation in 3D around X-axis Rotating in a plane parallel to the YZ -plane P(x,y,z) Same as rotating in 2D P'(x',y',z') keep the X -coordinate the same α P(x,y,z) P'(x',y',z') α
Rotation in 3D around X-axis Rotating in a plane parallel to the YZ -plane P(x,y,z) Same as rotating in 2D P'(x',y',z') keep the X -coordinate the same α 1 0 0 0 x x' = 0 0 cos α -sin α y y' * P(x,y,z) P'(x',y',z') z z' 0 sin α cos α 0 1 1 α 0 0 0 1
Rotation around arbitrary axis P'(x',y',z') A(ax,ay,az) α P(x,y,z) can reduce to rotation around Z -axis by realignment of coordinate system
Rotation around arbitrary axis A(ax,ay,az) P(x,y,z)
Rotation around arbitrary axis compute A',A” s.t. A,A',A” perpend. A(ax,ay,az) A(ax,ay,az) P(x,y,z) P(x,y,z) A”(ax”,ay”,az”) A'(ax',ay',az')
Rotation around arbitrary axis compute A',A” s.t. A,A',A” perpend. A(ax,ay,az) A(ax,ay,az) P(x,y,z) P(x,y,z) A”(ax”,ay”,az”) align A',A”,A with A'(ax',ay',az') main axes X,Y,Z P(x,y,z) A”(ax”,ay”,az”) A'(ax',ay',az') A(ax,ay,az)
Rotation around arbitrary axis compute A',A” s.t. A,A',A” perpend. A(ax,ay,az) A(ax,ay,az) P(x,y,z) P(x,y,z) A”(ax”,ay”,az”) align A',A”,A with A'(ax',ay',az') main axes X,Y,Z P(x,y,z) A”(ax”,ay”,az”) M ax' ay' az' 0 ax” ay” az” 0 A'(ax',ay',az') ax ay az 0 0 0 0 1 A(ax,ay,az)
Rotation around arbitrary axis compute A',A” s.t. A,A',A” perpend. A(ax,ay,az) A(ax,ay,az) P(x,y,z) P(x,y,z) A”(ax”,ay”,az”) align A',A”,A with A'(ax',ay',az') main axes X,Y,Z P(x,y,z) A”(ax”,ay”,az”) M ax' ay' az' 0 P'(x',y',z') ax” ay” az” 0 α A'(ax',ay',az') ax ay az 0 0 0 0 1 ca -sa 0 0 sa ca 0 0 R A(ax,ay,az) rotate around z 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1
Rotation around arbitrary axis P'(x',y',z') compute A',A” s.t. A,A',A” perpend. A(ax,ay,az) A(ax,ay,az) α P(x,y,z) P(x,y,z) A”(ax”,ay”,az”) r e s t align A',A”,A with A'(ax',ay',az') o r e main axes X,Y,Z a l i g M' n m e n P(x,y,z) ax' ax” ax 0 t A”(ax”,ay”,az”) M ay' ay” ay 0 az' az” az 0 ax' ay' az' 0 0 0 0 1 P'(x',y',z') ax” ay” az” 0 α A'(ax',ay',az') ax ay az 0 0 0 0 1 ca -sa 0 0 sa ca 0 0 R A(ax,ay,az) rotate around z 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1
Rotation around arbitrary axis P'(x',y',z') A(ax,ay,az) α P(x,y,z) can reduce to rotation around Z -axis by realignment of coordinate system R = M' * R z * M multiply top of stack by R
Rendering Pipeline http://www.songho.ca/opengl/gl_transform.html M model M view *M proj World space View space Screen space P’ = M proj M view M model * P
The Camera Model (2D) u u e e v v camera parameters: e – eye point coordinates v – the directions of the view u – up vector e – what is the position (ex,ey) of the camera in the world The camera parameters and the coordinates of the model v – what are the coordinates are specifjed in world space (vx,vy) of the viewing direction in the world u – a vector perpendicular to v
The Camera Model (2D) To render the model need to: represent it from world space to camera view space coordinates – M view project it on the camera film – M proj u u y' e e v v y x' x
The Camera Model (2D) World to View space transformation ( M view ) – align camera axes with the world axes u v e
The Camera Model (2D) World to View space transformation ( M view ) – align camera axes with the world axes T u v e R
The Camera Model (2D) World to View space transformation ( M view ) – align camera axes with the world axes 1 0 -ex 0 1 -ey T u 0 0 1 v e R
The Camera Model (2D) World to View space transformation ( M view ) – align camera axes with the world axes 1 0 -ex 0 1 -ey T u 0 0 1 v e R vx vy 0 ux uy 0 0 0 1
The Camera Model (2D) World to View space transformation ( M view ) – align camera axes with the world axes 1 0 -ex 0 1 -ey T u 0 0 1 v e R vx vy 0 ux uy 0 0 0 1 M view = R*T
Recommend
More recommend