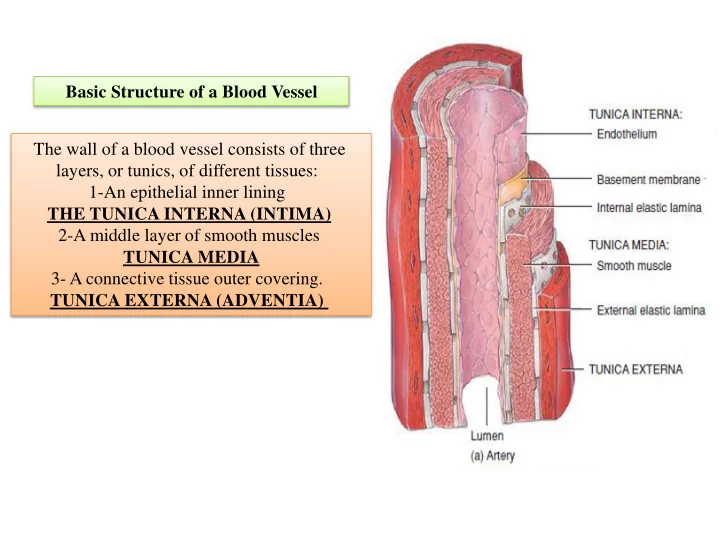

Basic Structure of a Blood Vessel The wall of a blood vessel consists of three layers, or tunics, of different tissues: 1-An epithelial inner lining THE TUNICA INTERNA (INTIMA) 2-A middle layer of smooth muscles TUNICA MEDIA 3- A connective tissue outer covering. TUNICA EXTERNA (ADVENTIA)
1- 2- 3-
1-Tunica Interna (Intima) The tunica interna forms the inner lining of a blood vessel and is in direct contact with the blood as it flows through the lumen The main component of the intima is simple sqaumous epithelium Called ENDOTHELIUM that lines the inner surface of the entire cardiovascular system (heart and blood vessels) 2-Tunica Media The tunica media (media middle) is made of a muscular (smooth 3-Tunica Externa muscle) and connective tissue layer The outer covering of a blood vessel, the tunica externa smooth muscle cells, which ( outermost) extend circularly around the consists of elastic and collagen fibers lumen like a ring The tunica externa contains numerous nerves and tiny blood vessels that supply the tissue of the vessel wall. `
An increase in ! sympathetic stimulation typically stimulates the smooth muscle to contract and narrowing the lumen. Such a decrease in the diameter of the lumen of a blood vessel is called vasoconstriction In contrast, decreases, or in the presence of certain chemicals (such as nitric oxide) or in response to blood pressure, smooth muscle fibers relax. The resulting increase in lumen diameter is called vasodilatation
The five main types of blood vessels are STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION 1- ARTERIES OF BLOOD VESSELS 2-ARTERIOLES 3-CAPILLARIES C- CAPILLARIES The thin 4-VENULES walls of capillaries allow the 5-VEINS exchange of substances between the blood and body tissues. 1-ARTERIES Groups of capillaries within carry blood away from the heart to other organs a tissue reunite to form small A-LARGE, ELASTIC ARTERIES leave the veins called: heart and divide into B- MEDIUM-SIZED, MUSCULAR ARTERIES that branch out into the various regions of the body. Medium-sized arteries then divide into small D-VENULES arteries, which in turn divide into still smaller These in turn merge to form arteries called : progressively larger blood vessels called veins. B- ARTERIOLES As the arterioles enter a tissue, E-Veins are the blood vessels that they branch into numerous tiny convey blood from the tissues back : vessels called to the heart:
2-Arterioles Small arteries arterioles are abundant microscopic vessels that regulate the flow of blood into the capillary . Arterioles have a thin tunica interna resistance vessels
3-Capillaries The smallest of blood vessels, connect the arterial outflow to the venous return The flow of blood from a metarteriole through capillaries and into a postcapillary venule (venule that receives blood from a capillary) is called the microcirculation of the body. The primary function of capillaries is the exchange of substances between the blood and different tissues
The body contains three different types of capillaries: A- Continuous Capillaries B-Fenestrated Capillaries C -sinusoids Most capillaries are a- CONTINUOUS CAPILLARIES, in which the plasma membranes of endothelial cells form a continuous tube inside the capillary Continuous capillaries are found in the central nervous system, lungs, skin, muscle tissue, and the skin
B-fenestrated capillaries The plasma membranes of the endothelial cells in these capillaries have many fenestrations . Can be found, for example, in kidneys, villi of the small intestine
C-Sinusoids are wider and more winding than other capillaries. Their endothelial cells may have unusually large fenestrations . For example, newly formed blood cells enter the bloodstream through the sinusoids of red bone marrow. Can be found, for example, in The spleen, the liver
4-Venules They have thin walls Venules drain the capillary blood and begin the return flow of blood back toward the heart Many veins, especially those in the limbs, also contain valves, thin folds of tunica 5-Veins The valves aid in venous return by preventing the backflow of Although veins are composed of essentially the blood same three layers as arteries, the relative thicknesses of the layers are different. The tunica interna of veins is thinner than that of arteries; the tunica media of veins is much thinner than Vein in arteries, with relatively little smooth muscle and elastic fibers. The tunica externa of veins is the thickest layer and consists of collagen and elastic fibers.
Recommend
More recommend