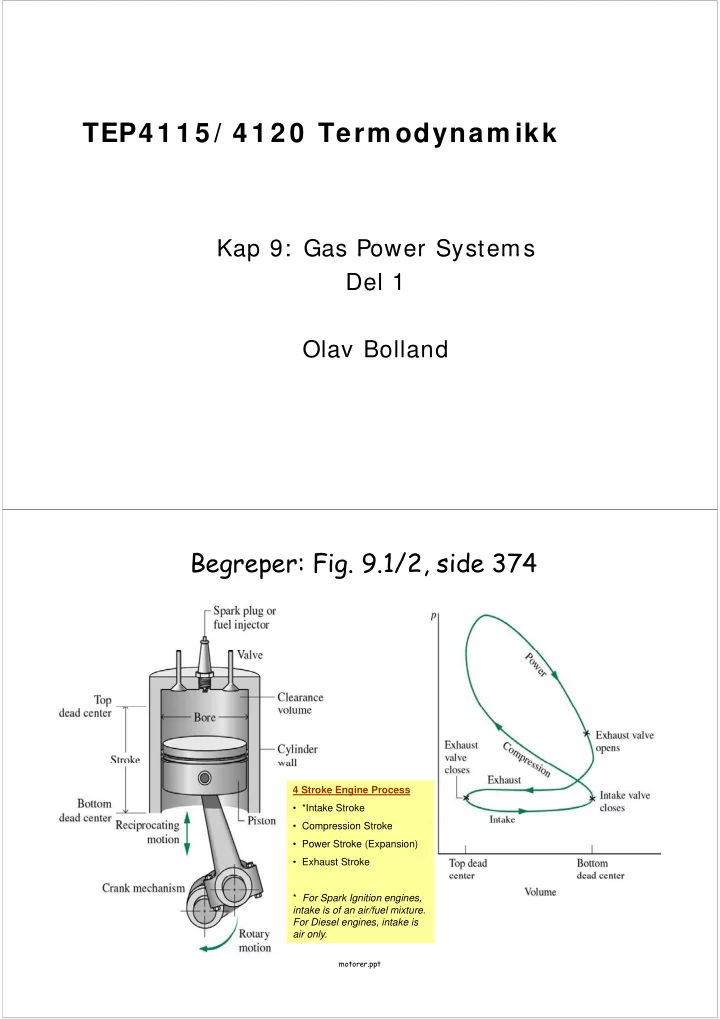

TEP4 1 1 5 / 4 1 2 0 Term odynam ikk 5 / 0 ody Kap 9: Gas Power Systems Kap 9: Gas Power Systems Del 1 Olav Bolland Begreper: Fig. 9.1/2, side 374 4 Stroke Engine Process • *Intake Stroke • Compression Stroke • Power Stroke (Expansion) • Exhaust Stroke * For Spark Ignition engines, intake is of an air/fuel mixture. For Diesel engines, intake is air only air only. motorer.ppt
Work closed/open systems First law for an open system (steady-state): First law for a closed system: dU dU Q W m h m h 0 Q W U U 1 2 2 1 dt Relating heat to entropy: Relating heat to entropy: 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 Q T dS dU pdV Q T dS 1 1 1 1 and and T dS dU PdV T dS dH Vdp T dS T dS dU dU PdV PdV H U pV dU dH pdV Vdp 2 2 2 2 2 Q T dS dU pdV Q dH V dp 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 U U pdV W U U Q m dh V dp 2 1 2 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 m h ( h ) V dp W m h ( h ) 0 W pdV 2 1 1 2 1 1 2 W W V dp V dp 1 motorer.ppt Air Standard Analysis Air Standard Analysis The following assumptions are made: The following assumptions are made: • Air, an Ideal Gas, is the working fluid • Combustion is replaced with Heat Addition (see Chap 13 for details) • No exhaust and intake strokes – constant volume heat rejection volume heat rejection • All processes are internally reversible For Cold-Air Standard, Specific Heats are also assumed constant For Cold Air Standard, Specific Heats are also assumed constant motorer.ppt
Otto Cycle Otto Cycle *Cycle Analysis: Cycle Analysis: W m 12 u u 1 2 m W 34 u u 3 3 4 4 m Q m 23 u u u u 3 2 Fig. 9.3, page 376 4 Internally Reversible Processes: Q Q m 41 41 • Isentropic Compression • Isentropic Compression u u 1 4 • Constant Volume Heat Addition • Isentropic Expansion * Sign Conventions (Work in • Constant Volume Heat Rejection Constant Volume Heat Rejection negative, etc.) are sometimes ti t ) ti changed for cycle applications motorer.ppt Diesel Cycles Diesel Cycles *Cycle Analysis: Cycle Analysis: W m 12 u u 1 2 m W 34 u u 3 3 4 4 m W 23 p p v v v v Fig 9 5 page 406 Fig. 9.5, page 406 2 2 3 3 2 2 m 4 Internally Reversible Processes: Q m 23 h h h h • Isentropic Compression • Isentropic Compression 3 2 • Constant Pressure Heat Addition • Isentropic Expansion Q Q • Constant Volume Heat Rejection Constant Volume Heat Rejection m 41 41 u u 1 4 motorer.ppt
Ottomotor - prinsipp motorer.ppt Otto 4-takts motor motorer.ppt
Totakts-motor motorer.ppt http://science.howstuffworks.com/two-stroke2.htm Diesel vs Otto • Diesel engines, with higher compression ratios (20: 1 for a typical diesel vs. 8: 1 for a typical gasoline engine), tend to be heavier than an equivalent gasoline engine than an equivalent gasoline engine • Diesel engines, because of the high compression ratio, tend to have lower maximum RPM ranges than gasoline engines. This g g g makes diesel engines high torque rather than high horsepower. • Diesel engines must be fuel injected, and in the past fuel injection was expensive and less reliable • Diesel engines tend to produce more smoke and "smell funny" • Diesel engines are harder to start in cold weather, and if they contain glow plugs, diesel engines can require you to wait before starting the engine so the glow plugs can heat up • Diesel engines are much noisier and tend to vibrate motorer.ppt
Hva er bensin/diesel ? C m H n bensin ( C 9 H 20 ), diesel ( C 14 H 30 ), paraffin ( C 12 ) flytende ved omgivelsestilstand flytende ved omgivelsestilstand Greit å huske 1 liter bensin = 9.7 10 kWh varmeverdi (35 MJ) 1 liter diesel = 11.4 11 kWh varmeverdi (41 MJ) 1 Sm 3 naturgass 10 kWh varmeverdi 1 Sm 3 naturgass 10 kWh varmeverdi Sm 3 er vanlig mengdemål for naturgass (trykk 1.013 bar, 15 °C) S g g g ( y , C) Nm 3 er ellers vanlig mengdemål for gasser (trykk 1.013 bar, 0 °C) motorer.ppt Verdens største dieselmotor Wärtsila-Sulzer RTA96-C Total engine weight: 2300 tons Height: 13.4m Max power: 108920 hp at 102 rpm Max power: 108920 hp at 102 rpm 81 MW Emma Maersk 81 MW from RTA96-C 30 MW from 5*Caterpillar 397m long, >1400 containers motorer.ppt 157 tonnes (deadweight)
Stirling motor - prinsipp motorer.ppt Stirling motor - prinsipp motorer.ppt
Recommend
More recommend