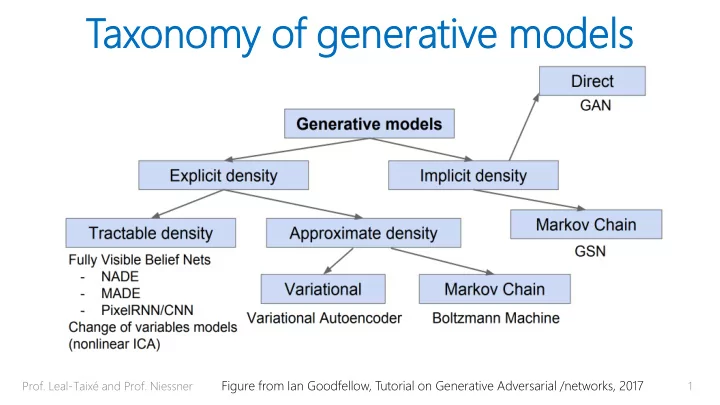

Tax axono onomy my of f ge generativ erative e mo models dels Prof. Leal-Taixé and Prof. Niessner Figure from Ian Goodfellow, Tutorial on Generative Adversarial /networks, 2017 1
Tax axono onomy my of f ge generativ erative e mo models dels Prof. Leal-Taixé and Prof. Niessner Figure from Ian Goodfellow, Tutorial on Generative Adversarial /networks, 2017 2
Ge Gene nerative rative Ad Adver ersarial sarial Ne Networks tworks Prof. Leal-Taixé and Prof. Niessner 3
Generat rativ ive Ad Adve versari sarial al Netw tworks rks (GAN ANs) s) Prof. Leal-Taixé and Prof. Niessner 4 https://github.com/hindupuravinash/the-gan-zoo
Conv nvolutio olution n an and Dec d Deconv onvolution olution Output Output Input Input Convolution Transposed convolution no padding, no stride no padding, no stride https://github.com/vdumoulin/conv_arithmetic
Autoencod oencoder er Conv Deconv
Rec econstru onstruction: ction: Autoencod oencoder er Reconstruction Loss (often L2) Input Image Output Image Conv Deconv
Tra raining ning Autoencoder oencoders Input images Reconstruction x’ Input x Reconstructed images Latent space z dim (z) < dim (x)
De Deco coder der as as Ge Generativ nerative Mo Mode del Reconstruction Loss (often L2) “Test time”: -> reconstruction from ‘random’ vector Output Image Latent space z dim (z) < dim (x)
De Deco coder der as as Ge Generativ nerative Mo Model Interpolation between two chair models [Dosovitsky et al. 14] Learning to Generate Chairs
De Deco coder der as as Ge Generativ nerative Mo Mode del Morphing between chair models [Dosovitsky et al. 14] Learning to Generate Chairs
De Deco coder der as as Ge Generativ nerative Mo Mode del Reconstruction Loss Often L2, i.e., sum of squared dist. -> L2 distributes error equally -> mean is opt. -> res. Is blurry “Test time”: -> reconstruction from ‘random’ vector Instea ead d of L L2, , can we we Latent space z “learn”a los oss funct ction? ion? dim (z) < dim (x)
Generat rativ ive Ad Adve versari sarial al Netw tworks rks (GAN ANs) s) 𝐸 𝐻 𝑨 𝐻(𝑨) 𝐸(𝐻(𝑨)) Prof. Leal-Taixé and Prof. Niessner [Goodfellow et al. 14] GANs (slide McGuinness) 13
Generat rativ ive Ad Adve versari sarial al Netw tworks rks (GAN ANs) s) 𝑦 𝐸(𝑦) 𝐸 𝐻 𝑨 𝐻(𝑨) 𝐸(𝐻(𝑨)) Prof. Leal-Taixé and Prof. Niessner [Goodfellow et al. 14] GANs (slide McGuinness) 14
Generat rativ ive Ad Adve versari sarial al Netw tworks rks (GAN ANs) s) real data fake data [Goodfellow et al. 14/16] GANs
GA GANs: Ns: Loss ss Fu Functions nctions Discriminator loss binary cross entropy Generator loss • Minimax Game: – G minimizes probability that D is correct – Equilibrium is saddle point of discriminator loss -> D provid vides supervi visio ion n (i.e., e., gradi dients nts) ) for r G [Goodfellow et al. 14/16] GANs
GA GANs: Ns: Loss ss Fu Functions nctions Discriminator loss Generator loss • Heuristic Method (often used in practice) – G maximizes the log-probability of D being mistaken – G can still learn even when D rejects all generator samples [Goodfellow et al. 14/16] GANs
Alter ernating nating Gr Grad adient ent Up Upda dates es • Step 1: Fix G, and perform gradient step to • Step 2: Fix D, and perform gradient step to Prof. Leal-Taixé and Prof. Niessner 18
Van anilla illa GA GAN Prof. Leal-Taixé and Prof. Niessner 19 https://papers.nips.cc/paper/5423-generative-adversarial-nets
Tra raining ning a G a GAN https://medium.com/ai-society/gans-from-scratch-1-a-deep-introduction-with-code-in-pytorch-and-tensorflow-cb03cdcdba0f Prof. Leal-Taixé and Prof. Niessner 20
GA GANs: Ns: Loss ss Fu Functions nctions Minimax Heuristic [Goodfellow et al. 14/16] GANs
DCGAN: GAN: Gener nerat ator or Generator of Deep Convolutional GANs DCGAN: https://github.com/carpedm20/DCGAN-tensorflow
DC DCGAN: GAN: Res esult ults Results on MNIST Prof. Leal-Taixé and Prof. Niessner DCGAN: https://github.com/carpedm20/DCGAN-tensorflow 23
DC DCGAN: GAN: Res esult ults Results on CelebA (200k relatively well aligned portrait photos) DCGAN: https://github.com/carpedm20/DCGAN-tensorflow
DC DCGAN: GAN: Res esult ults Asian face dataset Prof. Leal-Taixé and Prof. Niessner DCGAN: https://github.com/carpedm20/DCGAN-tensorflow 25
DC DCGAN: GAN: Res esult ults Prof. Leal-Taixé and Prof. Niessner DCGAN: https://github.com/carpedm20/DCGAN-tensorflow 26
DC DCGAN: GAN: Res esult ults Loss of D and G on custom dataset Prof. Leal-Taixé and Prof. Niessner DCGAN: https://github.com/carpedm20/DCGAN-tensorflow 27
“Bad” Training Curves https://stackoverflow.com/questions/44313306/dcgans-discriminator-getting-too-strong-too-quickly-to-allow-generator-to-learn Prof. Leal-Taixé and Prof. Niessner 28
“Good” Training Curves Prof. Leal-Taixé and Prof. Niessner https://medium.com/ai-society/gans-from-scratch-1-a-deep-introduction-with-code-in-pytorch-and-tensorflow-cb03cdcdba0f 29
“Good” Training Curves Prof. Leal-Taixé and Prof. Niessner https://stackoverflow.com/questions/42690721/how-to-interpret-the-discriminators-loss-and-the-generators-loss-in-generative 30
Tra raining ning Sch chedul edules es • Adaptive schedules • For instance: while loss_discriminator > t_d: train discriminator while loss_generator > t_g: train generator Prof. Leal-Taixé and Prof. Niessner 31
Wea eak vs s Str trong ong Di Discriminat criminator or Need balance • Discriminator too weak? – No good gradients (cannot get better than teacher…) • Generator too weak? – Discriminator will always be right Prof. Leal-Taixé and Prof. Niessner 32
Mo Mode de Coll llaps apse • min 𝐻 max 𝑊 𝐻, 𝐸 ≠ max min 𝐻 𝑊(𝐻, 𝐸) 𝐸 𝐸 • 𝐸 in inner loop -> convergence to correct dist. • 𝐻 in inner loop -> easy to convergence to one sample Prof. Leal-Taixé and Prof. Niessner [Metz et al. 16] 33
Mo Mode de Coll llaps apse • Data dim. Fixed (512) • Performance correlates with # of modes -> More modes, smaller recovery rate! -> part of the reason, why we often see GAN-results on specific domains (e.g., faces) Prof. Leal-Taixé and Prof. Niessner 34 Slide credit Ming-Yu Liu
Mo Mode de Coll llaps apse • Performance correlates with dim of manifold -> Larger latent space, more mode collapse Prof. Leal-Taixé and Prof. Niessner 35 Slide credit Ming-Yu Liu
Prob oblems lems wi with th Gl Global al Struc tructu ture Prof. Leal-Taixé and Prof. Niessner 36
Prob oblems lems wi with th Count unting ing Prof. Leal-Taixé and Prof. Niessner 37
Ev Evaluation aluation of f GA GAN N Per erformance formance Prof. Leal-Taixé and Prof. Niessner 38
Ev Evaluation aluation of f GA GAN N Per erformance formance • Main difficulty of GANs: we don’t know how good they are • People cherry pick results in papers -> some of them will always look good, but how to quantify? • Do we only memorize or do we generalize? • GANs are difficult to evaluate! [This et al., ICLR 2016] Prof. Leal-Taixé and Prof. Niessner 39
Ev Evaluation aluation of f GA GAN N Per erformance formance Human evaluation: - Every n updates, show a series of predictions - Check train curves - What does ‘look good’ mean at the beginning? - Need variety! - But don’t have ‘realistic’ predictions yet… - If it doesn’t look good? Go back, try different hyperparameters … Prof. Leal-Taixé and Prof. Niessner 40
Ev Evaluation aluation of f GA GAN N Per erformance formance Incept ceptio ion n Score (IS) - Measures saliency and diversity - Train an accurate classifier - Train a image generation model (conditional) - Check how accurate the classifier can recognize the generated images - Makes some assumptions about data distributions… Prof. Leal-Taixé and Prof. Niessner 41
Ev Evaluation aluation of f GA GAN N Per erformance formance Incept ceptio ion n Score (IS) - Saliency: check whether the generated images can be classified with high confidence (i.e., high scores only on a single class) - Diversity: check whether we obtain samples from all classes What t if w we only have ve one good d image ge per class? Prof. Leal-Taixé and Prof. Niessner 42
Ev Evaluation aluation of f GA GAN N Per erformance formance • Could also look at discriminator – If we end up with a strong discriminator, then generator must also be good – Use D features, for classification network – Only fine-tune last layer – If high class accuracy -> we have a good D and G Caveat: not sure if people do this... Couldn’t find paper Prof. Leal-Taixé and Prof. Niessner 43
Ne Next: xt: Ma Making ng GA GANs Ns Work rk in Pra ractice ctice • Training / Hyperparameters (most important) • Choice of loss function • Choice of architecture Prof. Leal-Taixé and Prof. Niessner 44
Recommend
More recommend