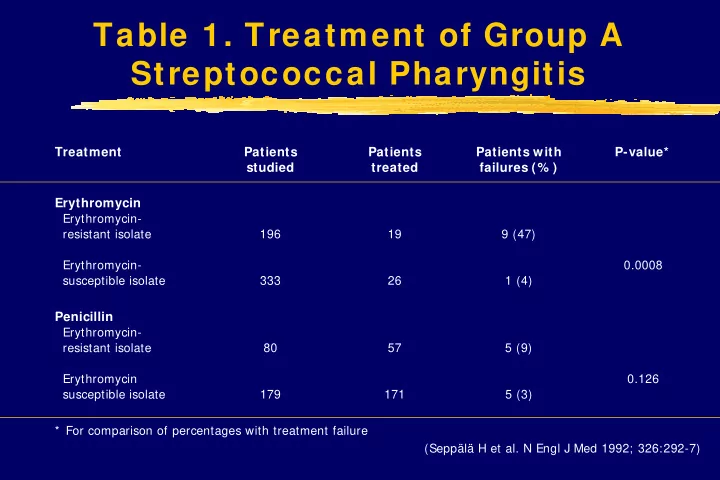

Table 1. Treatment of Group A Streptococcal Pharyngitis Treatment Patients Patients Patients with P-value* studied treated failures (% ) Erythromycin Erythromycin- resistant isolate 196 19 9 (47) Erythromycin- 0.0008 susceptible isolate 333 26 1 (4) Penicillin Erythromycin- resistant isolate 80 57 5 (9) Erythromycin 0.126 susceptible isolate 179 171 5 (3) * For comparison of percentages with treatment failure (Seppälä H et al. N Engl J Med 1992; 326:292-7)
Table 2. Results of follow -up study: eradication of Streptococcus pyogenes in relation to treatment of pharyngitis in pediatric patients in Italy Antibiotic No. of patients No. (% ) of S. 95 % CI treatment treated (n= 668) pyogenes eradications Penicillins 208 175 (84.1) 78.3-88.7 Cephalosporins 139 115 (82.7) 75.4-88.6 Macrolides 321 230 (71.7) 66.5-76.4 Erythromycin- susceptible strains 187 150 (80.2) 73.8-85.7 Erythromycin- resistant strains 134 80 (59.7) 50.9-68.1 (Varaldo PE et al. Clin Infect Dis 1999; 29:869-73)
Table 3. Treatment of children w ith acute otitis media caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae. Effect of resistance of amoxicillin and macrolides on the efficacy of amoxicillin/clavulanate and azithromycin Treatment No. of patients No. (% ) of patients with treated bacteriological success Amoxicillin/ clavulanate Amoxi/clav-susceptible isolates * 20 18 (90) Amoxi/clav-nonsusceptible isolates * * 9 9 (100) Azithromycin Azithromycin-susceptible isolates * 25 23 (92) Azithromycin-resistant P= 0.004 isolates * * * 8 3 (38) * MIC < 0.25 µ g/ml, * * MIC > 0.5 µ g/ml, * * * MIC > 2 µ g/ml (Dagan et al. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2000; 19:95-104)
Table 4. Treatment of children w ith acute otitis media caused by Streptococcus pneumonia. Bacteriologic efficacy of azithromycin and cefaclor Treatment No. of patients No (%) of patients with treated bacteriologic failure Azithromycin Azithromycin-susceptible isolates (MIC < 0.06 µ g/ml) 12 0 (0) Azithromycin-resistant isolates (MIC > 32.0 µ g/ml) 6 6 (100) Cefaclor Cefaclor-susceptible isolates (MIC < 0.5 µ g/ml) 14 3 (21) Cefaclor-nonsusceptible isolates (MIC > 0.5 µ g/ml) 19 13 (68) (Dagan R et al. Antimicrob Ag Chemother 2000; 44:43-50)
Table 5. Outcomes in patients w ith macrolide-resistant pneumococcal infections experiencing clinical failure w hile undergoing treatment w ith macrolides Macrolide Days treated Type of infection Outcome (no. of patients) (median) (no. of patients) Erythromycin (3) 3-8 (4) Pneumonia (4) Cured (penicillin or cefotaxime) Azithromycin (4) 2-5 (3) Pneumonia (3 Cured (amoxicillin, Bacteremia (1) penicillin or ceftriaxone) Clarithromycin (3) 2-3 (3) Pneumonia (2) Cured (ceftriaxone, Pneumonia + cefuroxime or empyema (1) cefotaxime) Josamycin (2) 2-4 Pneumonia (1) Cured (cefotaxime or Bacteremia (1) amoxicillin/clavulanate (Garau J. Respir Med 2001; 95 (Suppl A), S5-S11)
Table 6. Outcomes in patients w ith macrolide-resistant* pneumococcal infections experiencing clinical failure w hile undergoing treatment w ith macrolides Patient; Macrolide; Disease Outcome gender, days treated age (yrs) Male 46 Azithromycin; 3 Pneumonia Cured (vancomycin + Hypertension ceftriaxone) Female 58 Azithromycin; 5 Pneumonia Cured (cefotaxime, Diabetes mellitus azithromycin, levofloxacin) Male 77 Clarithromycin; 3 Pneumonia Cured (vancomycin) Multiple myeloma Female 5 Azithromycin, 5 Otitis media Cured (ceftriaxone) Acute lymphocytic leukemia * Erythromycin MICs 8-16 µ g/ml (Kelley M et al. Clin Infect Dis 2000; 31:1008-11)
Recommend
More recommend