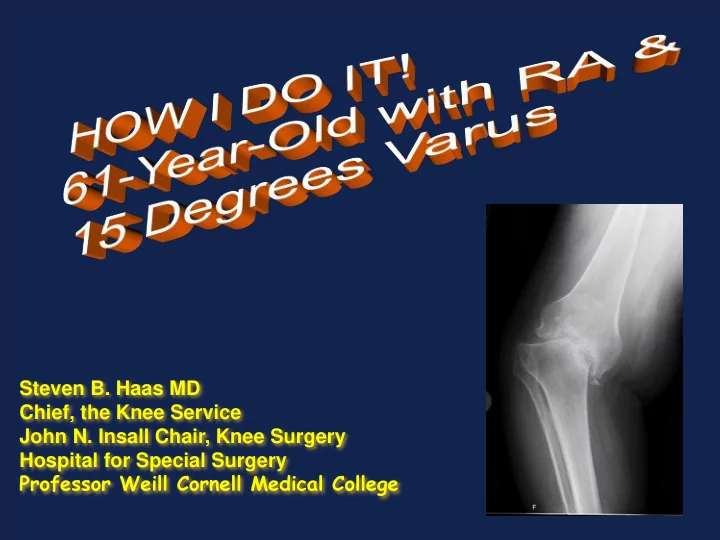

Steven B. Haas MD Chief, the Knee Service John N. Insall Chair, Knee Surgery Hospital for Special Surgery Professor Weill Cornell Medical College
Disclosure – Smith & Nephew Orthopaedics • Designer (Royalty income), Consultant and Research Support on Knee Products for – OpLogix Technology • Ownership ADULT RECONSTRUCTION AND JOINT REPLACEMENT
Incision • Fragile Skin • Extend Incision as Needed! ADULT RECONSTRUCTION AND JOINT REPLACEMENT
Several Approach to TKR Medial Parapatellar Midvastus
Balancing The Varus Knee ADULT RECONSTRUCTION AND JOINT REPLACEMENT
Soft Tissue Balancing in the Varus Knee Principles • Goal – Rectangular flexion & extension gaps – Symmetric medial & lateral soft tissue tension ADULT RECONSTRUCTION AND JOINT REPLACEMENT
Balancing The Varus Knee • Items for consideration: – Fixed versus flexible – Tightness: • Flexion • Extension or both ! – Osteophytes – Bone Loss – Subluxation and or effect upon rotation – Flexion Contracture ADULT RECONSTRUCTION AND JOINT REPLACEMENT
Preoperative planning Mechanical Alignment • Distal femur • Medial Bone Loss • Causes additional distal resection • Tibia 90 ° • Often Minimal or no medial resection 90 ° • Estimate resection thickness • Measure intraop • Plan releases ADULT RECONSTRUCTION AND JOINT REPLACEMENT
Dissection around medial tibia - EXPOSURE-VARUS KNEE Subperiosteal Release Deep MCL ADULT RECONSTRUCTION AND JOINT REPLACEMENT
Osteophytes removal Tibia - Externaly rotate to get posteriorly ADULT RECONSTRUCTION AND JOINT REPLACEMENT
Osteophytes removal Postero-medial corner Reduces tension on posterior capsule and posterior oblique fibers of deep medial collateral ligament which are two of the main medial joint stabilizers at 0 ° to 20 ° of flexion ADULT RECONSTRUCTION AND JOINT REPLACEMENT Whiteside J. Arthroplasty 2003
Osteophytes removal Medial femoral condyle ADULT RECONSTRUCTION AND JOINT REPLACEMENT
Soft tissue balancing Spacer block in flexion Spacer block in extension ADULT RECONSTRUCTION AND JOINT REPLACEMENT
Release Semimembranosis Postero-medial corner Reduces tension on posterior capsule and posterior oblique fibers of deep medial collateral ligament which are two of the main medial joint stabilizers at 0 ° to 20 ° of flexion ADULT RECONSTRUCTION AND JOINT REPLACEMENT
Medial Reduction Osteotomy Severe Varus Knee Remove medial edge of tibia Elevate MCL distally ADULT RECONSTRUCTION AND JOINT REPLACEMENT
Medial Reduction Osteotomy Shift-and-resect technique Uncovered area is resected vertically Tension on superficial MCL is reduced, bone gaps open a few mm medially ADULT RECONSTRUCTION AND JOINT REPLACEMENT
Severe Deformities ADULT RECONSTRUCTION AND JOINT REPLACEMENT
Subperiosteal release MCL Severe Varus Knee ADULT RECONSTRUCTION AND JOINT REPLACEMENT
Alternative MCL release: needle puncturing Progressive stretching of MCL (step by step) Both in extension and flexion (?) ADULT RECONSTRUCTION AND JOINT REPLACEMENT
MCL release: needle puncturing MCL release in extension in flexion ADULT RECONSTRUCTION AND JOINT REPLACEMENT
Summary • TKA is a “soft tissue” operation – Every knee has its own identity • Classic Method of bone resection – Re-establish mechanical axis – Appropriate soft tissue releases – Balance the flexion and extension gaps ADULT RECONSTRUCTION AND JOINT REPLACEMENT
ADULT RECONSTRUCTION AND JOINT REPLACEMENT
Recommend
More recommend