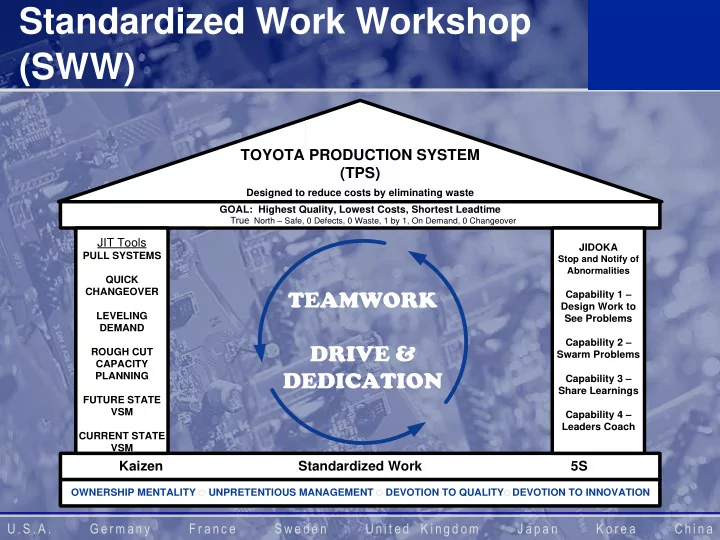

Standardized Work Workshop (SWW) TOYOTA PRODUCTION SYSTEM (TPS) Designed to reduce costs by eliminating waste GOAL: Highest Quality, Lowest Costs, Shortest Leadtime True Gentex True North – Safe, 0 Defects, 0 Waste, 1 by 1, On Demand, 0 Changeover JIT Tools JIDOKA PULL SYSTEMS Stop and Notify of Abnormalities QUICK TEAMWORK CHANGEOVER Capability 1 – Design Work to LEVELING See Problems DEMAND Capability 2 – DRIVE & ROUGH CUT Swarm Problems CAPACITY DEDICATION PLANNING Capability 3 – Share Learnings FUTURE STATE VSM Capability 4 – Leaders Coach CURRENT STATE VSM Kaizen Standardized Work 5S OWNERSHIP MENTALITY UNPRETENTIOUS MANAGEMENT DEVOTION TO QUALITY DEVOTION TO INNOVATION U. S . A . G er m any F r anc e S we de n Uni t ed K i ngd om J ap a n K o r e a Chi n a
Agenda 1. Introduction to TPS 2. Standardized Work Presentation 3. Other TPS Foundations (If time allows) 4. Questions 5. 15 Minute Break 6. Pen Build Activity 7. Questions 2
Standardized Work TOYOTA PRODUCTION SYSTEM (TPS) Designed to reduce costs by eliminating waste GOAL: Highest Quality, Lowest Costs, Shortest Leadtime Gentex True North – Safe, 0 Defects, 0 Waste, 1 by 1, On Demand, 0 Changeover JIT Tools JIDOKA PULL SYSTEMS Stop and Notify of Abnormalities If our goal is to improve, QUICK CHANGEOVER Capability 1 – first we must build a Design Work to LEVELING See Problems DEMAND strong foundation. Capability 2 – ROUGH CUT Swarm Problems CAPACITY PLANNING Capability 3 – Share Learnings FUTURE STATE VSM Capability 4 – Leaders Coach CURRENT STATE VSM Kaizen Standardized Work 5S OWNERSHIP MENTALITY UNPRETENTIOUS MANAGEMENT DEVOTION TO QUALITY DEVOTION TO INNOVATION 3
Standardized Work (SW) What is Standardized Work? Currently the best method for efficient production considering safety and quality while focusing on human movements. Organizes and defines operators movements into a repeatable and predictable pattern. Standardized Work Prespecifies the following: • Elements • Sequence Process • Location Design • Timing • Output 4
Standardized Work (SW) What is Standardized Work? 3 Elements of Standardized Work 1. Takt Time TAKT Time = Available Time Demand 2. Work Sequence 3. In-Process Stock Minimum necessary process inventory to maintain Standardized Work 5
Standardized Work Why should we practice Standardized Work? Management’s job is to provide valuable work for our operators. People have the ambition and ability to add value. We must be sure we are respecting our operators abilities. Standardized Work allows us to see problems People are born problem solvers We must be able to see problems 6
Standardized Work Why should we practice Standardized Work? (Continued) Starting point for kaizen activity Supports operator to management communication about how a job can be improved. Common reference point for sincere communication The absence of Standardized Work means that each individual will find their own way to build products for our customers. Devotion to Quality and Safety?? 7
Standardized Work Mr. Ohno’s thoughts on Standardized Work from Workplace Management Author: Taiichi Ohno When creating Standard Work, Difficult to establish a standard if you are trying to achieve the ‘best way’…big mistake. Document exactly what you are doing now. If you make it better than now, it is Kaizen. Years ago, I made them hang standard work documents on the shop floor. After a year I said to a teamleader, “The color of the paper has changed, which means you have been doing it the same way, so you have been a salary thief for the last year.” 8
Standardized Work Worksheets How to Implement Standardized Work? The Four Standardized Work Tools: 1 Work Balance Chart 2 Standardized Capacity Sheet 3 Standardized Work Chart 4 Standardized Work Combination Table 9
Takt Time Purpose: Pace of Production = Pace of Sales Basis for allocating work between operators to balance line Available Time TAKT Time = Demand 10
Cycle Time Vs Takt Time Cycle Time is measured at the process. Takt Time is calculated based on customer demand. Do NOT have the same definitions Different terms Different meanings TAKT Time = Available Time Demand 11
Takt Time Example Total Time = Time team members are at work Available Time = Time allotted for production Total Time – (lunches, breaks, scheduled meetings, etc.) Demand = Parts required for shipment during the time being analyzed for the numerator TAKT Time = Available Time Demand 12
Takt Time Example Hours: Each shift has: 1 st Shift: 6 am – 2 pm Lunch: 20 min 2 nd Shift: 2 pm – 10 pm 1 Break: 10 min Total Time = 6 am 2 pm = 8 hrs x 60 min/hr = 480 min/shift 2 pm 10 pm = 8 hrs x 60 min/hr = 480 min/shift Total Time = 480 min per shift - 20 min lunch per shift - 10 min break per shift Available Time= 450 min per shift x 2 shifts = 900 min/day 13
Takt Time Example Available Time = 900 min/day Demand = 2000 pcs/day TAKT Time = Available Time Demand TAKT Time = 900 min/day X 60 sec/min = 54,000 seconds/day = 2000 pcs/day 2000 pcs/day TAKT Time = 27 sec/pc 14
Cycle Time Vs Takt Time Comparison between Cycle Time (C/T) & Takt Discuss each scenario – good or bad – why? (a) Cycle Time > Takt Time (b) Cycle Time < Takt Time (c) Cycle Time = Takt Time 15
Takt Time Example Max Cycle Time = Greatest cycle time after outliers are removed Lowest Repeatable Cycle Time = 2 nd least cycle time Average Cycle Time = Average of cycle times w/o outliers Periodic work= Work that must be done but not during each cycle 16
Work Balance Chart Elements of a Work Balance Chart: Maximum Cycle Time Average Cycle Time Takt Time Periodic Work Lowest Repeatable Cycle Time 17
Cycle Time Examples X Set 1: 5, 4, 7, 9, 5 Set 2: 4, 9, 4, 7, 30 9 9 Max Time = Max Time = 5 4 Lowest repeatable = Lowest repeatable = 6 6 Average = Average = 18
Periodic Work Items that don’t happen each cycle, but are inherent in our process design. Scanning flow schedules Periodic Work Material movement Changing PPE Scanning boxes We will divide the time for a period task over the frequency in which it occurs. Periodic Work Time / X pcs = Periodic Work / Pc. 19
STD Work Pretest 20
5S What is 5S? Based on Japanese words that begin with ‘S’, the 5S Philosophy focuses on effective work place organization and standardized work procedures. 5S simplifies your work environment, reduces waste and non-value activity while improving quality efficiency and safety. Japanese English 1. Seiri (Sort) 2. Seiton (Straighten) 3. Seiso (Shine) 4. Seiketsu (Standardize) 5. Shitsuke (Sustain) Collectively, they mean the maintaining of an orderly, clean and efficient working environment. 21
7 Wastes What are the 7 Wastes? Based on a philosophy that the 7 wastes are symptoms to problems and there causes can be countermeasured to reduce cost in a value stream. Recognize the waste and start asking why, why, why? The 7 Wastes 1. Waste of Waiting 2. Waste of Conveyance 3. Waste of Over-Processing 4. Waste of Inventory 5. Waste of Motion 6. Waste of Correction 7. Waste of Over-Production 22
True North True North? Based on a philosophy that if we implement countermeasures that are in line with True North we will improve our key measures. 23
Kaizen Kaizen Ideas? “Kai” = “Change” or “the action to correct” “zen” = “good” or “for the better” Kaizen = Change for the good What improvements can we make based on what your Standardized Work Combination Table is showing you? Be mindful of 5S, The 7 Wastes and Gentex True North when looking for improvements. 24
Break 15 Minute Break 25
ACTIVITY: Pen Build Activity Goal: Build 20 pens in 100 seconds. Demand = 20 Pens Time = 100 seconds (1’ 40”) Intended Learning Work Balance Chart 1 26
ACTIVITY: Pen Build Pen Assembly: 1. Pen Body 2. Ink 3. Threaded End Cap 4. Cap 5. Final Assembly 27
ACTIVITY: Pen Build Pen Specifications: 1. Threaded end cap must be finger tight on the Pen Body 2. Cap must be fully seated, “snapped”, onto the Pen Body 3. Pens must be loaded into shipping pallets 4. Each shipping pallet must have 5 pens 28
ACTIVITY: Pen Build Activity Rules: 1. Only the specified builders can participate once the time starts. 2. Remaining team members are observing the operation. 29
ACTIVITY: Pen Build What would you like to know? 30
ACTIVITY: Pen Build Pen Build Simulation 31
Work Balance Chart Highlights of a Work Balance Chart: 1. Visually shows if we are meeting our customers’ demand 2. Visually shows the relationship of our operators from station to station. 3. Visually shows the fluctuation at each station (Max – Lowest Repeatable = Fluctuation) • Higher fluctuations show that a job is difficult to do (Mira). 4. Visually shows how much periodic work is being performed at each station. 32
STD Work Pretest 33
Recommend
More recommend