
Synthesis of Calcium Carbonate Particles with Different Geometries L.I. Fatkhutdinova 1 , H. Bahrom 2 , A.A. Goncharenko 3 , O. Peltek 1 , A. Muslimov 4 , A. Manchev 2 , I. Shishkin 1 , R.E. Noskov 2 , A.S. Timin 3 , P. Ginzburg 2 and M.V. Zyuzin 1 1 ITMO University, 3 Peter the Great St. Petersburg 4 St. Petersburg Academic University, 2 Tel-Aviv University, Saint Petersburg, Polytechnic University, Saint Petersburg, Tel-Aviv, Russian Federation Russian Federation Israel Saint Petersburg, Russian Federation Particle formation Thermal behaviour Surface properties Conclusions Introduction In vitro studies Spheroids Figures, text etc (Column 1)
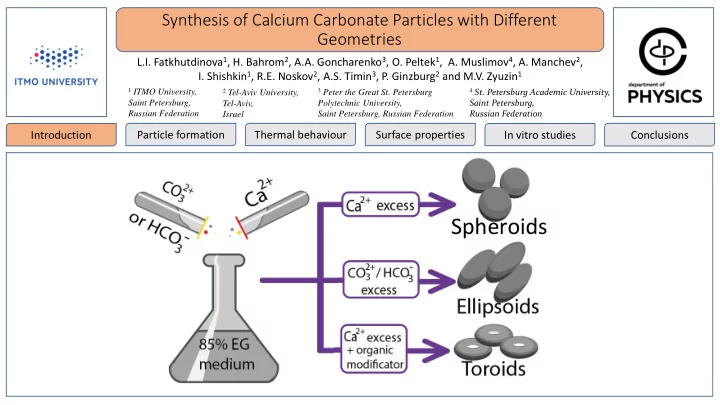
Synthesis of Calcium Carbonate Particles with Different Geometries L.I. Fatkhutdinova 1 , H. Bahrom 2 , A.A. Goncharenko 3 , O. Peltek 1 , A. Muslimov 4 , A. Manchev 2 , I. Shishkin 1 , R.E. Noskov 2 , A.S. Timin 3 , P. Ginzburg 2 and M.V. Zyuzin 1 1 ITMO University, 3 Peter the Great St. Petersburg 4 St. Petersburg Academic University, 2 Tel-Aviv University, Saint Petersburg, Polytechnic University, Saint Petersburg, Tel-Aviv, Russian Federation Russian Federation Israel Saint Petersburg, Russian Federation Particle formation Thermal behaviour Surface properties In vitro studies Conclusions Introduction Relevance Why Calcium Carbonate? Vaterite [1] delivery platform for biologically active low cost compounds nanoparticles: loading capacity stability biocompatibility pH-sensitivity sustained drug release control size, shape and porosity porosity by changing the synthetic conditions controllable physicochemical properties safety biodegradability controllable synthesis of biocompatible containers References different shaped particles for drug delivery into cells [1] Trofimov, A. D. et. al. Pharmaceutics, 10(4), 167
Synthesis of Calcium Carbonate Particles with Different Geometries L.I. Fatkhutdinova, H. Bahrom, A.A. Goncharenko, O. Peltek, A. Muslimov, A. Manchev, I. Shishkin, R.E. Noskov, A.S. Timin, P. Ginzburg and M.V. Zyuzin Introduction Particle formation Thermal behaviour Surface properties In vitro studies Conclusions Influence of salt concentrations SEM images of products of reactions A-I, A-II, A-III (Molar salt ratio = 1:1) in 5 min Reaction A-I Reaction A-III Reaction A-II c( CaCl 2 ) = 5 ∙ 10 -4 M c( CaCl 2 ) = 5 ∙ 10 -3 M c( CaCl 2 ) = 5 ∙ 10 -2 M c( Na 2 CO 3 ) = 5 ∙ 10 -4 M c( Na 2 CO 3 ) = 5 ∙ 10 -3 M c( Na 2 CO 3 ) = 5 ∙ 10 -2 M Molar salt ratio = 1:1 Molar salt ratio = 1:1 Molar salt ratio = 1:1
Synthesis of Calcium Carbonate Particles with Different Geometries L.I. Fatkhutdinova, H. Bahrom, A.A. Goncharenko, O. Peltek, A. Muslimov, A. Manchev, I. Shishkin, R.E. Noskov, A.S. Timin, P. Ginzburg and M.V. Zyuzin Introduction Particle formation Thermal behaviour Surface properties In vitro studies Conclusions Dependence on the reaction time & ion excess concentration B-I B-II B-III Reaction CaCl 2 : Na 2 CO 3 5:1 1:1 1:5 30 min 60 min 24 h SEM images of reactions B-I, B-II, B-III in 30 min, 60 min, 24 h
Synthesis of Calcium Carbonate Particles with Different Geometries L.I. Fatkhutdinova, H. Bahrom, A.A. Goncharenko, O. Peltek, A. Muslimov, A. Manchev, I. Shishkin, R.E. Noskov, A.S. Timin, P. Ginzburgand M.V. Zyuzin Introduction Particle formation Thermal behaviour Surface properties In vitro studies Conclusions - ions Influence of HCO 3 Reaction C-I C-II C-III C-IV C-V CaCl 2 : NaHCO 3 5:1 1:1 1:5 1:10 1:15
Synthesis of Calcium Carbonate Particles with Different Geometries L.I. Fatkhutdinova, H. Bahrom, A.A. Goncharenko, O. Peltek, A. Muslimov, A. Manchev, I. Shishkin, R.E. Noskov, A.S. Timin, P. Ginzburg and M.V. Zyuzin Introduction Particle formation Thermal behaviour Surface properties In vitro studies Conclusions Influence of organic additive Scheme of toroid formation by introducing PSS as organic additive SEM images of products of reactions D-I, D-II, D-III, in 24 h Molar ratio с( PSS ), Reaction CaCl 2 : Na 2 CO 3 mg/mL D-I 5:1 0.5 D-II 5:1 1 XRD analysis of CaCO 3 D-III 5:1 2 samples obtained by reactions D-I, D-II, D-III poly(styrene sulfonate) sodium – PSS
Synthesis of Calcium Carbonate Particles with Different Geometries L.I. Fatkhutdinova, H. Bahrom, A.A. Goncharenko, O. Peltek, A. Muslimov, A. Manchev, I. Shishkin, R.E. Noskov, A.S. Timin, P. Ginzburg and M.V. Zyuzin Introduction Particle formation Thermal behaviour Surface properties In vitro studies Conclusions Conclusion
Synthesis of Calcium Carbonate Particles with Different Geometries L.I. Fatkhutdinova, H. Bahrom, A.A. Goncharenko, O. Peltek, A. Muslimov, A. Manchev, I. Shishkin, R.E. Noskov, A.S. Timin, P. Ginzburg and M.V. Zyuzin Introduction Particle formation Thermal behaviour Surface properties In vitro studies Conclusions Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC)
Synthesis of Calcium Carbonate Particles with Different Geometries L.I. Fatkhutdinova, H. Bahrom, A.A. Goncharenko, O. Peltek, A. Muslimov, A. Manchev, I. Shishkin, R.E. Noskov, A.S. Timin, P. Ginzburg and M.V. Zyuzin Introduction Particle formation Thermal behaviour Surface properties In vitro studies Conclusions Surface properties of differently shaped CaCO 3 particles Adsorption isotherm curves for TRITC adsorption of CaCO 3 particles. Adsorption capacity of spherical (red), Percentage of released TRITC from toroidal (blue) and ellipsoidal (green) CaCO 3 particles shaken in water with CaCO 3 particles incubated with TRITC at time (0-24 h) b – the Langmuir isotherm constant concentration C e = 0.5 mg/mL. Q max – theoretical monolayer saturation capacity of the TRITC C – equilibrium concentration of TRITC
Synthesis of Calcium Carbonate Particles with Different Geometries L.I. Fatkhutdinova, H. Bahrom, A.A. Goncharenko, O. Peltek, A. Muslimov, A. Manchev, I. Shishkin, R.E. Noskov, A.S. Timin, P. Ginzburg and M.V. Zyuzin Introduction Particle formation Thermal behaviour Surface properties In vitro studies Conclusions Surface properties of differently shaped CaCO 3 particles Spheroids Toroids Ellipsoids Specific surface 40.6 75.5 43.1 area, m 2 /g Pore volume, 0.127 0.084 0.172 cm 3 /g Pore diameter, 12.7 15.7 3.57 nm ζ -potential, -0.8 -2 -12 mV
Synthesis of Calcium Carbonate Particles with Different Geometries L.I. Fatkhutdinova, H. Bahrom, A.A. Goncharenko, O. Peltek, A. Muslimov, A. Manchev, I. Shishkin, R.E. Noskov, A.S. Timin, P. Ginzburg and M.V. Zyuzin Introduction Particle formation Thermal behaviour Surface properties In vitro studies Conclusions Uptake efficiency Cytotoxicity Toroids Cntr Cntr Z-stack CLSM image confirming the internalization of particles labeled with TRITC with corresponding 3D reconstruction image of cells with internalized particles. Spheres 28 Toroids C6 glioma cells viability after Ellipsoids 24 incubation with different 20 Frequency f(x) of cells which have shaped CaCO 3 particles. 16 internalized x particles per cell after 24 h of f(x) 12 incubation cell-to-particle ratio = 1:10 8 4 Cntr 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 x
Synthesis of Calcium Carbonate Particles with Different Geometries L.I. Fatkhutdinova, H. Bahrom, A.A. Goncharenko, O. Peltek, A. Muslimov, A. Manchev, I. Shishkin, R.E. Noskov, A.S. Timin, P. Ginzburg and M.V. Zyuzin Introduction Particle formation Thermal behaviour Surface properties In vitro studies Conclusions Surface properties of differently shaped CaCO 3 particles the crystallinity of the resultant CaCO 3 particles depends on reaction conditions variations in reaction conditions allowed the formation of different shaped CaCO 3 particles (spheroids, ellipsoids and toroids) The outstanding surface properties of these CaCO 3 particles together with adsorption efficiency: toroids are characterized by the highest adsorption their solubility enables capacity them to be used as drug delivery carriers uptake efficiency study on a sample of C6 glioma cells: cell uptake depended on the ellipsoids had the highest shape of the CaCO 3 particles internalizing rate cytotoxicity study: the different shaped CaCO 3 particles non-toxicity used did not show any cytotoxic effects biocompatibility
Recommend
More recommend