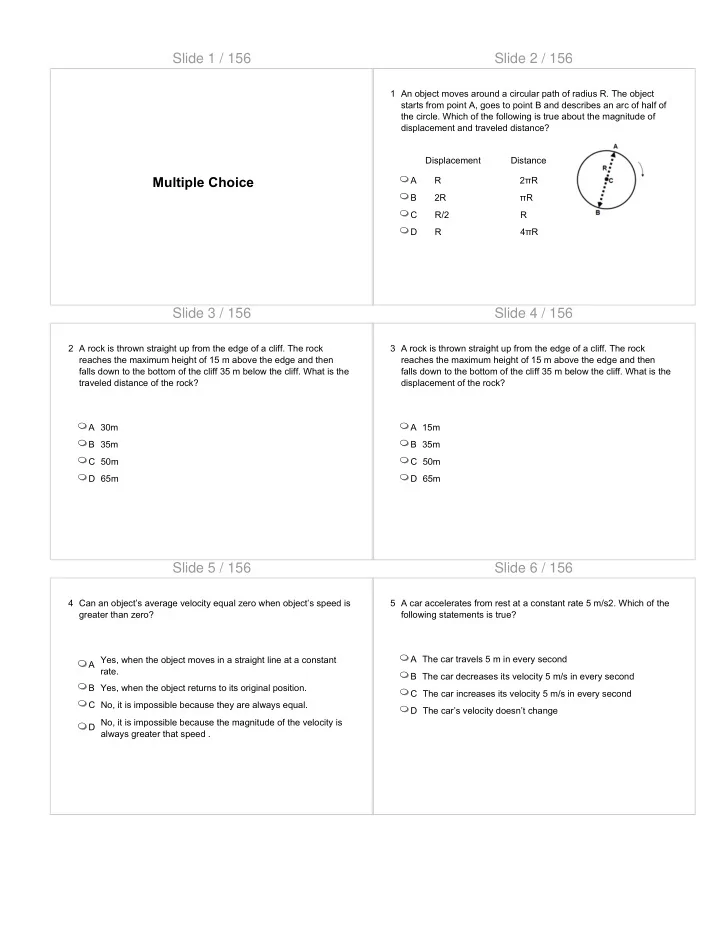

Slide 1 / 156 Slide 2 / 156 1 An object moves around a circular path of radius R. The object starts from point A, goes to point B and describes an arc of half of the circle. Which of the following is true about the magnitude of displacement and traveled distance? Displacement Distance Multiple Choice A R 2πR B 2R πR C R/2 R D R 4πR Slide 3 / 156 Slide 4 / 156 2 A rock is thrown straight up from the edge of a cliff. The rock 3 A rock is thrown straight up from the edge of a cliff. The rock reaches the maximum height of 15 m above the edge and then reaches the maximum height of 15 m above the edge and then falls down to the bottom of the cliff 35 m below the cliff. What is the falls down to the bottom of the cliff 35 m below the cliff. What is the traveled distance of the rock? displacement of the rock? A 30m A 15m B 35m B 35m C 50m C 50m D 65m D 65m Slide 5 / 156 Slide 6 / 156 4 Can an object’s average velocity equal zero when object’s speed is 5 A car accelerates from rest at a constant rate 5 m/s2. Which of the greater than zero? following statements is true? A The car travels 5 m in every second A Yes, when the object moves in a straight line at a constant rate. B The car decreases its velocity 5 m/s in every second B Yes, when the object returns to its original position. C The car increases its velocity 5 m/s in every second C No, it is impossible because they are always equal. D The car’s velocity doesn’t change D No, it is impossible because the magnitude of the velocity is always greater that speed .
Slide 7 / 156 Slide 8 / 156 6 An object is thrown straight up with an initial velocity v 0 . The graph 7 An object is thrown straight up with an initial velocity v 0 . The graph represents the object’s vertical displacement as a function of time. represents the object’s vertical displacement as a function of time. What is the total flying time of the object? At what time the object reaches its maximum height? A 2s A 2s B 4s B 4s C 6s C 6s D 8s D 8s Slide 9 / 156 Slide 10 / 156 8 An object is thrown straight up with an initial velocity v 0 . The graph 9 Which of the following graphs represents the velocity as a function represents the object’s vertical displacement as a function of time. of time of an object thrown straight up? What is the initial velocity of the object? A B A 20m/s B 60m/s C 80m/s D 50m/s C D Slide 11 / 156 Slide 12 / 156 10 Which of the following graphs represents the acceleration as a 11 The relationship between the position and time of a moving object function of time of an object thrown straight up? is shown on the graph. What is the instantaneous speed of the object at 4 s? A B A 1 m/s B 2 m/s C 3 m/s D 4 m/s C D
Slide 13 / 156 Slide 14 / 156 12 The relationship between the position and time of a moving object 13 The graph to the right describes the relationship between is shown on the graph. During which of the following times does velocity and time for a moving object. What is the acceleration the object accelerate? at time t = 1 s? A 0 to 2s A 4 m/s 2 B 2 to 4s B 2 m/s 2 C 0 to 4s C -2 m/s 2 D 4 to 8s D -4 m/s 2 Slide 15 / 156 Slide 16 / 156 14 The graph to the right describes the relationship between 15 The graph to the right describes the relationship between velocity and time for a moving object. What is the acceleration velocity and time for a moving object. What is the acceleration at time t = 8 s? at time t = 6 s? A 4 m/s 2 A 1 m/s 2 B -2 m/s 2 B 2 m/s 2 C -4 m/s 2 C -4 m/s 2 D 0 m/s 2 D 0 m/s 2 Slide 17 / 156 Slide 18 / 156 16 The graph to the right describes the relationship between 17 The graph to the right describes the relationship between velocity and time for a moving object. What is the total velocity and time for a moving object. What is the total traveled displacement for the entire trip? distance for the entire trip? A 18 m A 18 m B 12 m B 12 m C 6 m C 6 m D 30 m D 30 m
Slide 19 / 156 Slide 20 / 156 19 A rock is thrown straight up with twice the initial velocity of another. 18 The graph to the right describes the relationship between How much higher will the first rock be at its apex? velocity and time for a moving object. Between what times does the object approach the origin at the constant speed? A 2 times A 2 to 5s B 4 times B 6 to 7s C 16 times C 7 to 9s D They will reach the same apex. D 9 to 10s Slide 21 / 156 Slide 22 / 156 20 A student drops a pebble from the edge of a vertical cliff. The 21 A student drops a pebble from the edge of a vertical cliff. The pebble hits the ground 4 s after it was dropped. What is the speed pebble hits the ground 4 s after it was dropped. What is the height of the pebble just before it hits the ground? of the cliff? A 20 m/s A 20m B 40 m/s B 40m C 60 m/s C 60m D 80 m/s D 80m Slide 23 / 156 Slide 24 / 156 22 An Astronaut on the Moon simultaneously drops a bird feather and 23 A marble launcher shoots a marble horizontally from the height of a screw driver. The fact that two objects reach the surface at the 0.2 m above a horizontal floor. The marble lands on the floor 5 m same time can be explained by which of the following? away from the launcher. How long did the marble stay in are? A The Moon has no gravity A 0.1s B The Moon’s gravity is much weaker than the Earth’s gravity B 0.2s C 0.3s C The same gravitational force is applied on both objects on the Moon D 0.4s D At the given location all objects fall with the same acceleration in the absence of air resistance
Slide 25 / 156 Slide 26 / 156 25 A bicyclist moves a long a straight line with an initial velocity v 0 24 A marble launcher shoots a marble horizontally from the height of and slows down. Which of the following the best describes the 0.2 m above a horizontal floor. The marble lands on the floor 5 m signs set for the initial position, initial velocity and the away from the launcher. What is the initial speed of the marble? acceleration? A 5 m/s B 10 m/s Position Velocity Acceleration C 15 m/s A Positive Positive Negative D 25 m/s B Negative Positive Negative C Negative Negative Positive D Negative Negative Negative Slide 27 / 156 Slide 28 / 156 26 Which of the following is a vector quantity? 27 Which of the following is not a vector quantity? A Traveled distance A Velocity B Displacement B Displacement C Area C Momentum D Mass D Traveled distance Slide 29 / 156 Slide 30 / 156 28 A vector of displacement D is placed in X-Y coordinate system 29 A vector of displacement D is placed in X-Y coordinate system shown in the diagram to the right. What is the x-component of shown in the diagram to the right. What is the y-component of vector D? vector D? A 2m A 2m B 3m B 3m C 4m C 4m D 5m D 5m
Slide 31 / 156 Slide 32 / 156 31 An object changes its velocity from V 1 30 A vector of displacement D is placed in X-Y coordinate system to V 2 during a time interval Δt. Which shown in the diagram to the right. What is the magnitude of vector of the following is the correct direction D? for the object’s acceleration? A 2m B 3m A B C 4m D 5m C D Slide 33 / 156 Slide 34 / 156 32 A projectile is fired at 60 ̊ above the horizontal line with an initial 33 When a projectile reaches the highest point the vertical component velocity v 0 . At which of the following angles the projectile will land of the acceleration is: at the same distance as it is landed in the first trial? A 20 o A Greater than g B 30 o B Positive g C 40 o C Negative g D 45 o D Zero Slide 35 / 156 Slide 36 / 156 34 When a projectile reaches the highest point the horizontal 35 An object is thrown in horizontal with an initial velocity v0= 5 m/s component of the acceleration is: from the roof of a building 40 m tall. How much later does it hit the ground? A Greater than g A 4s B Positive g B √5s C Negative g C √8s D Zero D 10s
Slide 37 / 156 Slide 38 / 156 36 An object is thrown in horizontal with an initial velocity v0= 10 m/s 37 The diagram to the right represents a swimmer. The swimmer is from the roof of a building 20 m tall. How far from the building does capable to swim in a still water with a velocity V 1 = 1 m/s. He aims it hit the ground? his body directly across a 100 m wide river whose current has a velocity V 2 = 2 m/s. How much time it will take for the swimmer to cross the river? A 5m B 10m A 10s C 15m B 20s D 20m C 50s D 100s Slide 39 / 156 Slide 40 / 156 38 The diagram to the right represents a swimmer. The swimmer is 39 The diagram to the right represents a swimmer. The swimmer is capable to swim in a still water with a velocity V 1 = 1 m/s. He aims capable to swim in a still water with a velocity V 1 = 1 m/s. He aims his body directly across a 100 m wide river whose current has a his body directly across a 100 m wide river whose current has a velocity V 2 = 2 m/s. How far downstream will he land? velocity V 2 = 2 m/s. What is the velocity of the swimmer relative to the river bank? A 100m A 1m/s B 200m B 2m/s C 150m C √3m/s D 180m D √5m/s Slide 41 / 156 Slide 42 / 156 40 The graphs above represent the position, velocity, and acceleration as a function of time for a marble moving in one dimension. Which of the following could describe the motion of the marble? Multiple Answer A Rolling along the floor and then bouncing off a wall. B Rolling down one side of a bowl and then rolling up the other side. C Rolling up a ramp and then rolling back down. D Falling and then bouncing elastically off a hard floor.
Recommend
More recommend