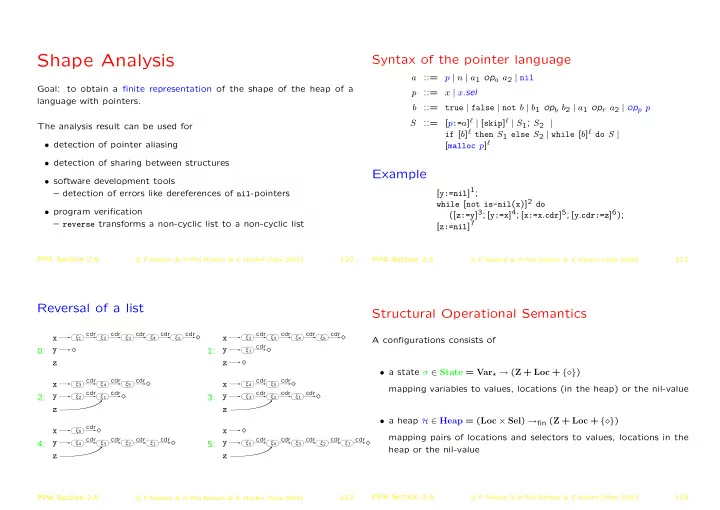

Shape Analysis Syntax of the pointer language p | n | a 1 op a a 2 | nil a ::= Goal: to obtain a finite representation of the shape of the heap of a ::= x | x. sel p language with pointers. b ::= true | false | not b | b 1 op b b 2 | a 1 op r a 2 | op p p [ p := a ] � | [ skip ] � | S 1 ; S 2 | ::= S The analysis result can be used for if [ b ] � then S 1 else S 2 | while [ b ] � do S | [ malloc p ] � • detection of pointer aliasing • detection of sharing between structures Example • software development tools [ y:=nil ] 1 ; – detection of errors like dereferences of nil -pointers while [ not is-nil ( x )] 2 do • program verification ([ z:=y ] 3 ; [ y:=x ] 4 ; [ x:=x . cdr ] 5 ; [ y . cdr:=z ] 6 ); – reverse transforms a non-cyclic list to a non-cyclic list [ z:=nil ] 7 PPA Section 2.6 110 PPA Section 2.6 111 � F.Nielson & H.Riis Nielson & C.Hankin (May 2005) c � F.Nielson & H.Riis Nielson & C.Hankin (May 2005) c Reversal of a list Structural Operational Semantics � � � cdr � � cdr � � cdr � � cdr � � � � � cdr � � cdr � � cdr � � cdr � cdr � � � � � � � � � � x x ξ 1 ξ 2 ξ 3 ξ 4 ξ 5 ξ 2 ξ 3 ξ 4 ξ 5 � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � A configurations consists of � � � � � cdr � y y � 0: 1: ξ 1 � � � � z z • a state σ ∈ State = Var � → ( Z + Loc + {�} ) � � � cdr � � cdr � � � � � cdr � � cdr � cdr � � � � � � x ξ 3 ξ 4 ξ 5 x ξ 4 ξ 5 � � � � � � � � � � mapping variables to values, locations (in the heap) or the nil-value � � � cdr � � � � � cdr � � cdr � � cdr � cdr � y � � y � � � 2: ξ 2 ξ 1 3: ξ 3 ξ 2 ξ 1 � � � � � � � � � � � � z z • a heap H ∈ Heap = ( Loc × Sel ) → fin ( Z + Loc + {�} ) � � � � � cdr � � x x ξ 5 � � mapping pairs of locations and selectors to values, locations in the � � � cdr � � cdr � � cdr � � � � � cdr � � cdr � � cdr � � cdr � � cdr � cdr � � � � � � � � � � y y 4: ξ 4 ξ 3 ξ 2 ξ 1 5: ξ 5 ξ 4 ξ 3 ξ 2 ξ 1 � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � heap or the nil-value � � z z PPA Section 2.6 113 PPA Section 2.6 c 112 � F.Nielson & H.Riis Nielson & C.Hankin (May 2005) c � F.Nielson & H.Riis Nielson & C.Hankin (May 2005)
Statements Pointer expressions Clauses for assignments: � [ x := a ] � , σ, H � → � σ [ x �→ A [ [ a ] ]( σ, H )] , H � ℘ : PExp → ( State × Heap ) → fin ( Z + {�} + Loc ) if A [ [ a ] ]( σ, H ) is defined is defined by ℘ [ [ x ] ]( σ, H ) = σ ( x ) � [ x. sel := a ] � , σ, H � → � σ, H [( σ ( x ) , sel ) �→ A [ [ a ] ]( σ, H )] � H ( σ ( x ) , sel ) if σ ( x ) ∈ Loc and A [ [ a ] ]( σ, H ) is defined if σ ( x ) ∈ Loc and H is defined on ( σ ( x ) , sel ) ℘ [ [ x. sel ] ]( σ, H ) = Clauses for malloc: undefined otherwise � [ malloc x ] � , σ, H � → � σ [ x �→ ξ ] , H � where ξ does not occur in σ or H Arithmetic and boolean expressions A : AExp → ( State × Heap ) → fin ( Z + Loc + {�} ) � [ malloc ( x. sel )] � , σ, H � → � σ, H [( σ ( x ) , sel ) �→ ξ ] � B : BExp → ( State × Heap ) → fin T where ξ does not occur in σ or H and σ ( x ) ∈ Loc PPA Section 2.6 114 PPA Section 2.6 115 � F.Nielson & H.Riis Nielson & C.Hankin (May 2005) c � F.Nielson & H.Riis Nielson & C.Hankin (May 2005) c Example Abstract Locations Shape graphs In the semantics: The abstract location n X represents The analysis will operate on shape graphs (S , H , is) consisting of the location σ ( x ) if x ∈ X � � � � � � cdr � cdr cdr � � � � x ξ 3 ξ 4 ξ 5 � � � � � � • an abstract state, S, � � � � cdr � cdr The abstract location n ∅ is called the � � � y ξ 2 ξ 1 � � � � � abstract summary location : n ∅ rep- • an abstract heap, H, and z resents all the locations that cannot • sharing information, is, for the abstract locations. be reached directly from the state without consulting the heap In the analysis: The nodes of the shape graphs are abstract locations: � � Invariant 1 If two abstract locations cdr � cdr � n { x } � � x n ∅ n X and n Y occur in the same shape ALoc = { n X | X ⊆ Var � } graph then either X = Y or X ∩ Y = ∅ cdr y � n { y } � n { z } � Note: there will only be finitely many abstract locations z PPA Section 2.6 116 � F.Nielson & H.Riis Nielson & C.Hankin (May 2005) c PPA Section 2.6 117 � F.Nielson & H.Riis Nielson & C.Hankin (May 2005) c
Reversal of a list Abstract states and heaps � � cdr � � � cdr cdr � n { x } � � x n ∅ � cdr � n { x } � � x n ∅ 0: 1: y � n { y } S ∈ AState = P ( Var � × ALoc ) abstract states H ∈ AHeap = P ( ALoc × Sel × ALoc ) abstract heap � � cdr � cdr cdr � n { x } � � � n { x } � x n ∅ x n ∅ � cdr cdr cdr y � n { y } � y � n { y } � n { z } n { z } 2: 3: � � Invariant 2 If x is mapped to n X by z z � � cdr the abstract state S then x ∈ X � cdr � n { x } � � x n ∅ � � � � cdr cdr � � � n { x } � � x n ∅ n ∅ cdr y � n { y } � n { z } Invariant 3 Whenever ( n V , sel , n W ) � cdr � cdr � cdr cdr y y and ( n V , sel , n W � ) are in the abstract � n { y } � n { z } � n { y } � n { z } 4: 5: z heap H then either V = ∅ or W = W � � � z z PPA Section 2.6 118 � F.Nielson & H.Riis Nielson & C.Hankin (May 2005) c PPA Section 2.6 119 � F.Nielson & H.Riis Nielson & C.Hankin (May 2005) c Examples: sharing in the heap Sharing in the heap � � � � � � cdr cdr � � cdr � � � x ξ 1 ξ 2 ξ 3 � � � � � � � cdr � n { x } � � x n ∅ � cdr � � ξ 4 � � � � � � � � � � � � � � cdr cdr cdr cdr � � � � � � y � n { y } x ξ 1 ξ 2 ξ 3 x ξ 1 ξ 2 ξ 3 � � cdr � � � � � � � � � � � � cdr � � cdr � � cdr � cdr � � y ξ 5 � � � � � � cdr � � � cdr � � ξ 4 ξ 4 ξ 5 � � � � � � � cdr � � � cdr � � � � � � � � � y y ξ 5 cdr cdr � � cdr � � � � � x ξ 1 ξ 2 ξ 3 � � � � � � � cdr � n { x } � � x n ∅ � cdr � � � � cdr � cdr � � ξ 4 ξ 5 � � � � y � n { y } � � cdr Give rise to the same shape graph: is: the abstract locations that might y be shared due to pointers in the � � cdr � heap: cdr � � � � � � � n { x } � � x n ∅ cdr cdr � � cdr � � ξ 2 ξ 3 ξ 4 � � � � � � � n X is included in is if it might repre- � n { x } � x n ∅ � cdr � � � � y � n { y } cdr � � cdr sents a location that is the target of � � cdr � � cdr x ξ 1 ξ 5 � � � � y � n { y } � � more than one pointer in the heap cdr y PPA Section 2.6 120 � F.Nielson & H.Riis Nielson & C.Hankin (May 2005) c PPA Section 2.6 121 � F.Nielson & H.Riis Nielson & C.Hankin (May 2005) c
Recommend
More recommend