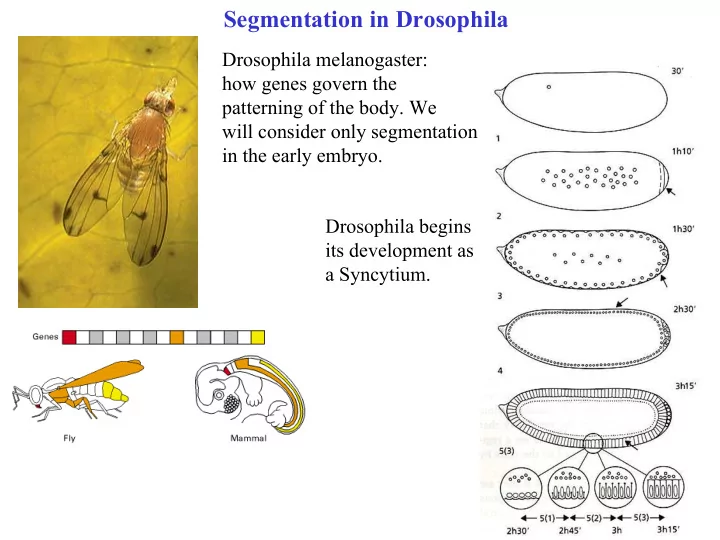

Segmentation in Drosophila Drosophila melanogaster: how genes govern the patterning of the body. We will consider only segmentation in the early embryo. Drosophila begins its development as a Syncytium.
Two independent orthogonal sets of egg-polarity genes specify 2 main axes. Anterior (4), posterior (11), terminal (6) genes govern expressions of other genes that refine the plan.
Anterior-posterior axis is controlled by substances localized at the ends of the egg (maternal bicoid mRNA). Most notably, egg-polarity gene Bicoid produces the gradient of Bicoid protein. This gradient guides segmentation that depends on about 25 segmentation genes. First, 6 gap genes mark out the coarsest subdivision. Then, 8 pair-rule genes , and finally, 10 segment-polarity genes , refine the pattern.
Bicoid activates Kruppel and hunchback and others; their proteins spread and activate pair-rule genes, etc. Sequential subdivision strategy . Pair-rule gene ftz is expressed in striped pattern Genes from the same group affect each other, next tier does not affect previous one. Fuzzy segmentation is adjusted by other genes in each group. Just 4 cells per band!
Activation of a gene, G , by a protein gradient signal, S . Transcription of G is promoted linearly by S and autocatalytically by G : 2 dg k g = + − k S 2 k g 1 4 + 2 dt k g 3 dg ∂ 2 dS S = − λ + S D dt ∂ 2 dt x g Precision: = − α α = λ x S S e , / D 0 ∆ 1 S 1 S = ∆ = 0 x ln , | x | α α S S th th α and S have to be large th
Besides errors in positional information, problem with scaling. Bicoid is noisy, Hunchback is precise. No other gene/protein affects Hunchback’s precision (including Kruppel). All genes downstream of Hunchback display the same spatial precision as Hunchback. Hunchback filters out noise and establishes scaling. Only maternal gene staufen that prodices some product localizing to egg’s poles affects the precision and scaling properties of Hunchback.
+ a s positive - - + + a feedback system − − s Short range activator, long range inhibitor: burning grass and sweating grasshoppers.
a h activator-inhibitor system + − a + − h
Recommend
More recommend