:: Research Report:: WORKF KFORCE AL ALLOCAT ATIO ION N BA - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Industrial Engineering Department Faculty of Industrial Technology Institut Teknologi Sepuluh Nopember Surabaya :: Research Report:: WORKF KFORCE AL ALLOCAT ATIO ION N BA BASE SED ON N TI TIME ST STUD UDY Y AN AND WORK K BA
Industrial Engineering Department Faculty of Industrial Technology Institut Teknologi Sepuluh Nopember Surabaya :: Research Report:: WORKF KFORCE AL ALLOCAT ATIO ION N BA BASE SED ON N TI TIME ST STUD UDY Y AN AND WORK K BA BALAN ANCIN ING (CAS ASE STU TUDY Y : P PT T MAD ADUS USAR ARI I MAS AS – RUN UNGK GKUT UT BR BRAN ANCH) H) GUIDED AND :: BY SUPERVISED BY Edwin Saferian Arief Rahman, S.T., MT 2510100006
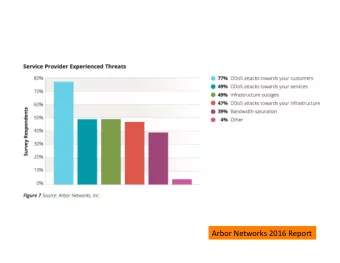
Research Background (1) Percentage of Industries Use Outsourced Worker Source : PPM Riset Manajemen
Research Background (2) Office Support (Cleaning and maintenance) PT MADUSARI MAS Driver and transportation Private Security
Research Background (3) Madusari Needs to Compete Productivity should be optimized Optimization of productivity can be conducted by distributing the workload in equal measure “Equalized” workload doesn’t mean that every worker have the same scoring attribute, considering the area in charge, hazard rate of area and other allowances Rumahindahdanbersih.blogspot.com
Problem Statement “How to calculate the workers’ workload and work force allocation in order to increase productivity using work study approach of stopwatch time study and work balancing. Optimization uses an integer programming to equalize the level of workload. ”
Research Objective Determine the number of work force based on capacity need
Research Benefits 2 1 Providing new assessment Optimal workload and mechanism for workload manpower in Madusari - auditing for future Rungkut Branch can be reference obtained
Research Scopes Research object is PT Madusari Mas – Rungkut Branch This research is focusing in main activities such as cleaning and facility maintenance Field study and data gathering are conducted between March 2013 to May 2013 Observation is conducted only in two of three shift, the morning shift and the evening shift.
Research Scopes (2) Job description will not be changed during this research Work elements that being identified are the main job (incidental work not included)
Writing Systematic Chapter 3 Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Research Preface Literature Review Methodology Chapter 4 Chapter 5 Chapter 6 Data Gathering and Data Analysis and Conclusion and Processing Interpretation Recommendation
Literature Review Operation Research Knapsack Theory Work Measurement Prod Leveling/Work Balancing Stopwatch Time Study WORKF KFORCE AL ALLOCAT ATIO ION N BA BASED ON N TI TIME STU TUDY Y AN AND LIN INE BA BALAN ANCIN ING
Literature Review : Stopwatch Time Study time study is a direct and continuous (Groover, 2007) observation of a task, using a timekeeping device The Industrial Engineering Terminology Standard a work measurement technique consisting of careful time measurement of the task with a time measuring instrument, adjusted for any observed variance from normal effort or pace and to allow adequate time for such items as foreign elements, unavoidable or machine delays, rest to overcome fatigue, and personal needs
Literature Review : Stopwatch Time Study Data Adequacy Test Data Uniformity Test This test is conducted to find out whether the Uniformity test is used to find out if the amount of collected data is adequate or not uniformity of sampled data 2 Z . S N ' 𝑉𝐷𝑀 = 𝑌 + 3ơ . X k 𝑀𝐷𝑀 = 𝑌 − 3ơ N’ = Number of Observation should be conducted Z = Trust Index (95% ≈ index 2) s = Standard deviation of data UCL / LCL = Upper/Lower Classified Level = Mean of uniformed data X k = level of error (5%) X = Mean of collected data Ơ = Standard deviation obtained
Variable Allowance Male Female Literature Review : Stopwatch Time Study a. Standing 2 4 b. Work Postion Rather Kneel 0 1 Kneeling 2 3 Lay down 7 7 c. Energy 0 1 2,5 kg Determine the Performance Rating 1 2 5 kg 2 3 7,5 kg and Allowances 3 4 10 kg 4 6 12,5 kg 6 9 15 kg 8 12 17,5 kg Unilever Allowances Fixed Allowance 10 15 20 kg 12 18 Male Female 22,5 kg No Standard 14 - 25 kg Calculating Normal Time 1 Personal Need 5 6 19 - 30 kg 2 Fatigue 4 4 33 - 40 kg Total 58 - 50 kg Variable Allowance Male Female d. Lightning Normal time = a. Standing 2 4 0 0 Standard b. Work Postion 2 2 Below Average Actual time x Performance Rather Kneel 0 1 Above Average Kneeling 2 3 5 5 Rating Lay down 7 7 c. Energy e. Temperature 0 1 2,5 kg 0 0 Fresh 1 2 5 5 5 kg Normal 7,5 kg 2 3 5 15 Hot 3 4 10 kg f. Environment 4 6 12,5 kg 0 0 Normal 6 9 15 kg 2 2 Dusty 8 12 17,5 kg 5 5 10 15 Hazardous 20 kg 12 18 22,5 kg g. Noise 25 kg 14 - 0 0 Repetitive 19 - 30 kg 2 2 Randomly 33 - 40 kg 5 5 High Ptched 58 - 50 kg d. Lightning 0 0 Standard
Literature Review : Stopwatch Time Study Calculating Standard Time Calculating Workload 𝑂𝑝𝑠𝑛𝑏𝑚 𝑢𝑗𝑛𝑓𝑦 100% St = 100%−𝑏𝑚𝑚𝑝𝑥𝑏𝑜𝑑𝑓 𝑇𝑢𝑏𝑜𝑒𝑏𝑠𝑒 𝑢𝑗𝑛𝑓 𝑦 𝐺𝑠𝑓𝑟 𝑦 𝑂𝑝𝑉 WL = 𝑈𝑝𝑢𝑏𝑚 𝑋𝑝𝑠𝑙 𝑈𝑗𝑛𝑓
Literature Review : Work Balancing Work Balancing, also known as production (Baybar, 1986) leveling or assembly line balancing, is a technique for reducing the work deviation. The assembly line balancing problem is a well-studied problem with many applications, including the automotive industry, consumer electronics, and household items Improvised by Genichi Taguchi, Imperial Navy Engineer and Toyota Corporation Consultan
Literature Review : Work Balancing 30 30 Takt (25 hrs) 25 20 15 17 15 10 5 1 2 3 Improvised by Genichi Taguchi, Imperial Navy Engineer and Toyota Takt (25 hrs) 30 25 25 25 Corporation Consultan 20 12 15 10 5 1 2 3
Literature Review : Linear Programming Operations research, or management sciences, is a discipline that deals with the application of advanced analytical methods to help make better decisions. It is often considered to be a sub-field of mathematics (Wetherbee, 1979)
Literature Review : Linear Programming The knapsack theory problem or rucksack Knapsack Theory problem is a problem in combinatorial optimization: Given a set of items, each item with a mass itself, determine the number of each item to include in a collection so that the total weight is less than or equal to a given limit Also known as burglar theory
Literature Review : Linear Programming Knapsack Theory = Item(s) Weight Knapsack Capacity Maximum-Filled Knapsack = Optimal Workload Given Max Work hour Work(s) time completion
Research Methodology
Research Methodology 1
Research Methodology 1 2
Research Methodology 2 Takt level = 100% 3
Research Methodology
Data Collecting and Processing
Data Collecting Time Windows Work Shifts First half Second half Evening Shift Morning Shift Night Shift Number of Number of Area Number of Workforce Area Workforce Area Workforce 1 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 4 1 4 1 5 1 5 1 3 1 6 1 6 1 4 1 7 1 7 1 5 1 9 1 9 1 6 1 10 1 10 1 Total 7 7 1 Total 7 8 1 9 1 10 1 Total 10
Data Collecting Work Area 4 Work Area 2 Work Area 3 Sub Area : Office Sub Area : Waste and Wash Sub Area : Hall A Sub Area : Engine Work Area 1 Sweeping Teraso Conveyor Sub Area : Relig Building Sub Area ; Office Sweeping Epoxy Seeping Bordest Mopping Teraso Chalk cleaning Ablution Water Main Office PC Mopping Epoxy Sweeping Epoxy Sub Area : Office Sub Area :Drum Office Cleaning Waste Disposal Stainless Fence TPM PC Dusting Wall Mooping Bordest Second Sterilization Office Cleaning Washbay Teraso Polish Window List Meeting Room Piping Tank Mopping Epoxy Colouring Room Drum Streilization Tube Scrapping Shuttle Door Waste Disposal Packaging Dusting Piping System Cabinet Liquid Puder Drum Packing Layer Scraoping Windows Cleaning Wooden Wall List Office Toilet Waste Disposal Office Desk SLS Nedel Second Sterilization Walling Bordet Floor PC Lobby Sub Area : Hall B Drum Box Wash Piping Dispensing Stair Trap Sweeping Epoxy Piping Tank Clean Drum Packing Washbay Polishing Musholla Vaccuum Mopping Epoxy Dusting Piping System Garbaging Conveyor Dusting Wall Waste Disposal Sub Area : Waste Hall Cleaning Waste Chem Treatment Work Area 5 Hall Cleaning Hall A Cleaning Module 1 Module 6 Hall Cleaning Take Waste Work Area 6 Retrieve waste Sweeping Epoxy Sweeping Epoxy Sub Area : Packing Line Sub Area : Cabinet Roo Mopping Epoxy Mopping Epoxy Dispensing Display Rack Sweeping Teraso Sweeping Teraso Control Panel Cabinet filling Mopping Teraso Mopping Teraso P3 Domino Waste Speaker Cleaning Machining Machining Stair Bordes Sweeping Epoxy Module 5 Mazanine Piping Mopping Epoxy Sweeping Epoxy Sweeping Epoxy Machining Sweeping Teraso Mopping Epoxy Mopping Epoxy Wall Dusting Mopping Teraso Sweeping Teraso Sweeping Teraso Ceramic Wall Mopping Teraso Mopping Teraso Bin Cleaning Machining Machining Wall List Cleaning
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.