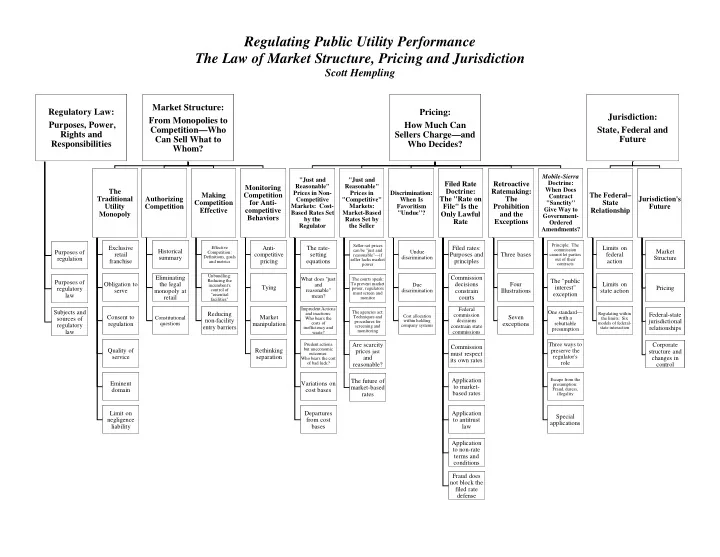

Regulating Public Utility Performance The Law of Market Structure, Pricing and Jurisdiction Scott Hempling Market Structure: Regulatory Law: Pricing: Jurisdiction: From Monopolies to Purposes, Power, How Much Can Competition — Who State, Federal and Rights and Sellers Charge — and Can Sell What to Future Responsibilities Who Decides? Whom? Mobile-Sierra "Just and "Just and Doctrine: Filed Rate Retroactive Reasonable" Reasonable" Monitoring When Does The Doctrine: Ratemaking: Prices in Non- Prices in Discrimination: Making Competition The Federal – Contract Traditional Authorizing The "Rate on The Jurisdiction's Competitive "Competitive" When Is Competition for Anti- "Sanctity" State Utility Competition Markets: Cost- Markets: Favoritism File" Is the Prohibition Future Give Way to Effective competitive Relationship Based Rates Set Market-Based "Undue"? Monopoly Only Lawful and the Government- Behaviors by the Rates Set by Rate Exceptions Ordered Regulator the Seller Amendments? Principle: The Seller-set prices Exclusive Effective Anti- The rate- Filed rates: Limits on commission Historical can be "just and Market Purposes of Undue Competition: retail competitive setting Purposes and Three bases federal reasonable" — if cannot let parties Definitions, goals discrimination summary Structure regulation seller lacks market out of their franchise pricing equations principles action and metrics power contracts Unbundling: Eliminating Commission What does "just The courts speak: Reducing the The "public Purposes of Obligation to the legal To prevent market decisions Four Limits on incumbent's and Due Tying interest" Pricing regulatory power, regulators serve monopoly at control of reasonable" discrimination constrain Illustrations state action must screen and exception law "essential mean? retail courts monitor facilities" Imprudent Actions Federal Subjects and The agencies act: One standard — Reducing and inactions: Regulating within Federal-state commission Cost allocation Consent to Market Techniques and Seven Constitutional with a sources of Who bears the the limits: Six non-facility within holding decisions jurisdictional procedures for regulation questions manipulation costs of exceptions rebuttable models of federal- regulatory company systems screening and constrain state entry barriers inefficiency and state interaction relationships presumption law monitoring commissions waste? Prudent actions Are scarcity Three ways to Corporate Commission but uneconomic Quality of Rethinking prices just preserve the structure and must respect outcomes: regulator's service separation and changes in Who bears the cost its own rates role of bad luck? reasonable? control Application Escape from the The future of Eminent Variations on presumption: to market- market-based domain cost bases Fraud, duress, based rates rates illegality Limit on Departures Application Special negligence from cost to antitrust applications liability bases law Application to non-rate terms and conditions Fraud does not block the filed rate defense
Regulatory Law: Purposes, Power, Rights and Responsibilities Subjects and sources of Purposes of regulation Purposes of regulatory law regulatory law Economists: Powers Subjects Exploit economies of scale, address market imperfections Residential customers: Responsibilities Sources Protect us from abuse Industrial customers: Rights Set rates so we can compete globally Shareholders: Procedures Give us a chance for a fair return Lenders: Ensure cash flow sufficient to pay off debt Competitors: Lower entry barriers, give us a shot Environmentalists: Limit environmental damage 1
The Traditional Utility Monopoly Exclusive Limit on Obligation to Consent to Quality of Eminent retail negligence serve regulation service domain franchise liability Regulatory Components of Seven The anti- Power, General Franchise options for quality: Regulatory Exclusivity variations on discrimination Statutory bases purposes and limitation and express in statute revocation franchise Traditional and requirements exclusivity objective limits its justifications accountability new New service Legal sources: Revocation The citizen Public – private Parties and offered by non- Rules, statutes authority access objective overlap defenses incumbent and orders Types of The economic regulatory Customer self- Revocation Exceptions to development requirements: Federal roles service justifications the general rule objective Inputs and outcomes Remedies: Limits on the No immunity: Group self- Financial obligation to Gross service penalties and serve negligence directed actions Adjacent The Contracts that monopolies as “management Federal – state rivals: Locational undermine the prerogative” relations and fringe obligation constraint competition Exclusive franchise for a specific service Competition for the exclusive franchise No statutory exclusivity 2
Authorizing Competition Eliminating the Historical Constitutional legal monopoly at summary questions retail Definitions: Shareholder Shareholder Power of Limited Concluding Exclusive Obligation to Consent to Quality of “Sunk costs” expectations expectation of Electricity eminent liability for constitutional franchise serve regulation service and “future of future sunk cost domain negligence thoughts profits” profits recovery Contract Takings Policy Gas Type of seller precluding Case law Clause outcomes competition No contract Electricity Telecommuni Type of precluding sales at cations technology competition wholesale Three Electric sales variables at retail Natural gas pipelines Telecom Contract Clause 3
Making Competition Effective Effective Competition: Unbundling: Reducing Reducing non-facility Definitions, goals and the incumbent's control entry barrier metrics of "essential facilities" Statutory Unbundled Unbundling's New Definitions Separation to Entry Product Entrenched foundation: Entry barriers Unbundling The antitrust rates for effects on bottlenecks Long-term of reduce barriers promotion customer in regulated The prohibition defined foundation competitive vertical and new contracts against "undue utility markets competition temptation defined advantages preferences neutrality economies tensions preference" Electricity's Monopolists Gas and ancillary Goals of Cost Functional Changing may not electricity at services and Broadband competition unbundling unbundling suppliers efficiency monopolize wholesale losses Essential Effective Total element Gas and Gas facilities Corporate Monthly competition: long-run electricity at marketing Smart grid Meanings and doctrine: incremental unbundling billing retail data measurements cost Origins Telecommunic Knowledge Essential ations: From Telecommun Codes of of the facility alien ications conduct customer attachments to examples base broadband Limits on Incumbent’s Transfer of incumbent’s refusal to control to Incumbent's share: obligation to independent name Business share entity justifications facilities Antitrust's role in utility Divestiture regulation 4
- Monitoring Competition for Anti-competitive Behaviors Anti-competitive pricing Tying Market manipulation Rethinking separation Sufficient Price squeeze Definition and examples competition scenario Insufficient "Technology tying" in utility Predatory pricing industries competition scenario 5
Recommend
More recommend