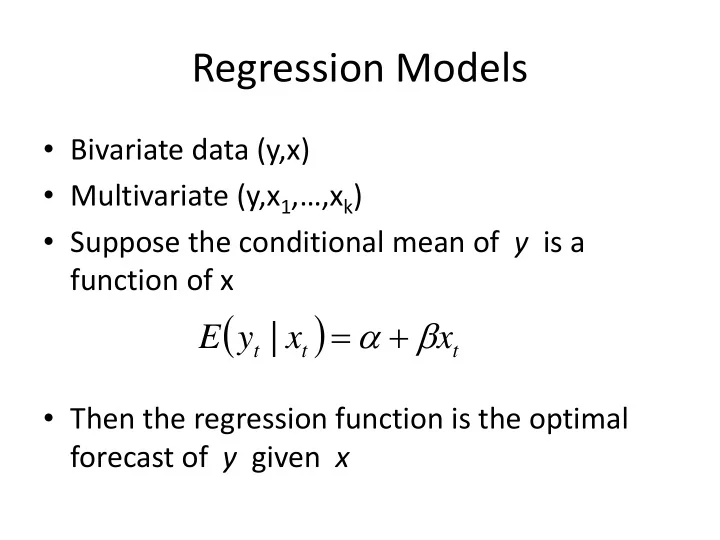

Regression Models • Bivariate data (y,x) • Multivariate (y,x 1 ,…,x k ) • Suppose the conditional mean of y is a function of x ( ) = α + β | E y x x t t t • Then the regression function is the optimal forecast of y given x
Regression • Model = α + β + y x e t t t • Estimation: Least-Squares • Example: Interest Rates – Monthly – Rates on 3-month and 1-year U.S. Treasury Bonds – 3-month bond series dates from 1934m1 – 1-year bond series dates from 1953m4
Interest Rates on Treasury Bonds 20 15 10 5 0 1940m1 1960m1 1980m1 2000m1 2020m1 time 3-Month Treasury One-Year Treasury
Least-Squares, 3-month on 1-year rate = − + ˆ 0 . 18 0 . 93 y x t t . reg t3month t1year, r Linear regression Number of obs = 743 F( 1, 741) =21167.67 Prob > F = 0.0000 R-squared = 0.9869 Root MSE = .35034 Robust t3month Coef. Std. Err. t P>|t| [95% Conf. Interval] t1year .9344078 .0064224 145.49 0.000 .9217994 .9470161 _cons -.1826507 .0261585 -6.98 0.000 -.2340043 -.1312971
Forecast = α + β + y x e + + + n h n h n h = α + β ˆ y x + + | n h n n h • A forecast of y n+h requires x n+h • This is not typically feasible, as x n+h is unknown at time n.
Regressor forecast • Suppose we have a forecast for x • Then = α + β ˆ ˆ y x + + | n h n n h • For example, if ( ) Ω = γ + φ | E x x − − t t h t h then = γ + φ ˆ x x + | n h n n
1-year Treasury on Lagged Value • Regress x t on x t-12 (12-month ahead forecast) . reg t1ye ar L12.t1year, r Linear regression Number of obs = 731 F( 1, 729) = 1246.67 Prob > F = 0.0000 R-squared = 0.7549 Root MSE = 1.6102 Robust t1year Coef. Std. Err. t P>|t| [95% Conf. Interval] t1year L12. .8787321 .0248874 35.31 0.000 .8298725 .9275917 _cons .5951917 .1089506 5.46 0.000 .3812972 .8090862 = + ˆ 0 . 60 0 . 88 x x − 12 t t
Interest Rate Forecast, h=12 • Estimates = − + ˆ 0 . 18 0 . 93 y x t t = + ˆ 0 . 60 0 . 88 x x − 12 t t • Current: x 2015M2 = 0.22% = + × = ˆ 0 . 60 0 . 88 0 . 22 0 . 79 x 2016 2 M = − + × = ˆ 0 . 18 0 . 93 0 . 79 0 . 55 y 2016 2 M
Example • Current 3-month interest rate = 0.02% • Current 1-year interest rate = 0.22% • 12-step-ahead point forecast for 3-month rate – Regression model: 0.55% – AR(1) Model: 0.40%
Direct Method (preferred) • Combine ( ) = α + ϕ | E y x x t t t ( ) Ω = γ + φ | E x x − − t t h t h • We obtain ( ) ( ) Ω = α + ϕ Ω | | E y E x − − t t h t t h ( ) = α + ϕ γ + φ x − t h = µ + β x − t h
Forecast Regression • h-step-ahead = µ + β + y x e − t t h t • Forecast = µ + β y x + | n h n n
3-month rate on Lagged 1-year rate . reg t3mo nth L12.t1year, r Linear regression Number of obs = 731 F( 1, 729) = 954.87 Prob > F = 0.0000 R-squared = 0.7333 Root MSE = 1.5807 Robust t3month Coef. Std. Err. t P>|t| [95% Conf. Interval] t1year L12. .8149486 .0263729 30.90 0.000 .7631727 .8667245 _cons .4042153 .1126674 3.59 0.000 .1830241 .6254065 = + 0 . 40 . 81 y x + | n h n n = + × = ˆ 0 . 40 . 81 0 . 22 0 . 58 y + n | n h
AR(q) Regressors • Suppose x is an AR(q) = α + β + y x e t t t = γ + φ + φ + + φ + x x x x u − − − 1 1 2 2 t t t q t q t • Then a one-step forecasting equation for y is = µ + β + β + + β + y x x x e − − − 1 1 2 2 t t t q t q t • And an h-step is = µ + β + β + + β + y x x x e − − − − + − 1 2 1 1 t t h t h q t h q t
T-Bill example: AR(12) for 1-year rate . reg t1ye ar L(12/23).t1year, r Linear regression Number of obs = 720 F( 12, 707) = 126.00 Prob > F = 0.0000 R-squared = 0.7592 Root MSE = 1.6013 Robust t1year Coef. Std. Err. t P>|t| [95% Conf. Interval] t1year L12. 1.372957 .2814601 4.88 0.000 .8203594 1.925555 L13. -.7196452 .412039 -1.75 0.081 -1.528612 .0893213 L14. .4363379 .5136813 0.85 0.396 -.5721853 1.444861 L15. -.2163055 .544078 -0.40 0.691 -1.284508 .8518965 L16. .2475704 .5375377 0.46 0.645 -.8077909 1.302932 L17. -.3194005 .5082699 -0.63 0.530 -1.3173 .6784986 L18. .3353347 .4830466 0.69 0.488 -.6130427 1.283712 L19. .0675064 .4976707 0.14 0.892 -.9095829 1.044596 L20. -.3464568 .4897085 -0.71 0.480 -1.307914 .6150001 L21. -.0125448 .453595 -0.03 0.978 -.9030993 .8780097 L22. -.0619694 .3943243 -0.16 0.875 -.8361562 .7122174 L23. .0775817 .209321 0.37 0.711 -.3333835 .488547 _cons .7096671 .1129813 6.28 0.000 .487848 .9314862
Regress 3-month on 12 lags of 12-month . reg t3month L(12/23).t1year, r Linear regression Number of obs = 720 F( 12, 707) = 105.20 Prob > F = 0.0000 R-squared = 0.7424 Root MSE = 1.5601 Robust t3month Coef. Std. Err. t P>|t| [95% Conf. Interval] t1year L12. 1.289686 .2898408 4.45 0.000 .7206346 1.858738 L13. -.7214219 .4242551 -1.70 0.089 -1.554372 .1115287 L14. .51203 .5445023 0.94 0.347 -.557005 1.581065 L15. -.1763848 .5959517 -0.30 0.767 -1.346432 .9936621 L16. .195117 .5862598 0.33 0.739 -.9559016 1.346136 L17. -.2585702 .5302889 -0.49 0.626 -1.2997 .7825594 L18. .3028809 .4831825 0.63 0.531 -.6457634 1.251525 L19. .0530733 .4897965 0.11 0.914 -.9085565 1.014703 L20. -.3137536 .4680439 -0.67 0.503 -1.232676 .6051687 L21. -.0624271 .4223551 -0.15 0.883 -.8916474 .7667933 L22. -.078967 .3699612 -0.21 0.831 -.8053211 .6473871 L23. .0496556 .2051073 0.24 0.809 -.3530366 .4523478 _cons .5500138 .1118904 4.92 0.000 .3303365 .7696911
Forecast • Predicted value for 2016M2=0.76 • Predicted value using 3 lags=0.61
Distributed Lags • This class of models is called distributed lags = µ + β + β + + β + y x x x e − − − 1 1 2 2 t t t q t q t = µ + + ( ) B L x e − 1 t t • If we interpret the coefficients as the effect of x on y , we sometimes say – β 1 is the immediate impact – β 1 + …+ β n = B(1) is the long-run impact
Regressors and Dynamics • We have seen AR forecasting models • And now distributed lag model • Add both together! = µ + + ( ) ( ) A L y B L x e − 1 t t t • or = µ + α + + α y y y − − 1 1 t t p t p + β + + β + x x e − − 1 1 t q t q t
h-step • Regress on lags of y and x, h periods back • Estimate by least squares • Forecast using estimated coefficients and final values = µ + α + + α y y y − − + − 1 1 t t h p t h p + β + + β + x x e − − + − 1 1 t h q t h q t
Recommend
More recommend