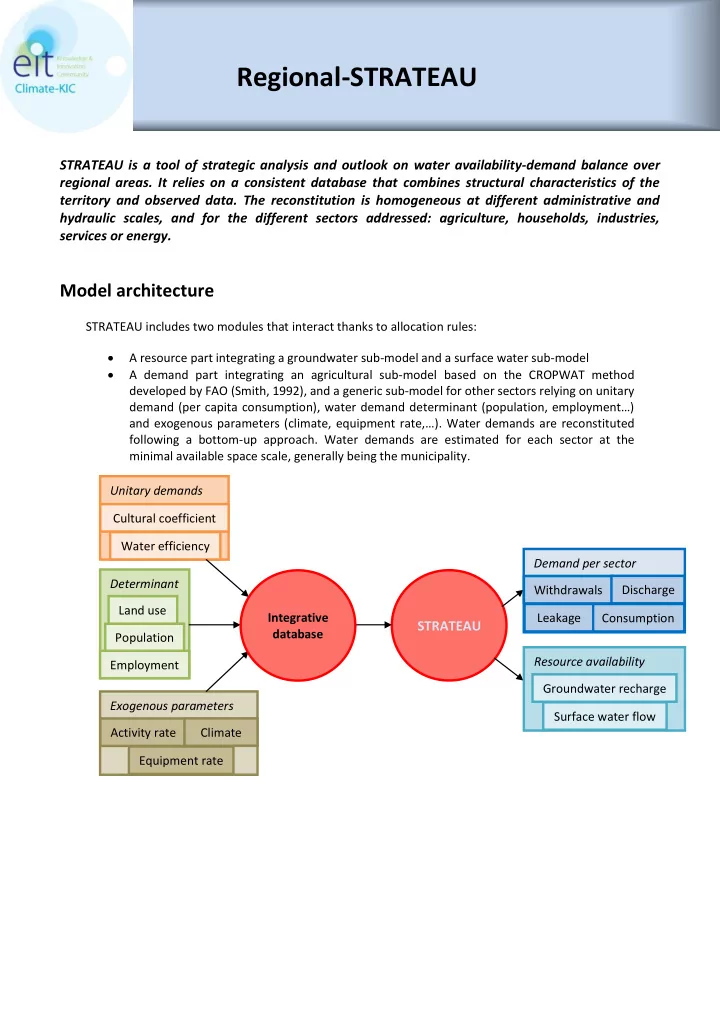

Regional-STRATEAU STRATEAU is a tool of strategic analysis and outlook on water availability-demand balance over regional areas. It relies on a consistent database that combines structural characteristics of the territory and observed data. The reconstitution is homogeneous at different administrative and hydraulic scales, and for the different sectors addressed: agriculture, households, industries, services or energy. Model architecture STRATEAU includes two modules that interact thanks to allocation rules: A resource part integrating a groundwater sub-model and a surface water sub-model A demand part integrating an agricultural sub-model based on the CROPWAT method developed by FAO (Smith, 1992), and a generic sub-model for other sectors relying on unitary demand (per capita consumption), water demand determinant (population, employment…) and exogenous parameters (climate, equipment rate,…) . Water demands are reconstituted following a bottom-up approach. Water demands are estimated for each sector at the minimal available space scale, generally being the municipality. Unitary demands Cultural coefficient Water efficiency Demand per sector Determinant Discharge Withdrawals Land use Integrative Leakage Consumption STRATEAU database Population Resource availability Employment Groundwater recharge Exogenous parameters Surface water flow Activity rate Climate Equipment rate
The outputs are available at four scales at a monthly time step: Two hydrologic scales: river basin or sub-river basin Two administrative scales: regional (country, region) or local scale (municipality) Homogeneous estimations are carried out at the municipal scale by prorating data available at the hydrologic scale (and conversely). Calculations are later undertaken at the smallest available scale (sub-basin and municipality) and results are aggregated to provide a representation at the regional or at the river-basin scale, following a bottom-up approach. Module description: Main processes being represented In the demand module, water requirement are calculated based on unitary demands, determinants and exogenous factors. These requirements are then fulfilled from the available resources (direct withdrawals from surface or underground resources, drinking water network). Leakages as well as consumptive uses are integrated and allow calculating water discharges in the different water bodies. In the resource module, aquifer recharge and river flows are impacted by withdrawals, leakages and discharges. Rainfalls are translated into runoffs to surface water and infiltration in aquifers based on
Footprint SUGAR index, which estimates the probability of rainfall to infiltrate or to run-off with surface water 1 . Description of the inputs Source of data Temporal / Default source of data in Input Type Variable identification and metric for future spatial scale past scenarios Area or Regionalized Climate Climatic grid SAFRAN (Fr), SIA (Es) Raster scenarios Percentage of each surface management type : - Irrigated / non irrigated acreage - Orchard - Wheat Corinne Land Cover (UE) - Rice Municipality Regionalized Land use - Garden Market Recensement Général or county scenarios - Grass irrigated / non irrigated Agricole (Fr), Censo Agrario - Vineyards (Es) - Olives … - Forest - Golf curses - Urban area IDPR (France), Regionalized Soil Infiltration rate (%) Area FootPrint SUGAR index (UE) scenarios Municipal population National Census, INSEE (Fr), Population Municipality Trends Dwelling type INE (Es) Employment Employees per sub-sector Municipality SIRENE (Fr), INE (Es) Trends Description of the outputs Various outputs can be provided through tables, charts or interactive maps: Territorialized water demands per sector (withdrawals, discharges, consumption) River flows and aquifer recharge Time scale: year or month. Space scale: hydrologic (sub-river basin or river basin) and administrative scale (municipality to region). 1 http://www.eu-footprint.org/sugar.html
Condition of access to the model codes Condition of access to the model codes - o Licensing condition or subcontracting: please contact French Water Embassy or SAFEGE (innovation@safege.fr) o Cost: according to the country and the river basin size. Bibliographie Smith, M. (1992). CROPWAT: A computer program for irrigation planning and management .46. Food & Agriculture Org.,
Recommend
More recommend