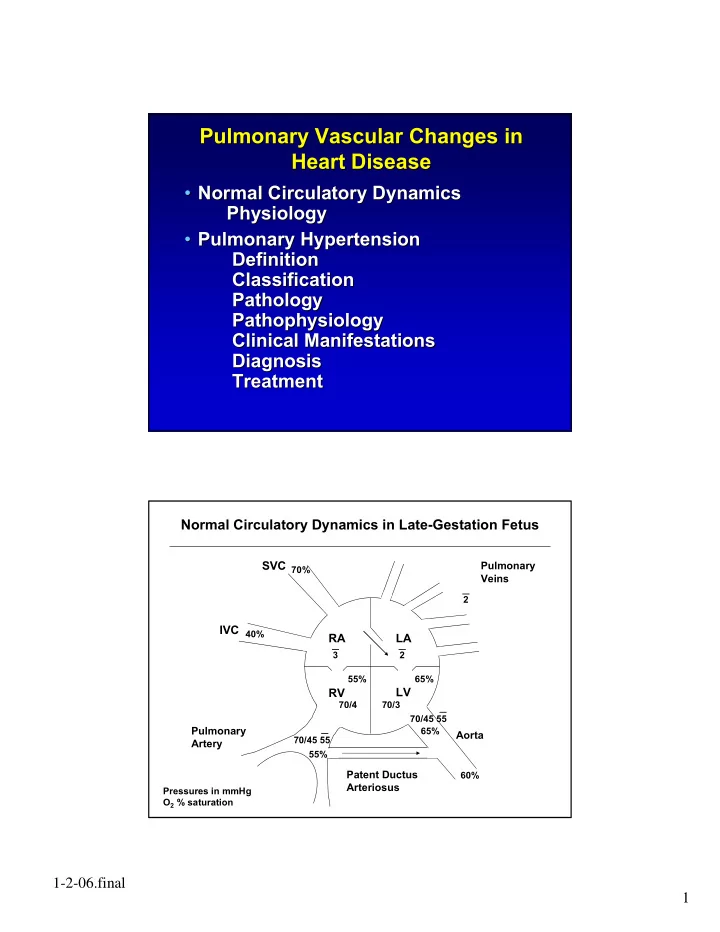

Pulmonary Vascular Changes in Pulmonary Vascular Changes in Heart Disease Heart Disease • Normal Circulatory Dynamics Normal Circulatory Dynamics • Physiology Physiology • Pulmonary Hypertension • Pulmonary Hypertension Definition Definition Classification Classification Pathology Pathology Pathophysiology Pathophysiology Clinical Manifestations Clinical Manifestations Diagnosis Diagnosis Treatment Treatment Normal Circulatory Dynamics in Late-Gestation Fetus SVC Pulmonary 70% Veins 2 IVC 40% RA LA 3 2 55% 65% LV RV 70/4 70/3 70/45 55 Pulmonary 65% Aorta 70/45 55 Artery 55% Patent Ductus 60% Arteriosus Pressures in mmHg O 2 % saturation 1-2-06.final 1
Normal Post- -Natal Changes in the Natal Changes in the Normal Post Pulmonary Circulation Pulmonary Circulation 12 12 Medial muscle Medial muscle 8 8 % vessel % vessel 4 4 diameter diameter 0 0 15 15 Pulmonary Pulmonary vascular vascular 10 10 resistance – – resistance 5 5 units • units • m m 2 2 0 0 12 12 9 9 Pulmonary flow Pulmonary flow l / min / m 2 l / min / m 2 6 6 3 3 90 90 Pulmonary arterial mean Pulmonary arterial mean 60 60 pressure - - mmHg mmHg pressure 30 30 0 0 0.5 0.5 1 1 2 2 3 4 5 6 7 3 4 5 6 7 Age (years) Age (years) Normal Circulatory Dynamics After Postnatal Adaptation ( I ) SVC Pulmonary Veins 8 95% 75% 95% IVC RA LA 3 8 75% 95% LV RV 30/3 100/8 100/60 83 Pulmonary Aorta 30/10 20 Artery 75% 95% Pressures in mmHg O 2 % saturation 1-2-06.final 2
Pulmonary Circulation Pulmonary Circulation • Low resistance, high compliance vascular Low resistance, high compliance vascular • bed bed • Only organ to receive entire cardiac output Only organ to receive entire cardiac output • (CO) (CO) • • Changes in CO as well as pleural/alveolar Changes in CO as well as pleural/alveolar pressure affect pulmonary blood flow pressure affect pulmonary blood flow • • Different reactions compared to the Different reactions compared to the systemic circulation systemic circulation • Normally in a state of mild vasodilation Normally in a state of mild vasodilation • Exercise Exercise • Pulmonary blood flow increases up to 4 Pulmonary blood flow increases up to 4- - • 5x BL 5x BL • Increased flow accommodated by both Increased flow accommodated by both • recruitment and vasodilation recruitment and vasodilation • Net effect is a decrease in pulmonary Net effect is a decrease in pulmonary • vascular resistance (PVR) vascular resistance (PVR) • No further decrease in PVR once all • No further decrease in PVR once all vessels fully recruited and dilated vessels fully recruited and dilated 1-2-06.final 3
Physiology: Circulatory Hemodynamics Physiology: Circulatory Hemodynamics Pressure* = Flow x Resistance Pressure* = Flow x Resistance • Systemic Circulation Systemic Circulation • − Pressure = Pressure = Pressure Pressure drop across systemic circulation (mmHg) = drop across systemic circulation (mmHg) = − Systemic Arterial Pressure (SAPm SAPm) ) - - Systemic Venous Pressure Systemic Venous Pressure Systemic Arterial Pressure ( ( (RAPm RAPm) ) † = Cardiac Index (CI; l/m/M − Flow = Systemic Blood Flow − Flow = Systemic Blood Flow † = Cardiac Index (CI; l/m/M 2 2 ) ) − − Resistance = Systemic Vascular Resistance (SVR; units Resistance = Systemic Vascular Resistance (SVR; units • • M M 2 2 ) ) • Pulmonary Circulation Pulmonary Circulation • − Pressure = Pressure = Pressure Pressure drop across pulmonary circulation (mmHg) = drop across pulmonary circulation (mmHg) = − Pulmonary Artery Pressure (PAPm) - - Pulmonary Venous Pressure Pulmonary Venous Pressure Pulmonary Artery Pressure (PAPm) (PCWPm) (PCWPm) † = Cardiac Index (CI; l/m/M − Flow = Pulmonary Blood Flow − Flow = Pulmonary Blood Flow † = Cardiac Index (CI; l/m/M 2 2 ) ) − − Resistance = Pulmonary Vascular Resistance (PVR; units Resistance = Pulmonary Vascular Resistance (PVR; units • • M M 2 2 ) ) *pressure drop across vascular bed † without congenital systemic to pulmonary shunts 1-2-06.final 4
Normal Pulmonary Hemodynamics at Normal Pulmonary Hemodynamics at Sea Level (Rest and Mild Exercise) and Sea Level (Rest and Mild Exercise) and at Elevated Altitude (Rest) at Elevated Altitude (Rest) Sea level Sea level Altitude Altitude Sea level Sea level Mild Mild (~15,000 ft) (~15,000 ft) Rest Rest Exercise Rest Exercise Rest Pulmonary arterial Pulmonary arterial pressure, (mean) pressure, (mean) 20/10(15) 20/10(15) 30/13(20) 30/13(20) 38/14(26) 38/14(26) mmHg mmHg Cardiac output, L/min 6.0 12.0 6.0 Cardiac output, L/min 6.0 12.0 6.0 Left atrial pressure Left atrial pressure 5.0 5.0 9.0 9.0 5.0 5.0 (mean), mmHg (mean), mmHg Pulmonary vascular Pulmonary vascular 1.7 1.7 0.9 0.9 3.3 3.3 resistance, units resistance, units 1-2-06.final 5
Normal Circulatory Dynamics ( II ) Pulmonary SVC Veins Pressure = Flow x Resistance 8 95% IVC 75% 95% RA LA 3 8 Systemic Circulation 75% 95% SAPm - RAPm = CI x SVR LV RV 83mmHg-3mmHg=5 l/min/M 2 x16 U•M 2 30/3 100/8 Pulmonary Pulmonary Circulation 100/60 83 Artery PAPm - PCWPm = CI x PVR 20mmHg-8mmHg=5 l/min/M 2 x2 U•M 2 30/10 20 Aorta 75% 95% Pressures in mmHg O 2 % saturation Pulmonary Hypertension: Pulmonary Hypertension: Definition Definition PAP mean ≥ ≥ 25 mm Hg at rest 25 mm Hg at rest PAP mean or ≥ ≥ 30 mmHg with exercise 30 mmHg with exercise or 1-2-06.final 6
Pulmonary Hypertension: Pulmonary Hypertension: The Clinical Context The Clinical Context Precapillary Pulmonary Pulmonary Hypertension Hypertension Postcapillary Pulmonary Hypertension Pulmonary Hypertension: Pulmonary Hypertension: Classification Classification PAH PAH LH disease LH disease pre- pre -capillary capillary post- post -capillary capillary PH PH Lung disease Lung disease Misc Misc Hypoxemia Hypoxemia CTEPH CTEPH 1-2-06.final 7
Localizing the Problem Pre-capillary Localizing the Problem Post-capillary 1-2-06.final 8
Pre- -capillary PH: capillary PH: Pre Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Definition Definition • PAP mean PAP mean ≥ ≥ 25 mmHg at rest or 25 mmHg at rest or • ≥ 30 mmHg with exercise 30 mmHg with exercise ≥ AND AND • PCWP or LVEDP • PCWP or LVEDP ≤ ≤ 15 mmHg 15 mmHg • PVRI • PVRI ≥ ≥ 3 units 3 units • • m m 2 2 • Normal LVEF • Normal LVEF • No left No left- -sided valvular disease sided valvular disease • Pulmonary Hypertension - Pre-Capillary ( I ) (Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension) SVC Pulmonary Veins 8 95% 75% 95% IVC RA LA 3 8 75% 95% LV RV 100/3 100/8 100/60 83 Pulmonary Aorta 100/40 68 Artery 75% 95% Pressures in mmHg O 2 % saturation 1-2-06.final 9
Pulmonary Hypertension - Pre-Capillary ( II ) (Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension) Pulmonary SVC Veins Pressure = Flow x Resistance 8 95% IVC 75% 95% RA LA 3 8 Systemic Circulation 75% 95% 83mmHg-3mmHg=5 l/min/M 2 x16 U•M 2 LV RV 100/3 100/8 Pulmonary Circulation Pulmonary 68mmHg-8mmHg=5 l/min/M 2 x12 U•M 2 100/60 83 Artery 100/40 68 Aorta 75% 95% Pressures in mmHg O 2 % saturation Pre- -capillary PH: capillary PH: Pre Classification Classification Idiopathic or Familial PAH Idiopathic or Familial PAH PAH PAH Associated with (APAH) Associated with (APAH) Connective tissue disease Connective tissue disease • thyroid disorders thyroid disorders Congenital syst- Congenital syst -pulm shunts pulm shunts • • glycogen storage glycogen storage Portal hypertension Portal hypertension • disease disease HIV infection HIV infection • Gaucher disease Gaucher disease Drugs and toxins Drugs and toxins • • hereditary hereditary Other Other • hemorrhagic hemorrhagic telangiectasia telangiectasia • hemoglobinopathies hemoglobinopathies • High PA pressure and normal High PA pressure and normal • myeloproliferative myeloproliferative • “downstream “ downstream” ” pressures pressures disorders disorders • splenectomy splenectomy • 1-2-06.final 10
Post- -capillary PH: capillary PH: Post Definition Definition • PAP mean PAP mean ≥ ≥ 25 mmHg at rest 25 mmHg at rest • or or ≥ ≥ 30 mmHg with exercise 30 mmHg with exercise AND AND • PCWP or LVEDP >15mmHg • PCWP or LVEDP >15mmHg Pulmonary Hypertension - Post-Capillary ( I ) (Pulmonary Venous Pulmonary Hypertension) SVC Pulmonary Veins 25 95% 75% 95% IVC RA LA 3 25 75% 95% LV RV 50/3 100/25 100/60 83 Pulmonary Aorta 50/20 35 Artery 75% 95% Pressures in mmHg O 2 % saturation 1-2-06.final 11
Recommend
More recommend