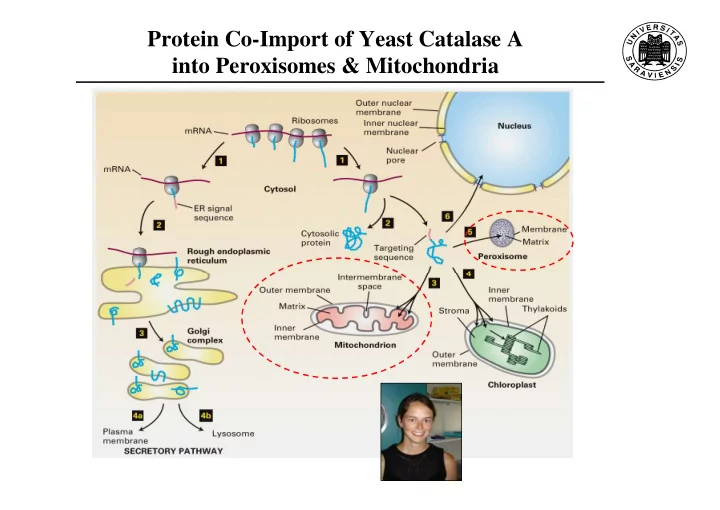

Protein Co-Import of Yeast Catalase A into Peroxisomes & Mitochondria
Protein Co-Import of Yeast Catalase A into Peroxisomes & Mitochondria • Yeast cells possess two types of catalase: (1) catalase T (cytosolic, Ctt1p) (2) catalase A (peroxisomal, Cta1p) catalase • Function : 2 H 2 O 2 2 H 2 O + O 2 homotetrameric catalase • catalase A contains two P eroxisomal- T argeting- S ignals (PTS): (1) PTS1 : carboyterminal SKF motif (2) internal PTS within the N-terminal part of Cta1p
Cta1p is Responsible for Mitochondrial Catalase Activity Cyt Mit Cyt Mit Catalase Activity (U/mg) 8 6.4 Pgk1p 6 5.6 fully restores catalase activity 4.7 Cox3p in yeast � cta1 mitochondria 4 2 anti-Pgk1p anti-Cox3p 0 0 � cta1 � ctt1 � cta1 cta1 CTA1 [pCTA1-GFP] ctt1 CTT1 Catalase A N- PTS PTS 1 GFP -C Expression of a Cta1p/GFP fusion protein in a � cta1 mutant
Co-expression of Cta1p/GFP and mt-DsRed / DsRed SKL Cta1p mt GFP + DsRed Merged Cta1p/GFP mt-DsRed Cta1p + GFP DsRed SKL Cta1p/GFP Merged DsRed SKL
Peroxisomal & mitochondrial cotargeting of Cta1p D-AAO [U/mg x 10 -2 ] Protein [mg/ml] Mitochondria 8.0 4.0 GDH [U/mg] Peroxisomes 6.0 3.0 4.0 2.0 2.0 1.0 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Fractions Cta1p-GFP Nycodenz gradient fractions D-AAO (D-amino acid oxidase, peroxisomal) GDH (glutamate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial)
Cell physiology & Cta1p cotransport to different organelles Glucose Oleate Raffinose peroxisomal mitochondrial fractions fractions Cta1p/GFP predominantly targets peroxisomes when cultivated on oleate Cta1p/GFP predominantly targets mitochondria when cultivated on raffinose
Cells lacking mitochondrial catalase accumulate reactive oxygen species (ROS) 8000 Relative ROS content (arbitrary units) 7000 wild-type � cta1 6000 5000 4000 3000 Antimycin-A blocks electron transport in the mitochondrial inner membrane and thus induces oxygen stress in mitochondria 2000 1000 0 10 5 2.5 1.25 0 Antimycin A (µg/ml)
Cta1p can drive mitochondrial import of Acp1p • Acp1p - A cyl C arrier P rotein (essential yeast protein in mitochondria) - component of mitochondrial fatty acid synthase - deletion: � reduced amount of fatty acids � respiratory defect, unable for growth on lactate � acp1 ACP1 lactate glucose lactate
Expression of ACP variants in a yeast � acp1 mutant mt-signal Acp1p GFP � Acp1p GFP � Acp1p GFP Cta1p Cta1p targets � Acp1p to mitochondria
Cta1p contains a mitochondrial targeting signal positive control � Acp1p GFP � ACP GFP Cta1p CTA 1 � Acp1p GFP � Cta1p � ACP GFP negative control CTA mt-signal mt-signal Acp1p GFP Acp1p Mitoleader Mitoleader ACP GFP ACP GFP Mitoleader ACP Cta1p targets � Acp1p to mitochondria allowing aerobic growth of a � acp1 mutant on lactate
Model of the Erv1–Mia40 disulfide relay. Schematic representation of the reactions that mediate redox-driven protein import into the IMS of mitochondria. The sulfhydryl oxidase Erv1 is a dimeric FAD-binding protein that maintains an oxidized state by the use of molecular oxygen as a final electron acceptor. Erv1 directly interacts with Mia40, which functions as a redox-activated import receptor. The oxidized active state of Mia40 can interact with newly imported precursor proteins by intermolecular disulfide bonds. It has been proposed that reshuffling of the disulfide bonds releases the substrates from Mia40 in a stably folded oxidized state. Because these folded proteins cannot traverse the protein-conducting channel of the TOM complex, they remain trapped in the IMS. Alternatively, Erv1 might directly interact with some incoming substrates and pass them on to Mia40, which might function as a protein disulfide isomerase. In both cases, the Erv1–Mia40 system constitutes a folding trap that is designed to mediate the unidirectional import of proteins into the IMS of mitochondria. Reduced and oxidized thiol groups are indicated by SH and SS.
Yeast Cta1/Erv1p and Erv1/Cta1p expression constructs
Experimental strategy and set-up for Cta1/Erv1p expression plasmid shuffling Transformation 5‘-FOA selection (ura - ) cell growth no cell growth
The signal for peroxisomal / mitochondrial cotargeting of catalase is localized within the N-terminal part of Cta1p N- MTS / PTS Catalase A -C PTS1
Summary & Relevance of Mitochondrial Catalase Targeting Catalase A cotargeting to yeast peroxisomes and mitochondria depends on the physiological status of the cell: � Cta1p targets peroxisomes during growth on oleate � Cta1p targets mitochondria under aerobic growth conditions (raffinose) Mitochondrial catalase level is significantly increased under oxygen stress (antimycin A) � Cta1p might be an essential component in oxidative stress response by maintaining mitochondrial cell functions � Protein cotargeting seems a general principle in eukaryotic cell biology that has recently been designated „ eclipsed distribution “ Kindly supported by a grant from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG)
Recommend
More recommend