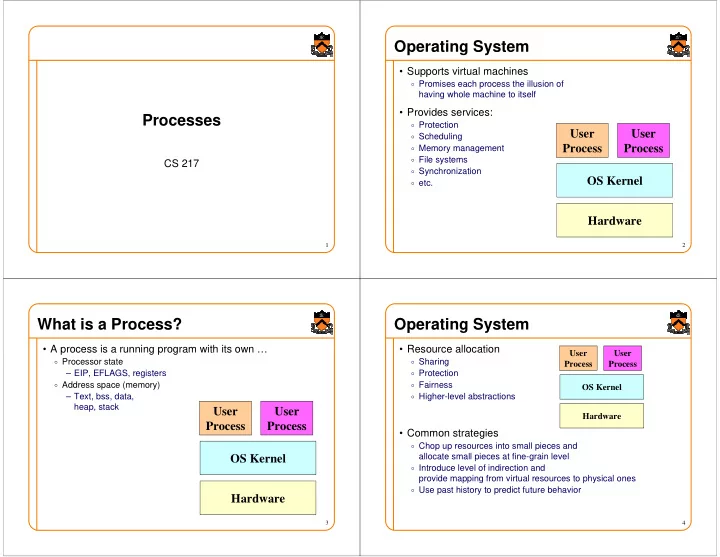

Operating System • Supports virtual machines o Promises each process the illusion of having whole machine to itself • Provides services: Processes o Protection User User o Scheduling o Memory management Process Process o File systems CS 217 o Synchronization OS Kernel o etc. Hardware 1 2 What is a Process? Operating System • A process is a running program with its own … • Resource allocation User User o Processor state o Sharing Process Process o Protection – EIP, EFLAGS, registers o Address space (memory) o Fairness OS Kernel – Text, bss, data, o Higher-level abstractions heap, stack User User Hardware Process Process • Common strategies o Chop up resources into small pieces and allocate small pieces at fine-grain level OS Kernel o Introduce level of indirection and provide mapping from virtual resources to physical ones o Use past history to predict future behavior Hardware 3 4
Life Cycle of a Process Context Switch • Running: instructions are being executed Process B Process A • Waiting: waiting for some event (e.g., i/o finish) Waiting Running Save context • Ready: ready to be assigned to a processor . . . Load context Waiting Running Create Ready Running Termination Save context . . . Load context Waiting Running Waiting 5 6 Overlap CPU with I/O operations Process Control Block • Schedule CPU for process B • For each process, the kernel keeps track of ... while process A is waiting for I/O o Process state (new, ready, waiting, halted) o CPU registers (EIP, EFLAGS, EAX, EBX, …) o Better utilize CPU o CPU scheduling information (priority, queues, ...) o Memory management information (page tables, ...) CPU I/O CPU I/O CPU I/O A: o Accounting information (time limits, group ID, ...) o I/O status information (open files, I/O requests, ...) CPU I/O CPU I/O CPU I/O B: 7 8
Fork Wait • Create a new process (system call) • Parent waits for a child (system call) o child process inherits state from parent process o blocks until a child terminates o parent and child have separate copies of that state o returns pid of the child process o parent and child share access to any open files o returns –1 if no children exist (already exited) o status pid = fork(); #include <sys/types.h> Parent if (pid != 0) { #include <sys/wait.h> /* in parent */ pid_t wait(int *status); ... } • Parent waits for a specific child to terminate Child /* in child */ #include <sys/types.h> ... #include <sys/wait.h> pid_t waitpid(pid_t pid, int *status, int options); 9 10 Fork Exec • Inherited: • Separate in child • Overlay current process image with a specified image file o user and group IDs o process ID o environment o address space (memory) (system call) o close-on-exec flag o file descriptors o signal handling settings o affects process memory and registers o active process group ID. o supplementary group IDs o parent process ID o has no affect on file table o set-user-ID mode bit o process locks, file locks, page locks, o set-group-ID mode bit text locks and data locks o profiling on/off/mode status • Example: o pending signals o debugger tracing status o nice value o timer signal reset times execlp( “ ls ” , “ ls ” , “ -l ” , NULL); o stdin o share mask fprintf(stderr, “ exec failed\n ” ); o scheduler class o all shared memory segments exit(1); o all mapped files o file pointers o non-degrading priority o process group ID o session ID o current working directory o root directory o file mode creation mask o resource limits o controlling terminal o all machine register states o control register(s) 11 12
Exec (cont) Fork/Exec • Commonly used together by the shell • Many variations of exec ... parse command line ... int execlp(const char *file, const char *arg, ...) pid = fork() int execl(const char *path, if (pid == -1) const char *arg, ...) fprintf(stderr, “ fork failed\n ” ); int execv(const char *path, else if (pid == 0) { char * const argv[]) /* in child */ int execle(const char *path, execvp(file, argv); const char *arg, ..., fprintf(stderr, “ exec failed\n ” ); char * const envp[]) } • Also execve and execvp else { /* in parent */ pid = wait(&status); } ... return to top of loop ... 13 14 System Summary • Convenient way to invoke fork/exec/wait • Operating systems manage resources o Forks new process o Divide up resources (e.g., quantum time slides) o Execs command o Allocate them (e.g., process scheduling) o Waits until it is complete • A processes is a running program with its own … o Processor state int system(const char *cmd); o Address space (memory) • Create and manage processes with ... • Example: o fork int main() o exec o system } { o wait system( “ echo Hello world ” ); Used in shell } 15 16
Recommend
More recommend