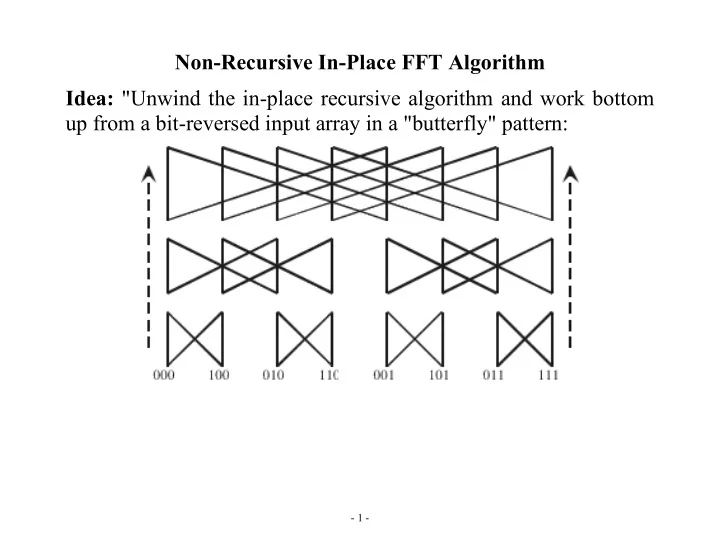

Non-Recursive In-Place FFT Algorithm Idea: "Unwind the in-place recursive algorithm and work bottom up from a bit-reversed input array in a "butterfly" pattern: - 1 -
(non-recursive in-place FFT algorithm continued) Non-recursive algorithm: The outer loop indexes the levels from bottom to top, the second loop indexes the butterflies along a given level, and the inner loop indexes the points on a given butterfly: input an array A [0] ...A [ n –1] , n a power of 2 r := a principal n th root of unity BITREVERSE( A ) for m := 0 to log 2 ( n )–1 do for j := 0 to n –2 m+ 1 by 2 m+ 1 do for k := 0 to 2 m –1 do begin ( ) ( ) k n / 2 m + 1 • A [ j + k + 2 m ] temp := r A [ j+k+ 2 m ] := A [ j+k ] – temp A [ j+k ] := A [ j+k ] + temp end Note : The limit of n –2 m+ 1 on the second loop can simply be replaced by n –1 since the next value of j will exceed n –1. - 2 -
Simplified Non-Recursive In-Place FFT Algorithm Idea: Accumulate powers of 2 as the algorithm progresses. Also, simplify the inner loop by making k start at j instead of 0. input an array A [0] ...A [ n –1] , n a power of 2 r := a principal n th root of unity BITREVERSE( A ) m := 1 while m ≤ n do begin m := 2 m w := r n /( 2m ) for j := 0 to n –1 by 2 m do begin v := 1 for k := j to j + m –1 do begin h := k + m temp := v • A [ h ] A [ h ] := A [ k ] – temp A [ k ] := A [ k ] + temp v := v • w end end end - 3 -
(simplified non-recursive in-place FFT continued) Further simplifications that can be made: • Pre-compute powers of r , etc. which are constant independent of the input. • Replace the two inner loops by a single loop from 0 to n –1 . The constant associated with the O ( n log( n )) time: Counting just the (complex) arithmetic operations involving elements of A , gives a total of: • n 2 log 2 ( n ) multiplications • n 2 log 2 ( n ) additions • n 2 log 2 ( n ) subtractions - 4 -
An Example Using the Simplified Algorithm Consider the input 1,2,3,4 (recall that the principal 4th roots of unity for the complex numbers are 1, � 1 , –1, � � 1 ): - 5 -
Recommend
More recommend