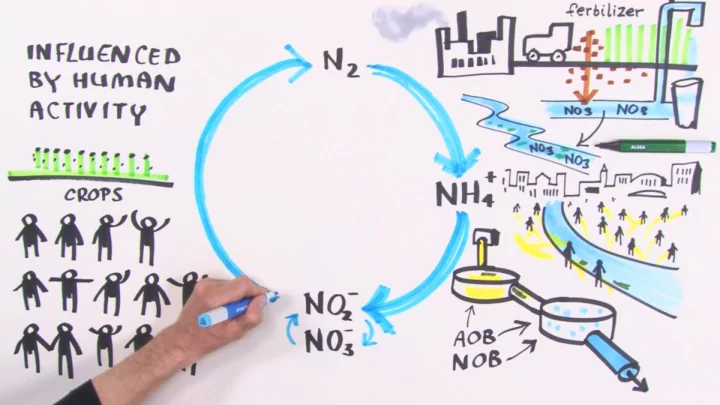

Natural ¡Nitrogen ¡Cycle ¡ A". ¡Paginagroot ¡N-‑cycle ¡
Nitrogen ¡Removal ¡ CTB3365x ¡Introduc1on ¡to ¡water ¡treatment ¡ Dr.ir. ¡Merle ¡de ¡Kreuk ¡ ¡
Nitrogen ¡in ¡nature ¡ Biomass ¡( C 5 H 7 O 2 N) ¡ ¡ C 18 H 19 O 9 N ¡+ ¡ 0.74 ¡NH 4 + ¡+ ¡ 8.8 ¡O 2 ¡→ ¡ 1.74 ¡C 5 H 7 O 2 N ¡+ ¡ 9.3 ¡CO 2 ¡+ ¡ 0.74 ¡H + ¡+ ¡ 4.52 ¡H 2 O ¡ ¡
Nitrogen ¡in ¡nature ¡ Biomass ¡( C 5 H 7 O 2 N) ¡
Biological ¡N-‑removal: ¡N ¡uptake ¡by ¡biomass ¡ Influent ¡in ¡the ¡Netherlands: ¡ BOD ¡= ¡180 ¡g ¡/ ¡L; ¡TN ¡= ¡40 ¡mg ¡/ ¡L ¡ Growth ¡Yield ¡of ¡ac1vated ¡sludge: ¡ 0.6 ¡g ¡VSS ¡/ ¡g ¡ BOD ¡ ¡ ¡Per ¡liter ¡influent ¡0.6 ¡* ¡180 ¡= ¡108 ¡g ¡VSS ¡produced, ¡containing ¡13.4 ¡g ¡N ¡/ ¡L ¡ Is ¡this ¡enough ¡to ¡reach ¡effluent ¡standard ¡ (10 ¡g ¡N ¡/ ¡L) ? ¡
Biological ¡N-‑removal ¡ NitrificaGon ¡ DenitrificaGon ¡
Biological ¡N-‑removal: ¡NitrificaGon ¡ ¡ 1 st step: NH 4 + + 1.5 O 2 → NO 2 - + 2 H + + H 2 O 2 nd step: NO 2 - + 0.5 O 2 → NO 3 - O 2 NH 4 + or NO 2 - CO 2 Aerobic ¡Chemo-‑Litho-‑Autotrophs ¡
Biological ¡N-‑removal: ¡NitrificaGon ¡ ¡ 1 st step: NH 4 + + 1.5 O 2 → NO 2 - + 2 H + + H 2 O 2 nd step: NO 2 - + 0.5 O 2 → NO 3 - ¡ Overall: ¡ ¡ ¡ NH 4 + + 2 O 2 NO 3 - + 2 H + + H 2 O Including ¡biomass ¡producGon: ¡4.2 ¡g ¡O 2 /g ¡NH 4 -‑N ¡
Heterotrophic ¡bacteria ¡vs. ¡Autotrophic ¡Nitrifiers ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ Heterotrophic ¡bacteria ¡ ¡ Autotrophic ¡nitrifying ¡bacteria ¡ • Need ¡ O 2 ¡ • Need ¡lots ¡of ¡ O 2 ¡ • Carbon ¡source: ¡ organic ¡C ¡ • Carbon ¡source: ¡ CO 2 ¡ • Electron ¡Donor: ¡ organic ¡C ¡ • Electron ¡Donor: ¡ NH 4 ¡ • Fast ¡growth: ¡~6 ¡d -‑1 ¡(Td ¡= ¡2.8 ¡h) ¡ • Slow ¡growth: ¡~0.8 ¡d -‑1 ¡(Td ¡= ¡21 ¡h) ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡Heterotrophic ¡act. ¡in ¡bioreactor ¡ ¡Nitrifica:on ¡in ¡bioreactor ¡ • B X ¡< ¡3 ¡kg ¡ BOD ¡. ¡kg ¡MLSS -‑1 d -‑1 ¡ • B X ¡< ¡0.15 ¡kg ¡ BOD ¡. ¡kg ¡MLSS -‑1 d -‑1 ¡ • Θ X ¡ ¡> ¡1 ¡day ¡ • Θ X ¡> ¡2.5 ¡days ¡ • O 2 ¡> ¡0.5 ¡g ¡m -‑3 ¡ • O 2 ¡> ¡2 ¡g ¡m -‑3 ¡
Biological ¡N-‑removal ¡ NitrificaGon ¡ DenitrificaGon ¡
Biological ¡N-‑removal: ¡DenitrificaGon ¡ ¡Preformed ¡by ¡heterotrophic ¡organisms ¡ ¡Use ¡ NO 2 -‑ ¡ or ¡ NO 3 -‑ ¡ as ¡electron ¡acceptor ¡ ¡Need ¡ organic ¡ carbon ¡source ¡
Biological ¡N-‑removal: ¡DenitrificaGon ¡ ¡Preformed ¡by ¡heterotrophic ¡organisms ¡ ¡Use ¡NO 3 -‑ ¡as ¡electron ¡acceptor ¡ ¡Need ¡organic ¡carbon ¡source ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ C 10 H 19 O 3 N ¡+ ¡ 10 ¡ NO 3 -‑ ¡ ¡5 ¡ N 2 ¡+ ¡ 10 ¡ CO 2 ¡+ ¡ 3 ¡ H 2 O ¡+ ¡ NH 3 ¡+ ¡ 10 ¡OH -‑ ¡ + ¡ Energy ¡ 10 ¡OH -‑ ¡ ¡ ¡ 6 ¡OH -‑ ¡ ¡ ¡ 5 ¡ CH 3 OH ¡+ ¡ 6 ¡ NO 3 -‑ ¡ ¡ 3 ¡ N 2 ¡+ ¡ 5 ¡ CO 2 ¡+ ¡7 ¡ H 2 O ¡+ ¡ 6 ¡OH -‑ ¡ + ¡ Energy ¡
Post-‑denitrificaGon ¡ / ¡Pre-‑denitrificaGon ¡ Extra ¡C-‑source ¡ Aerobic Anoxic tank tank NH 4 + ¡ + ¡ O 2 ¡ ¡NO 3 -‑ ¡ BOD ¡ + ¡NO 3 -‑ ¡ ¡N 2 ¡ + ¡CO 2 ¡ BOD ¡ + ¡O 2 ¡ ¡CO 2 ¡
Post-‑denitrificaGon ¡ / ¡Pre-‑denitrificaGon ¡ Anoxic Aerobic tank tank BOD ¡ + ¡NO 3 ¡ ¡N 2 ¡ + ¡CO 2 ¡ NH 4 ¡ + ¡ O 2 ¡ ¡NO 3 -‑ ¡ -‑ + BOD ¡ + ¡O 2 ¡ ¡CO 2 ¡
Post-‑denitrificaGon ¡/ ¡Pre-‑denitrificaGon ¡ Mass-‑balance ¡ ¡ Q ¡NO x ¡= ¡NO x,e ¡ ( ¡ Q ¡ + ¡f IR ¡ Q ¡ + ¡f R ¡Q) ¡ ¡ Nitrate ¡in ¡ Nitrate ¡in ¡return ¡ Kg/d ¡of ¡nitrate ¡ effluent ¡ + ¡ Nitrate ¡in ¡ = ¡ + ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ acevated ¡sludge ¡ produced ¡in ¡aerobic ¡ internal ¡ (RAS) ¡ zone ¡ recycle ¡ ¡ Internal ¡Recycle ¡Ra:on ¡(f IR ) ¡ ¡ f IR ¡= ¡NO x ¡ / ¡NO x,e ¡ ¡ ¡-‑ ¡1.0 ¡-‑ ¡f R ¡ ¡
DenitrificaGon ¡in ¡plug-‑flow ¡system ¡ ¡C ¡ E ¡ ¡B ¡ A. Aeraeon ¡circuit ¡ B. Denitrificaeon ¡zone ¡ C. Measurement ¡DO ¡ ¡A ¡ D. Surface ¡aerators ¡ E. Effluent ¡ ¡B ¡ F. Measurement ¡NO 3 -‑ ¡ concentraeon ¡ G. Return ¡sludge ¡ H. Influent ¡ ¡B ¡ D ¡
Novel ¡opportunity: ¡anaerobic ¡nutrient ¡removal ¡ Conveneonal ¡ electron-‑donor ¡ O 2 ¡ O 2 ¡ ¡ ¡ nitrificaeon ¡ denitrificaeon ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ NH 4 + ¡ NO 2 -‑ ¡ N 2 ¡ NO 3 -‑ ¡ ¡ Anammox ¡ (Anaerobic ¡Ammonium ¡Oxida1on) ¡ ¡ NH 4 + ¡+ ¡NO 2 -‑ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡N 2 ¡+ ¡2H 2 O ¡ ¡
Anammox: ¡advantages ¡ ¡Huge ¡savings ¡in ¡energy ¡requirements ¡ ¡ ¡No ¡need ¡for ¡addieonal ¡carbon ¡source ¡(e-‑donor) ¡ ¡To ¡combine ¡with ¡sludge ¡digeseon ¡ ¡
Anammox: ¡Two ¡step ¡reactor ¡ 95% ¡ N 2 ¡ 50% ¡ NO 2 -‑ ¡ NH 4 100% ¡ NH 4 + ¡ + ¡ 50% ¡ NH 4 + ¡ 5% ¡ NO 3 -‑ ¡ SHARON ¡ ANAMMOX ¡ ¡ O 2 ¡
Anammox: ¡One ¡step ¡reactor ¡ Anammox ¡
Current ¡removal: ¡ ¡ 5 ¡kg ¡N/(m 3 .d) ¡ ¡ ¡ ¡
Anammox ¡Pilot ¡Plant ¡ low ¡temperature ¡N-‑removal ¡by ¡Anammox ¡in ¡B-‑stage ¡of ¡an ¡A/B ¡system ¡
Nitrogen ¡Removal ¡ CTB3365x ¡Introduc1on ¡to ¡water ¡treatment ¡ Dr.ir. ¡Merle ¡de ¡Kreuk ¡ ¡
Recommend
More recommend