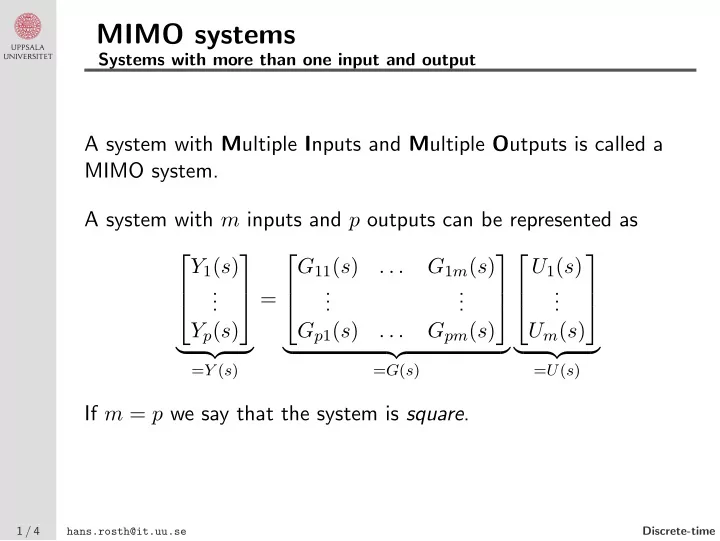

MIMO systems Systems with more than one input and output A system with M ultiple I nputs and M ultiple O utputs is called a MIMO system. A system with m inputs and p outputs can be represented as Y 1 ( s ) G 11 ( s ) . . . G 1 m ( s ) U 1 ( s ) . . . . . . . . = . . . . Y p ( s ) G p 1 ( s ) G pm ( s ) U m ( s ) . . . � �� � � �� � � �� � = Y ( s ) = G ( s ) = U ( s ) If m = p we say that the system is square . 1 / 4 hans.rosth@it.uu.se Discrete-time
MIMO systems Be careful! y r u � F r G + − F y The closed loop system: Y ( s ) = G ( s )( F r ( s ) R ( s ) − F y ( s ) Y ( s )) ( I + G ( s ) F y ( s )) Y ( s ) = G ( s ) F r ( s ) R ( s ) Y ( s ) = ( I + G ( s ) F y ( s )) − 1 G ( s ) F r ( s ) R ( s ) � �� � = G c ( s ) Sensitivity function: S ( s ) = ( I + G ( s ) F y ( s )) − 1 Complementary sensitivity function: T ( s ) = I − S ( s ) = S ( s )( S ( s ) − 1 − I ) = ( I + G ( s ) F y ( s )) − 1 G ( s ) F y ( s ) 2 / 4 hans.rosth@it.uu.se Discrete-time
MIMO systems Straightforward with state space representation Almost all formulas and results look the same for SISO and MIMO systems: � x = Ax + Bu, ˙ G ( s ) = C ( sI − A ) − 1 B + D y = Cx + Du Poles: 0 = det( sI − A ) � t x ( t ) = e A ( t − t 0 ) x ( t 0 ) + e A ( t − τ ) Bu ( τ ) dτ t 0 C CA � � A n − 1 B S = B AB . . . , O = . . . CA n − 1 Controllability and observability ⇔ S and O of full rank. 3 / 4 hans.rosth@it.uu.se Discrete-time
MIMO systems How to put up a state space representation Not obvious how to set up a state space model for a given MIMO G ( s ) . In general the controller and observer canonical forms do not work. Two exceptions: ◮ SIMO — one input: Controller canonical form works ◮ MISO — one output: Observer canonical form works 4 / 4 hans.rosth@it.uu.se Discrete-time
Recommend
More recommend