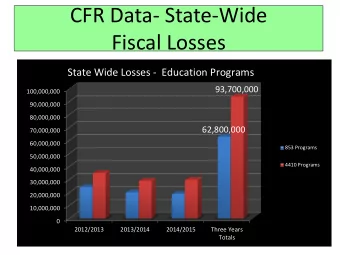
LOSSES OEE Workshop Siyambulela Bozo: Junior Project Manager AIDC - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
OEE VS 6 BIG LOSSES OEE Workshop Siyambulela Bozo: Junior Project Manager AIDC - TPM Pres resentation entation Ov Overview erview 1. What are Losses 2. Defining the 6 Big Losses 3. Measuring 6 Big Losses 4. How to Eliminate the 6 Big
OEE VS 6 BIG LOSSES OEE Workshop Siyambulela Bozo: Junior Project Manager AIDC - TPM
Pres resentation entation Ov Overview erview 1. What are Losses 2. Defining the 6 Big Losses 3. Measuring 6 Big Losses 4. How to Eliminate the 6 Big Losses? • Conclusion
1. 1. Wh What at A Are re Lo Losses sses? “ Losses in the production environment are those a reas where the greatest amounts of materials and time is wasted ” - Kunio Shirose, 1989 There are 16 Major Losses that can impede Improvement of Production Efficiency A) 7 Ma Major or Losses that can impede equipment efficiency B) 1 Ma Major or Loss that can impede machine loading time C) 5 Major or Losses that can impede improvement of work D) 3 Major or Losses that can impede effective use of production resources
2. 2.Defining Defining 6 B 6 Big g Lo Losses sses
2. 2. De Defining fining 6 B 6 Big g Lo Losses sses 1. 1. Failure/Brea re/Breakdown kdown Losses es Losses due to sporadic / chronic failures result in time losses (declining output) and volume losses (defects) Losses requiring replacement or repair of machine parts for machine to function Losses requiring 5-10 minute or more for repairs Sporadic Failures Attract major attention and countermeasures are immediately developed and implemented e.g. Tool Breakdown Chronic Failures Frequent failures which remain unresolved due to ineffective countermeasures
2. 2. De Defining fining 6 B 6 Big g Lo Losses sses 2. Set-up up and Adjustment tment losses es Time losses from end of the production of a previous item, through changeover and setup of new product tools Time losses after set-up by doing trial and error adjustments to buy-off good part after many parts try out 3. Cu Cuttin ting g Blade Losses Losses due to regular blade exchanges and other blade replacement by blade damages and volume losses Losses due to breakage and chipping of blade, blade tip rework Losses due to material and yield losses
2. 2. De Defining fining 6 B 6 Big g Lo Losses sses 4. Start rt-up p Losse ses Time losses from start-up after periodic repair Time losses from start-up after suspension (long-time stoppage) Time losses after lunch breaks 5. Min inor r St Stoppage page / Idli ling g Losses s Losses due to temporary malfunction of machine Losses requiring removal of abnormal work pieces and resetting
2. De 2. Defining fining 6 B 6 Big g Lo Losses sses 6. Speed ed losses sses Losses occurring due to slow equipment speed Losses due to difference between the design speed and the actual machine speed Losses caused when the design speed is slower than present technological standards or the desirable condition E.g. If standard cycle time is set at 60seconds, and actual operation time is 65seconds, speed loss is 5 seconds
3. 3. Measuri easuring ng 6 Bi 6 Big g Lo Losses sses
OE OEE in Ch n China ina
4. 4. Eliminating iminating 6 B 6 Big g Lo Losses sses
4. 4. Eliminating iminating 6 B 6 Big g Lo Losses sses
4. 4. Eliminating iminating 6 B 6 Big g Lo Losses sses
4. 4. Eliminating iminating 6 B 6 Big g Lo Losses sses
4. 4. Eliminating iminating 6 B 6 Big g Lo Losses sses
4. 4. Eliminating iminating 6 B 6 Big g Lo Losses sses
4. 4. Eliminating iminating 6 B 6 Big g Lo Losses sses
Conc Co nclusio lusion Down Time Break akdow downs ns due to equipment failure 1. 1. - Apply Ishikawa Root Cause Analysis as a Team and solve root cause of equipment 2. Setup up and adjus ustment tment (e.g. exchange of dies in injection molding machines) - Perform SMED Exercise Speed d Losses es Idling ng and minor or stoppage ppages (abnormal operation of sensor, etc.) 3. 3. - Cycle time analysis to see the process that frequently causes the stoppage Reduc uced ed speed eed (discrepancies between designed and actual speed of equipment) 4. 4. - Compare all cycle times to ideal cycle time and focus on eliminating errant times Defect cts Defects ts in proces ess and rework (scrap and quality defects requiring repair) 5. 5. - Six Sigma (DMAIC Process Improvement Approach) 6. Reduced uced yield d between en machine hine startup tup and d stable ble producti duction on - Six Sigma (DMAIC Process Improvement Approach)
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.