
• Key Concept: The nervous system controls and coordinates functions throughout the body and responds to internal and external stimuli.
• Neurons transmit electrical signals (nerve impulses) • Three types of neurons: • Sensory: sensory organs brain & spinal cord • Motor: brain & spinal cord muscles & glands • Interneurons: connect sensory & motor neurons • Draw and label a typical neuron (p. 897)
• Cell Body: contains nucleus • Axon terminals: synapse • Dendrites: to cell body • Myelin Sheath: insulates • Axon: from cell body • Nodes: gaps in between
• Outside: Na+, Inside: K+ • Resting potential: • Na+/K+ Pump: Na+ out; K+ in • Leak channels: K+ out • Inside is negative compared to outside • Action potential: moving impulse; charges reverse; Na+ in, K+ out; must reach threshold; all-or-none principle • Synapse: neuronal communication via neurotransmitters
Central Nervous System (CNS) Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) • CNS function: relay • PNS function: messages, processes • Sensory: transmits info from sense organs to CNS information, and • Motor: transmits info from analyzes information CNS to muscles or glands • Composed of the brain • Composed of all nerves and spinal cord and support cells outside of the CNS • Meninges and cerebrospinal fluid coat and protect
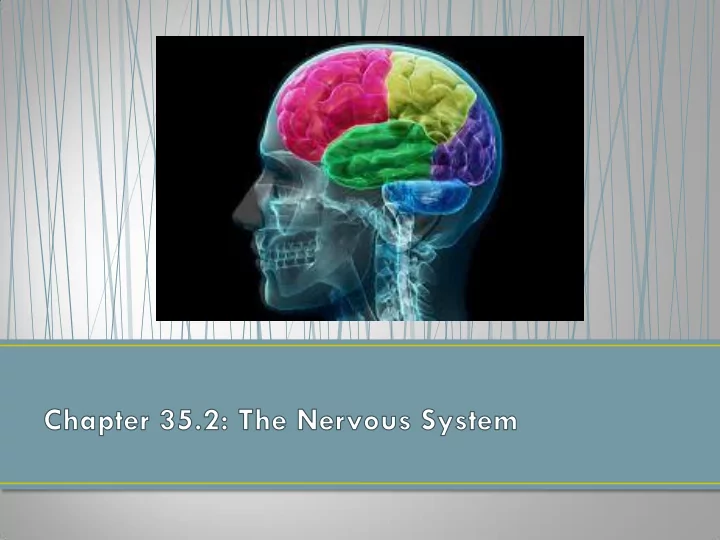
The Brain • Cerebrum: voluntary or conscious activities; intelligence; learning; judgment; divided into 4 lobes • Cerebellum: “little brain”; balance and fine movements • Brain Stem: connects brain and spinal cord; controls important bodily functions (i.e. blood pressure, heart rate) • Thalamus: relay center • Hypothalamus: recognition, appetite; body temp., hormones
The Spinal Cord • Connects the brain to the rest of the body • Coordinates reflexes (automatic responses)
Somatic Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System • Regulation of • Voluntary responses automatic or and movement involuntary responses • Reflex arc: sensory (i.e. heart rate, neuron, interneuron breathing, function of (some cases), motor internal organs, etc…) neuron • Sympathetic vs. Parasympathetic (fight or flight & rest and digest)
Recommend
More recommend