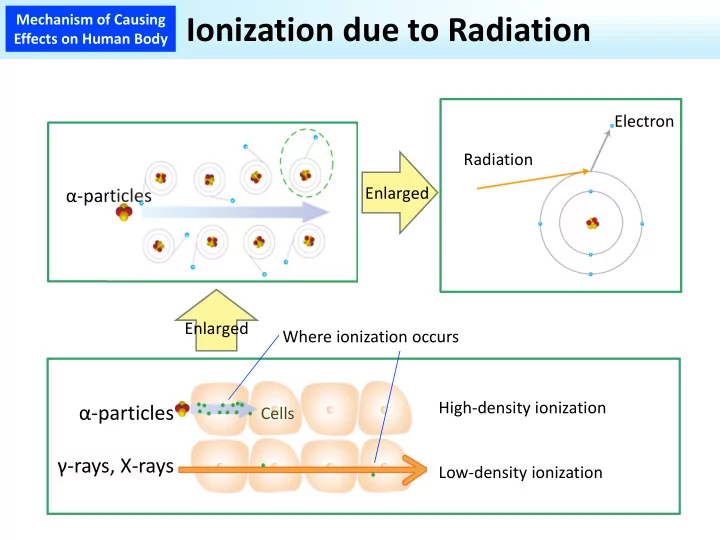

Mechanism of Causing Ionization due to Radiation Effects on Human Body Electron Radiation Enlarged α‐particles Enlarged Where ionization occurs High‐density ionization α‐particles Cells γ‐rays, X‐rays Low‐density ionization
Mechanism of Causing Damage and Repair of DNA Effects on Human Body Radiation Cell DNA Nucleus DNA Damage Repair Complete repair Partial or Repair Radiation incomplete enzyme repair
Mechanism of Causing DNA→Cells→Human Body Effects on Human Body Damage (chemical change) Cells Human DNA Repair enzyme Body Incomplete repair Repair succeeded Repair failed Mutation No hazard Cell death or cell degeneration Possibility of causing cancer Possibility of causing acute and hereditary effects effects and fetal effects
Mechanism of Causing Radiation Damage to DNA Effects on Human Body Radiation Damage per 1 mGy of X‐rays Damage per 1 mGy of X‐rays Cell (per cell) (per cell) DNA Nucleus Base damage 2.5 locations Single‐strand break 1 location Damage Double‐strand 0.04 locations breaks Radiation DNA Source: Morgan, Annual Meeting of the National Committee on Radiation Protection and Measurements (NCRP) (44th, 2008)
Mechanism of Causing Lapse of Time after Exposure and Effects Effects on Human Body One‐thousandth of a Physical process second after irradiation Time Biochemical process Year Biological process Clinical process Mutation Stochastic effects Cancer Hereditary effects Cell death or cell degeneration Deterministic effects Acute radiation syndromes Fetal effects Cataract
Mechanism of Causing Deterministic Effects Effects on Human Body Amount of Damaged Dead cells radiation cells Repaired cells No effects Temporary dysfunction ⇒ Recovery afterward There is the threshold dose for deterministic effects. Normal cells Loss of functions Morphological defects Permanent damage
Mechanism of Causing Radiosensitivity of Organs and Tissues Effects on Human Body Active cell division High sensitivity Hematopoietic system : Bone marrow and lymphatic tissues (spleen, thymus gland, lymph node) Reproductive system : Testis and ovary Gastrointestinal system : Mucous membrane and small‐intestinal villus Epidermis and eyes : Hair follicle, sweat gland, skin and lens Other : Lung, kidney, liver and thyroid gland Support system : Blood vessel, muscle and bone Transmission system : nerve No cell division Low sensitivity
Mechanism of Causing Stochastic Effects Effects on Human Body Radiation Cancer cell Proliferation Repair and elimination Normal cells Incidence of cancer Stochastic effects There is no threshold dose for stochastic effects Cancer and leukemia (assumption). Hereditary effects
Recommend
More recommend