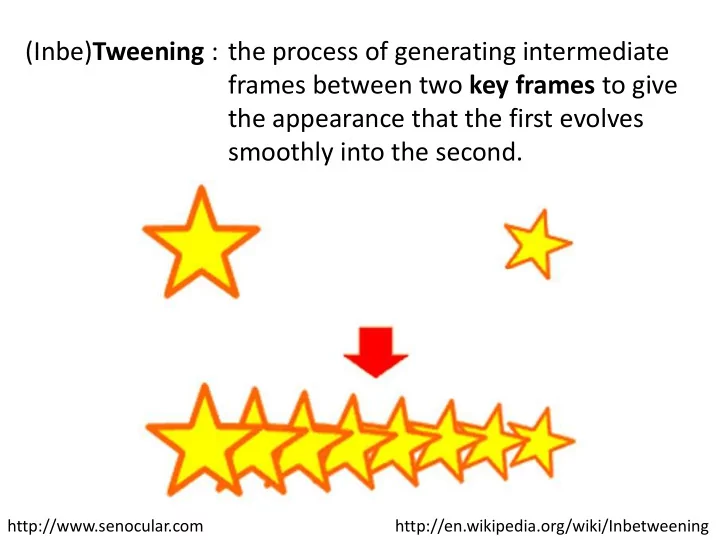

(Inbe) Tweening : the process of generating intermediate frames between two key frames to give the appearance that the first evolves smoothly into the second. http://www.senocular.com http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inbetweening
Easing Functions : Mathematical functions used by tweening algorithms to calculate property values at time points between key frames Ease-in : The gradual shift of a tweened property from a stationary value to full animation Ease-out : The gradual shift of a tweened property from full animation to a stationary value. Easing can be applied to any numeric property - x, y position - width, height - fill and line colors - line width … Easing.pde
Ease-in Functions N Value Time Ease-in 1 0.8 Fractional Value Change 0.6 Linear (N=1) Quadratic (N=2) Cubic (N=3) 0.4 Quartic (N=4) Quintic (N=5) 0.2 0 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1 Normalized Time EaseInRace.pde
Ease-out Functions N Value 1 ( 1 Time ) Ease-out 1 0.8 Fractonal Value Change 0.6 Linear (N=1) Quadratic (N=2) Qubic (N=3) 0.4 Quartic (N=4) Quintic (N=5) 0.2 0 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1 Normalized Time EaseOutRace.pde
Ease-in + Ease-out • First half – Scaled Ease in • Second half – Scaled and translated Ease out Ease-in + Ease-out 1 0.8 Fractional Value Change 0.6 Linear Quadratic Qubic 0.4 Quartic Quintic 0.2 0 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 Normalized Time EaseInOutRace.pde
Many other types of easing functions – Sinusoidal Easing – Exponential Easing – Circular Easing – Oscillatory Easing (passes target and returns)
Robert Penner's Easing Website – Sample chapter on easing http://www.robertpenner.com/easing/easing_demo.html
Implementing Easing in Processing 1. Develop Bullseye class and draw // BullsEye // Draw BullsEye void draw() { class BullsEye { pushMatrix(); float X; translate(X, Y); float Y; scale(0.5,0.5); stroke(0); BullsEye(float _X, float _Y) ellipseMode(CENTER); { fill(0); X = _X; ellipse(0,0,105,105); Y = _Y; fill(255,0,0); } ellipse(0,0,100,100); fill(255); ellipse(0,0,80,80); fill(255,0,0); ellipse(0,0,60,60); fill(255); ellipse(0,0,40,40); fill(0); noStroke(); ellipse(0,0,20,20); popMatrix(); } } Easing1.pde
// Easing1 BullsEye be; void setup() { size(500, 500); smooth(); be = new BullsEye(250, 250); } void draw() { background(255); be.draw(); } void mousePressed() { be.X = mouseX; be.Y = mouseY; } Easing1.pde
Implementing Easing in Processing 2. Build Linear Easing into BullsEye // BullsEye // Incrememt location class BullsEye { float next() { float X; float nextV; float Y; // Increment ease step // Parameters for easing currentStep++; float startV; float deltaV; // Only ease within step range float nSteps; if (currentStep > nSteps) float currentStep = 0.0; { boolean easing = false; currentStep = nSteps; nextV = startV + deltaV; BullsEye(float _X, float _Y) { easing = false; X = _X; currentStep = 0; Y = _Y; } } else { float fracT = currentStep/nSteps; nextV = startV + deltaV * fracT; } return nextV; } Easing2.pde
Implementing Easing in Processing 2. Build Linear Easing into BullsEye (2) // Easing2 BullsEye be; void setup() { size(500, 500); smooth(); be = new BullsEye(250, 250); } void draw() { background(255); if (be.easing) be.X = be.next(); be.draw(); } void mousePressed() { be.startV = be.X; be.deltaV = mouseX-be.X; be.nSteps = 50; be.easing = true; } Easing2.pde
Implementing Easing in Processing 3. Extract easing behavior into an Ease class // Class encapsulating easing behavior class Ease { // Incrememt location float startV; float next() { float deltaV; float nextV; float nSteps; float currentStep = 0.0; // Increment ease step currentStep++; Ease(float _startV, float _endV, // Only ease within step range float _nSteps) { if (currentStep > nSteps) startV = _startV; { deltaV = _endV - _startV; currentStep = nSteps; nSteps = _nSteps; nextV = startV + deltaV; } } else { float calcEase(float fracT) { float fracT = currentStep/nSteps; return fracT; nextV = startV + deltaV*calcEase(fracT); } } return nextV; } Easing3.pde
Implementing Easing in Processing 3. Extract easing behavior into an Ease class (2) // Easing3 // BullsEye BullsEye be; class BullsEye { float X; void setup() float Y; { size(500, 500); // Position easing objects smooth(); Ease easeX = null; be = new BullsEye(250, 250); Ease easeY = null; } BullsEye(float _X, float _Y) { void draw() { X = _X; background(255); Y = _Y; be.next(); } be.draw(); } // Increment Easing, // if an Ease object is specified void mousePressed() { void next() { // Set easing in on mouse pressed if (easeX != null) X = easeX.next(); be.easeX = new Ease(be.X, mouseX, 50); if (easeY != null) Y = easeY.next(); be.easeY = new Ease(be.Y, mouseY, 50); } } … Now, both X and Y (or any field) can be eased Easing3.pde
Implementing Easing in Processing 4. Create new kinds of Easing classes // Class encapsulating quadratic easing class QuadEaseIn { // Incrememt location float startV; float next() { float deltaV; float nextV; float nSteps; float currentStep = 0.0; // Increment ease step currentStep++; QuadEaseIn(float _startV, float _endV, // Only ease within step range float _nSteps) { if (currentStep > nSteps) startV = _startV; { deltaV = _endV - _startV; currentStep = nSteps; nSteps = _nSteps; nextV = startV + deltaV; } } else { float calcEase(float fracT) { float fracT = currentStep/nSteps; return pow(fracT, 2); nextV = startV + deltaV*calcEase(fracT); } } The only difference between Ease return nextV; } and QuadEaseIn is the name and part of the easing function Easing4.pde
Implementing Easing in Processing 4. Create new kinds of Easing classes (2) // BullsEye // Easing3 class BullsEye { BullsEye be; float X; float Y; void setup() { // Position easing objects size(500, 500); QuadEaseIn easeX = null; smooth(); QuadEaseIn easeY = null; be = new BullsEye(250, 250); } BullsEye(float _X, float _Y) { X = _X; Y = _Y; } void draw() { background(255); // Increment Easing, be.next(); // if an Ease object is specified be.draw(); void next() { } if (easeX != null) X = easeX.next(); if (easeY != null) Y = easeY.next(); } … void mousePressed() { // Set easing in on mouse pressed be.easeX = new QuadEaseIn (be.X, mouseX, 50); be.easeY = new QuadEaseIn (be.Y, mouseY, 50); } Easing4.pde
• In fact, if we want to change the easing behavior of the BullsEye class, we have to edit its source code every time! • There has to be a better way … … Hold that thought …
Object Oriented Programming – Encapsulation • Classes encapsulate state (fields) and behavior (methods) – Polymorphism • Signature Polymorphism – Overloading • Subtype Polymorphism – Inheritance
Creating a set of Graphic Object Classes • All have… • X, Y location • width and height fields • fill and stroke colors • A draw() method • A next() method defining how they move • … • Implementation varies from class to class
Creating a set of Graphic Object Classes • Problems How would you hold all your objects? – Array? – ArrayList or HashMap? What if one class had extra methods or special arguments? Sometimes you want to think of an object as a generic Graphic (X,Y location and draw() method) Sometimes you want to think of an object as a specific type (extra methods, extra fields, …)
Graphic Object Hierarchy X,Y fields Graphic draw() method … More Specific More General Rectangle Ellipse Arc Curve Shape diameter Square Circle Inheritance gives you a way to relate your objects in a hierarchical manner
Inheritance • Superclass (base class) – higher in the hierarchy • Subclass (child class) – lower in the hierarchy • A subclass is derived from from a superclass • Subclasses inherit the fields and methods of their superclass. – I.e. subclasses automatically "get" stuff in superclasses • Subclasses can override a superclass method by redefining it. – They can replace anything by redefining locally
// Ellipse base class // Circle derived class class Ellipse { class Circle extends Ellipse { Circle(float X, float Y, float D) { float X; float Y; super (X, Y, D, D); float W; float H; // Circles are always blue fillColor = color(0,255,0); } // Ellipses are always red color fillColor = } color(255,0,0); • The extends keyword creates Ellipse(float X, float Y, hierarchical relationship between float W, float H) classes. { this .X = X; • The Circle class gets all fields and this .Y = Y; methods of the Ellipse class, this .W = W; this .H = H; automatically. } • The super keyword refers to the base void draw() { class in the relationship. ellipseMode(CENTER); • The this keyword refers to the object fill(fillColor); ellipse(X, Y, W, H); itself. } } Graphics.pde
// Graphics Ellipse e = new Ellipse(150, 250, 150, 50); Circle c = new Circle(350, 250, 75); void setup() { size(500, 500); smooth(); } void draw() { e.draw(); c.draw(); } Graphics.pde
Recommend
More recommend