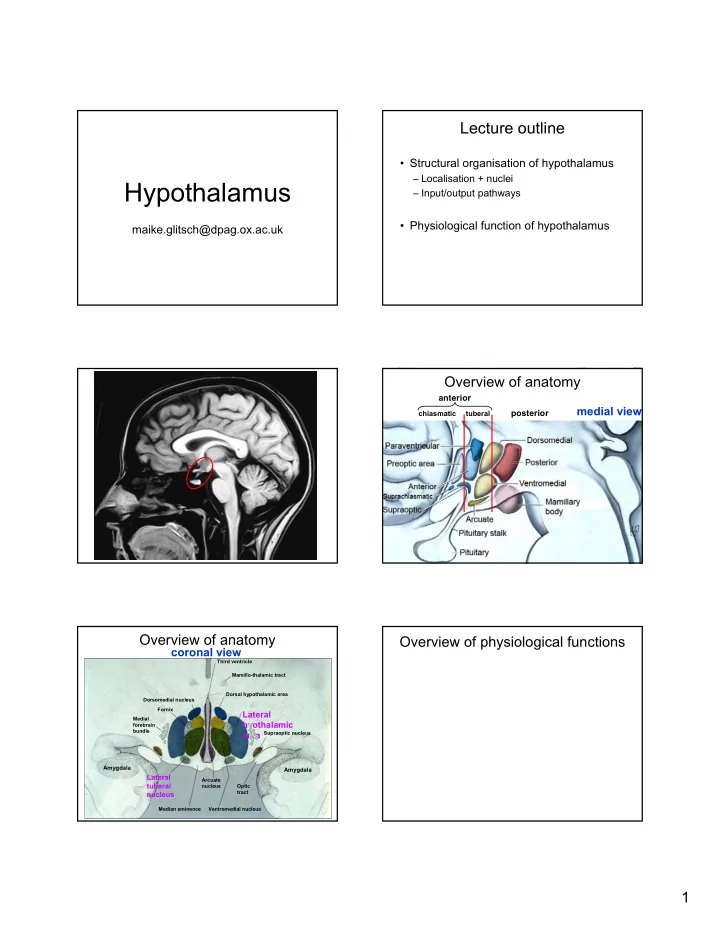

Lecture outline • Structural organisation of hypothalamus – Localisation + nuclei Hypothalamus – Input/output pathways • Physiological function of hypothalamus maike.glitsch@dpag.ox.ac.uk Overview of anatomy anterior medial view posterior chiasmatic tuberal Overview of anatomy Overview of physiological functions coronal view Third ventricle Mamillo-thalamic tract Dorsal hypothalamic area Dorsomedial nucleus Fornix Lateral Medial hyothalamic forebrain bundle area Supraoptic nucleus Amygdala Amygdala Lateral Arcuate tuberal nucleus Optic tract nucleus Median eminence Ventromedial nucleus 1
Overview of physiological functions Overview of physiological functions • Maintenance of milieu interne • Maintenance of milieu interne • Behaviour • Behaviour • Memory • Memory � Regulation of energy metabolism (food intake, metabolic � Regulation of energy metabolism (food intake, metabolic rate, temperature regulation, growth) rate, temperature regulation, growth) � Reproductive function (including milk production, social � Reproductive function (including milk production, social interactions) interactions) � Biological clock, sleep-wake cycles � Biological clock (sleep-wake cycles) � Control of blood flow (cardiac output, blood osmolarity � Control of blood flow (cardiac output, blood osmolarity and renal clearance, thirst regulation) and renal clearance, thirst regulation) Overview of physiological functions Overview of physiological functions • Detection of (changes in) � Regulation of the autonomic nervous system � Blood osmolarity � Blood nutrient levels � Release of hormones � Blood hormone levels Hypothalamic neurons can release hormones (neuro-endocrine) � Body temperature � Directly and indirectly Overview of connections Overview of connections • Output to • Input from � Thalamus (via mammillothalamic tract ( Papez circuit: cingulate � Retina (retinohypothalamic tract – terminates in SCN) gyrus – hippocampal formation – mammillary bodies – anterior thalamic nucleus – cingulate gyrus) ) � Olfactory receptors (medial forebrain bundle) (also mammillotegmental tract to midbrain tegmentum) � Amygdala (from medial hypothalamus) � Cutaneous receptors � Midbrain PAG (from medial hypothalamus) (aggression, rage, � Higher (limbic) system (hippocampal formation: fornix – to flight) mammillary bodies; amygdala: stria terminalis – to medial � Frontal and parietal lobes, habenular nucleus, midbrain… hypothalamus) � Blood stream (pituitary) � Viscera 2
Overview of basic functions Overview of basic functions • Feed-back system • Feed-back system • Feed-forward system – Hypothalamus corrects – Hypothalamus corrects – Hypothalamus can over- deviations from a given deviations from a given ride feed-back under set-point: set-point: special conditions • measures current value • measures current value • Stress responses • compares current value • compares current value • Fever (body T set point is with supposed value with supposed value changed to higher T) • makes adjustments to • makes adjustments to achieve supposed value achieve supposed value – helps maintain body – helps maintain body homeostasis homeostasis Overview of basic functions • Feed-back system • Feed-forward system • Look at neuroendocrine functions of – Hypothalamus corrects – Hypothalamus can over- deviations from a given ride feed-back under hypothalamus set-point: special conditions • measures current value • Stress responses • compares current value • Fever (body T set point is with supposed value changed to higher T) • Look at regulation of non-endocrine • makes adjustments to • Anticipation achieve supposed value functions (ANS) of hypothalamus – helps maintain body – Hypothalamus adjusts homeostasis its output to meet future needs • Insulin secretion prior to food intake Neuroendocrine hypothalamus Neuroendocrine hypothalamus • Via anterior pituitary • Hypothalamic neurons can act as neuroendocrine (adenohypophysis) cells – Hypothalamic parvocellular neurons release releasing or • Neurotransmitter = (neuro)hormone is released inhibiting hormones into hypothalamo-pituitary portal directly into blood stream veins – Hypothalmo-pituitary portal • Site of hormone release is pituitary gland veins carry these hormones to anterior pituitary • 2 principal pathways for eliciting hormone release: – Anterior pituitary has cells responding to the different releasing or inhibiting – Via the anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis) hormones • 2-tiers process – Responsive cells release or stop releasing hormones in response to binding of – Via the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) hypothalamic releasing or inhibiting hormones into • 1-step process systemic circulation 3
Neuroendocrine hypothalamus Neuroendocrine hypothalamus • Via anterior pituitary • Via anterior pituitary Hypothalamus Hypothalamus (adenohypophysis) (adenohypophysis) – Hypothalamic parvocellular – Hypothalamic parvocellular neurons secrete releasing or neurons secrete releasing or inhibiting hormones into inhibiting hormones into R I R I hypothalamo-pituitary portal hypothalamo-pituitary portal veins veins – Hypothalmo-pituitary portal – Hypothalamo-pituitary portal veins carry these hormones to veins carry these hormones to anterior pituitary anterior pituitary – Anterior pituitary has cells – Anterior pituitary has cells responding to the different responding to the different releasing or inhibiting releasing or inhibiting hormones hormones Anterior Anterior – Responsive cells release or – Responsive cells release or stop releasing hormones in stop releasing hormones in Pituitary Pituitary response to binding of response to binding of hypothalamic releasing or hypothalamic releasing or inhibiting hormones into inhibiting hormones into systemic circulation systemic circulation Neuroendocrine hypothalamus Neuroendocrine hypothalamus • Via anterior pituitary • Via anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis) Hypothalamus (adenohypophysis) Hypothalamus – Hypothalamic parvocellular – Hypothalamic parvocellular neurons secrete releasing or neurons secrete releasing or inhibiting hormones into inhibiting hormones into R I R I hypothalamo-pituitary portal hypothalamo-pituitary portal veins veins – Hypothalamo-pituitary portal – Hypothalamo-pituitary portal veins carry these hormones to veins carry these hormones to anterior pituitary anterior pituitary – Anterior pituitary has cells – Anterior pituitary has cells responding to the different responding to the different releasing or inhibiting releasing or inhibiting hormones hormones Anterior Anterior – Responsive cells release or – Responsive cells secrete or stop releasing hormones in stop secreting hormones in Pituitary Pituitary response to binding of response to binding of hypothalamic releasing or hypothalamic releasing or inhibiting hormones into inhibiting hormones into systemic circulation systemic circulation Rel./Inhib. Rel./Inhib. Ant. Pit. hormone: hormone: target cell: GnRH gonadotrope FSH+LH gonads GnRH gonadotrope FSH+LH gonads CRH corticotrope ACTH CRH corticotrope ACTH TRH thyrotrope TSH thyroid TRH thyrotrope TSH thyroid GHRH somatotrope GH GHRH somatotrope GH Sost somatotrope GH Sost somatotrope GH DA lactotrope prolactin DA lactotrope prolactin 4
Recommend
More recommend