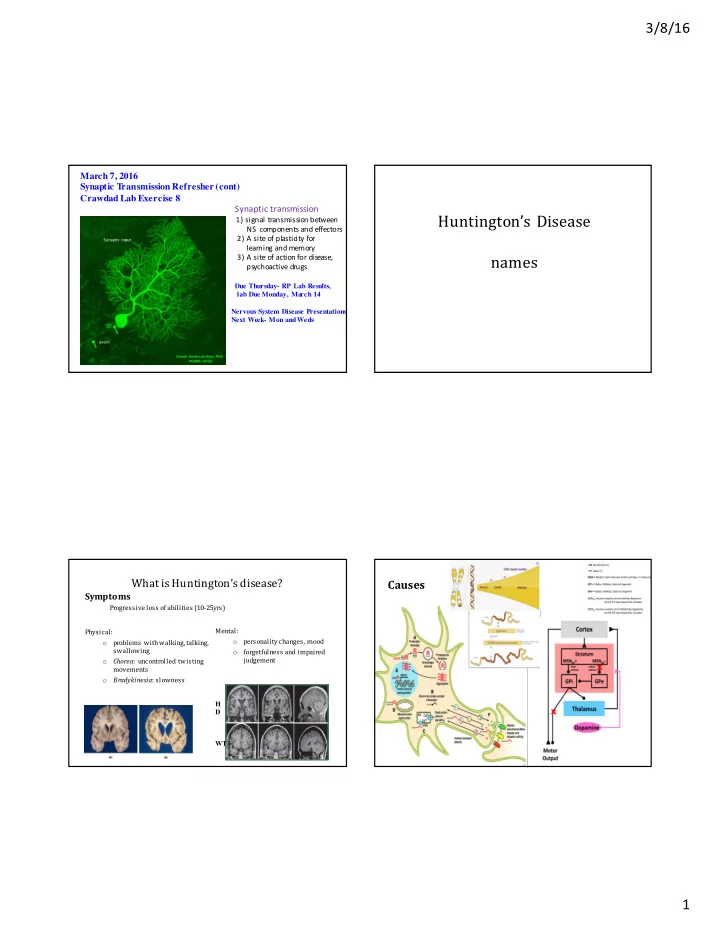

3/8/16 March 7, 2016 Synaptic T ransmission Refresher (cont) Crawdad Lab Exercise 8 Synaptic ¡transmission Huntington’s ¡Disease 1) ¡signal ¡transmission ¡between NS ¡ ¡components ¡and ¡effectors 2) ¡A ¡site ¡of ¡plasticity ¡for Synaptic ¡input learning ¡and ¡memory 3) ¡A ¡site ¡of ¡action ¡for ¡disease, names psychoactive ¡drugs Due Thursday- RP Lab Results, lab Due Monday, Ma rch 14 Nervous System Disease Presentations Next Week- Mon and Weds axon! What ¡is ¡Huntington’s ¡disease? Causes Symptoms Progressive ¡loss ¡of ¡abilities ¡(10-‐‒25yrs) Mental: Physical: personality ¡changes, ¡mood problems ¡with ¡walking, ¡talking, ¡ o o swallowing forgetfulness ¡and ¡impaired ¡ o judgement Chorea : ¡uncontrolled ¡twisting ¡ o X movements Bradykinesia : ¡slowness ¡ o H D X WT 1
3/8/16 Multiple ¡Sclerosis ¡(MS) H D Treatment Symptoms • No ¡cure • Support ¡ groups ¡and ¡therapy: WT speech, ¡physical, ¡occupational • Medications ¡to ¡reduce ¡Chorea: -‐‒ tetrabenazine ¡(2008) -‐‒ dopamine ¡blockers • gene ¡therapy Treatments ¡ for ¡MS ¡ ¡ Disease ¡ • Currently ¡not ¡curable Pathology • High-‑dose ¡corticosteroids – Reduce ¡inflammation ¡in ¡CNS ¡(exacerbations) • Disease-‑Modifying ¡Medication ¡ – Suppress ¡the ¡immune ¡system – Prevent ¡immune ¡cells ¡from ¡getting ¡into ¡the ¡brain • Rehabilitation ¡ – Help ¡patients ¡maintain ¡functions • Emotional ¡support 2
3/8/16 Sim5-‑ Neuromuscular ¡ Junction Crawdad ¡labs ¡8 ¡and ¡9 Crayfish ¡NMJ ¡as ¡a ¡model ¡for ¡human ¡brain ¡fast ¡synapses Neuromuscular ¡Innervation Uni-‑terminal Multi-‑terminal Uni-‑neuronal Poly-‑neuronal Excitation ¡ Only Inhibition Often ¡ no ¡APs Mammals Arthropods See ¡Synapse ¡Tutorial ¡on ¡class ¡web ¡site ¡for ¡review Steps ¡in ¡ionotropic chemical ¡synaptic ¡ Crayfish ¡NMJ ¡preparation transmission 1 Lab ¡8 ¡focuses on ¡2 ¡steps-‑ 2 3
3/8/16 Lab ¡8-‑ Synaptic ¡Inhibition 2 1 Map ¡Muscle ¡Innervation ¡Patterns Quantal nature ¡of ¡transmitter ¡release (Also ¡better ¡ distinguish ¡number ¡of ¡axons ¡in ¡nerve ¡3 ) Record ¡spontaneous ¡transmitter ¡release Synaptic ¡Integration-‑ Activate ¡tail ¡input “ Minis ” Synapse ¡tutorial MEPPs, ¡page ¡11, ¡12 4
3/8/16 Record ¡evoked ¡transmitter ¡release Spontaneous ¡“mini” ¡and ¡evoked ¡potentials-‑quantal steps Reduce ¡[Ca] o Quantal content: ¡m ¡= ¡mean ¡EPP/mean ¡MEPP Normally ¡around ¡300 ¡quanta ¡at ¡NMJ/AP (could ¡be ¡only ¡a ¡few ¡at ¡central ¡synapses) Physical ¡evidence ¡for ¡vesicle ¡fusion ¡for ¡transmitter ¡release Spontaneous ¡“mini” ¡synaptic ¡potentials Quantal hypothesis ¡of 4-‑AP ¡broadens ¡presynaptic ¡AP transmitter ¡releas e Post ¡synaptic ¡depolarization ¡ results ¡from ¡the ¡coordinated ¡ release ¡of ¡transmitter ¡packets ¡ (quanta) ¡from ¡the ¡vesicles as ¡the ¡AP ¡enters ¡the ¡terminal 5
3/8/16 Squid ¡giant ¡synapse ¡as ¡a ¡ Presynaptic ¡axon model ¡system giant ¡axon ~1 ¡mm Note ¡“omega” ¡figure Fusion ¡of ¡vesicles to ¡membrane EPSP Ca ++ channels George ¡Augustine, ¡Marine ¡ Biological ¡Laboratory, ¡2008 Technical ¡help-‑ Bruce ¡Johnson Block ¡transmitter ¡release ¡with ¡presynaptic ¡Ca buffer ¡or ¡Cadium Presynaptic Ca ¡injection ¡causes transmitter ¡release ¡and ¡Ca ¡indicator ¡dye shows ¡presynaptic Ca ¡entry Synapse ¡tutorial p. ¡17, ¡19 6
3/8/16 Any ¡depolarization ¡will ¡cause ¡transmitter ¡release, ¡even ¡high ¡Kout-‑ triggers ¡opening ¡of ¡voltage-‑gated ¡Ca ¡channels What ¡is ¡the ¡role ¡of ¡the ¡AP ¡in ¡ transmitter ¡release? Synapse ¡tutorial provides ¡ trigger ¡and ¡timing for ¡calcium ¡entry p. ¡21 7
Recommend
More recommend