Graphs Carola Wenk Slides courtesy of Charles Leiserson with - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
CMPS 6610/4610 Fall 2016 Graphs Carola Wenk Slides courtesy of Charles Leiserson with changes and additions by Carola Wenk CMPS 6610/4610 Fall 2016 1 Graphs Definition. A directed graph ( digraph ) G = ( V , E ) is an ordered pair
CMPS 6610/4610 – Fall 2016 Graphs Carola Wenk Slides courtesy of Charles Leiserson with changes and additions by Carola Wenk CMPS 6610/4610 – Fall 2016 1
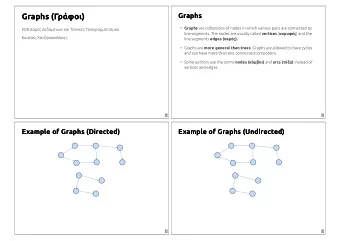
Graphs Definition. A directed graph ( digraph ) G = ( V , E ) is an ordered pair consisting of • a set V of vertices (singular: vertex ), • a set E V V of edges . In an undirected graph G = ( V , E ), the edge set E consists of unordered pairs of vertices. undirected graph directed graph 2 1 2 1 3 4 3 4 In either case, we have | E | = O (| V| 2 ). Moreover, if G is connected, then | E | | V | – 1. CMPS 6610/4610 – Fall 2016 2
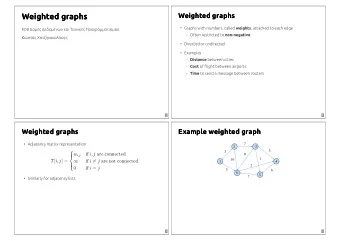
Adjacency-matrix representation The adjacency matrix of a graph G = ( V , E ), where V = {1, 2, …, n }, is the matrix A [1 . . n , 1 . . n ] given by 1 if ( i , j ) E, A [ i , j ] = 0 if ( i , j ) E. A 1 2 3 4 (| V| 2 ) storage 2 1 1 0 1 1 0 dense 2 0 0 1 0 representation. 3 0 0 0 0 3 4 4 0 0 1 1 CMPS 6610/4610 – Fall 2016 3
Adjacency-list representation An adjacency list of a vertex v V is the list Adj [ v ] of vertices adjacent to v . Adj [1] = {2, 3} 2 1 Adj [2] = {3} Adj [3] = {} 3 4 Adj [4] = {3, 4} For undirected graphs, | Adj [ v ] | = degree ( v ). For digraphs, | Adj [ v ] | = out-degree ( v ). CMPS 6610/4610 – Fall 2016 4
Adjacency-list representation Handshaking Lemma: Every edge is counted twice • For undirected graphs: v V degree(v) = 2 | E | • For digraphs: v V in-degree(v) = v V out-degree(v) = | E | adjacency lists use (| V| + |E| ) storage a sparse representation We usually use this representation, unless stated otherwise CMPS 6610/4610 – Fall 2016 5
Graph Traversal Let G =( V , E ) be a (directed or undirected) graph, given in adjacency list representation. | V | = n , | E | = m A graph traversal visits every vertex: • Breadth-first search (BFS) • Depth-first search (DFS) CMPS 6610/4610 – Fall 2016 6
Breadth-First Search (BFS) BFS( G= ( V,E )) Mark all vertices in G as “unvisited” // time=0 Initialize empty queue Q for each vertex v V do if v is unvisited visit v // time++ BFS_iter( G ) Q .enqueue( v ) while Q is non-empty do BFS_iter( G ) v = Q .dequeue() for each w adjacent to v do if w is unvisited visit w // time++ Add edge ( v , w ) to T Q .enqueue( w ) CMPS 6610/4610 – Fall 2016 7
Example of breadth-first search while Q is non-empty do v = Q .dequeue() for each w adjacent to v do if w is unvisited visit w // time++ Add edge ( v , w ) to T a i h Q .enqueue( w ) d b f e g c Q : CMPS 6610/4610 – Fall 2016 8
Example of breadth-first search while Q is non-empty do v = Q .dequeue() for each w adjacent to v do if w is unvisited visit w // time++ Add edge ( v , w ) to T a i h 0 Q .enqueue( w ) d b f e g c 0 Q: a CMPS 6610/4610 – Fall 2016 9
Example of breadth-first search while Q is non-empty do v = Q .dequeue() for each w adjacent to v do if w is unvisited visit w // time++ Add edge ( v , w ) to T a i h 0 Q .enqueue( w ) 2 d b f 1 e g c 1 2 Q: a b d CMPS 6610/4610 – Fall 2016 10
Example of breadth-first search while Q is non-empty do v = Q .dequeue() for each w adjacent to v do if w is unvisited visit w // time++ Add edge ( v , w ) to T a i h 0 Q .enqueue( w ) 2 d b f 1 e g c 4 3 2 3 4 Q: a b d c e CMPS 6610/4610 – Fall 2016 11
Example of breadth-first search while Q is non-empty do v = Q .dequeue() for each w adjacent to v do if w is unvisited visit w // time++ Add edge ( v , w ) to T a i h 0 Q .enqueue( w ) 2 d b f 1 e g c 4 3 3 4 Q: a b d c e CMPS 6610/4610 – Fall 2016 12
Example of breadth-first search while Q is non-empty do v = Q .dequeue() for each w adjacent to v do if w is unvisited visit w // time++ Add edge ( v , w ) to T a i h 0 Q .enqueue( w ) 2 d b f 1 e g c 4 3 4 Q: a b d c e CMPS 6610/4610 – Fall 2016 13
Example of breadth-first search while Q is non-empty do v = Q .dequeue() for each w adjacent to v do if w is unvisited visit w // time++ Add edge ( v , w ) to T a i h 0 Q .enqueue( w ) 2 d 5 b f 1 e g c 4 6 3 5 6 Q: a b d c e f g CMPS 6610/4610 – Fall 2016 14
Example of breadth-first search while Q is non-empty do v = Q .dequeue() for each w adjacent to v do if w is unvisited 7 visit w // time++ Add edge ( v , w ) to T a i h 0 Q .enqueue( w ) 2 d 5 b f 1 e g c 4 6 3 6 7 Q: a b d c e f g i CMPS 6610/4610 – Fall 2016 15
Example of breadth-first search while Q is non-empty do v = Q .dequeue() for each w adjacent to v do if w is unvisited 7 8 visit w // time++ Add edge ( v , w ) to T a i h 0 Q .enqueue( w ) 2 d a a 5 b f 1 e g c 4 6 3 7 8 Q: a b d c e f g i h CMPS 6610/4610 – Fall 2016 16
Example of breadth-first search while Q is non-empty do v = Q .dequeue() for each w adjacent to v do if w is unvisited 7 8 visit w // time++ Add edge ( v , w ) to T a i h 0 Q .enqueue( w ) 2 d a a 5 b f 1 e g c 4 6 3 8 Q: a b d c e f g i h CMPS 6610/4610 – Fall 2016 17
Example of breadth-first search while Q is non-empty do v = Q .dequeue() for each w adjacent to v do if w is unvisited 7 8 visit w // time++ Add edge ( v , w ) to T a i h 0 Q .enqueue( w ) 2 d a a 5 b f 1 e g c 4 6 3 Q: a b d c e f g i h CMPS 6610/4610 – Fall 2016 18
Example of breadth-first search while Q is non-empty do v = Q .dequeue() for each w adjacent to v do if w is unvisited 7 8 visit w // time++ Distance Add edge ( v , w ) to T a i h 0 to a : Q .enqueue( w ) 2 0 d a a 5 b f 1 1 e g c 4 6 3 2 3 4 Q: a b d c e f g i h CMPS 6610/4610 – Fall 2016 19
Breadth-First Search (BFS) BFS( G= ( V,E )) Mark all vertices in G as “unvisited” // time=0 O( n ) Initialize empty queue Q O(1) for each vertex v V do if v is unvisited O( n ) visit v // time++ BFS_iter( G ) without Q .enqueue( v ) while Q is non-empty do BFS_iter BFS_iter( G ) v = Q .dequeue() for each w adjacent to v do if w is unvisited O( m ) visit w // time++ O( deg ( v )) Add edge ( v , w ) to T Q .enqueue( w ) CMPS 6610/4610 – Fall 2016 20
BFS runtime • Each vertex is marked as unvisited in the beginning O( n ) time • Each vertex is marked at most once, enqueued at most once, and therefore dequeued at most once • The time to process a vertex is proportional to the size of its adjacency list (its degree), since the graph is given in adjacency list representation O( m ) time • Total runtime is O( n + m ) = O(|V| + |E|) CMPS 6610/4610 – Fall 2016 21
Depth-First Search (DFS) DFS( G= ( V,E )) Mark all vertices in G as “unvisited” // time=0 for each vertex v V do if v is unvisited DFS_rec( G , v ) DFS_rec( G, v ) mark v as “visited” // d [ v ]=++time for each w adjacent to v do if w is unvisited Add edge ( v , w ) to tree T DFS_rec( G , w ) mark v as “finished” // f [ v ]=++time CMPS 6610/4610 – Fall 2016 22
Example of depth-first search d / f 0/- a a i h d b f e g c DFS_rec( G, v ) mark v as “visited” // d [ v ]=++time : a b c d e f g h i for each w adjacent to v do if w is unvisited a Add edge ( v , w ) to tree T - DFS_rec( G , w ) Store edges in predecessor array mark v as “finished” // f [ v ]=++time CMPS 6610/4610 – Fall 2016 23
Example of depth-first search d / f 0/- a i h d 1/- b f e g c DFS_rec( G, v ) mark v as “visited” // d [ v ]=++time : a b c d e f g h i for each w adjacent to v do if w is unvisited a Add edge ( v , w ) to tree T - b DFS_rec( G , w ) Store edges in predecessor array mark v as “finished” // f [ v ]=++time CMPS 6610/4610 – Fall 2016 24
Example of depth-first search d / f 0/- a i h d 1/- b f e g 2/- 2/3 c DFS_rec( G, v ) mark v as “visited” // d [ v ]=++time : a b c d e f g h i for each w adjacent to v do if w is unvisited a Add edge ( v , w ) to tree T - b DFS_rec( G , w ) Store edges in predecessor array mark v as “finished” // f [ v ]=++time CMPS 6610/4610 – Fall 2016 25
Example of depth-first search d / f 0/- a i h d 1/- b f e g 2/3 c DFS_rec( G, v ) mark v as “visited” // d [ v ]=++time : a b c d e f g h i for each w adjacent to v do if w is unvisited a Add edge ( v , w ) to tree T - b b DFS_rec( G , w ) Store edges in predecessor array mark v as “finished” // f [ v ]=++time CMPS 6610/4610 – Fall 2016 26
Example of depth-first search d / f 0/- a i h d 1/- b f e g 4/- 2/3 c DFS_rec( G, v ) mark v as “visited” // d [ v ]=++time : a b c d e f g h i for each w adjacent to v do if w is unvisited a b e Add edge ( v , w ) to tree T - b DFS_rec( G , w ) Store edges in predecessor array mark v as “finished” // f [ v ]=++time CMPS 6610/4610 – Fall 2016 27
Example of depth-first search d / f 0/- a i h d 5/- 1/- b f e g 4/- 2/3 c DFS_rec( G, v ) mark v as “visited” // d [ v ]=++time : a b c d e f g h i for each w adjacent to v do if w is unvisited a e f Add edge ( v , w ) to tree T - b b DFS_rec( G , w ) Store edges in predecessor array mark v as “finished” // f [ v ]=++time CMPS 6610/4610 – Fall 2016 28
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.