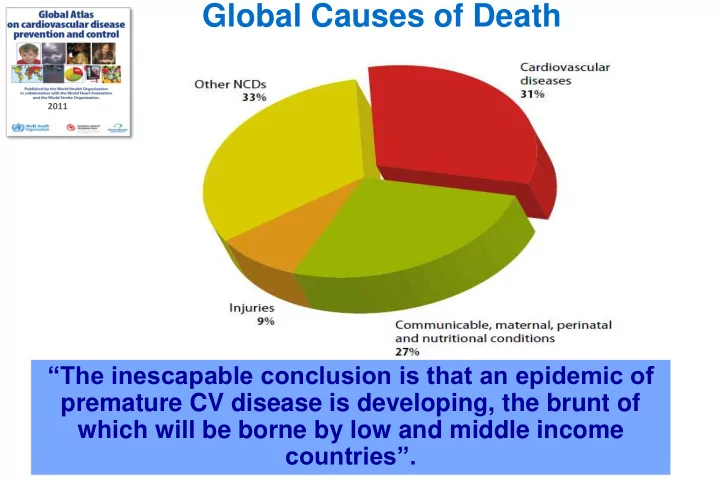

Global Causes of Death 2011 “The inescapable conclusion is that an epidemic of • NCDs cause 64% (35 million) of global deaths • 80% (28 million) are in LMICs premature CV disease is developing, the brunt of • NCDs will cost the world $47 trillion over the next 20 years which will be borne by low and middle income • CVD is responsible for around one third of all deaths worldwide countries”.
CVD Prevention Opportunity! Genetic Environmental Clinical Events Age (yrs) Fetus 0 20 40 60
Forecasting Future CVD in USA 900 800 700 600 Billions $ 500 400 300 >20% of cost of car from 200 staff health insurance Indirect Direct 100 0 2026 2024 2010 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2025 2027 2029 2030 2011 2028 Heidenreich Circ 2011; 123: 933-944
Most of us have Arterial Disease! 100 85% Atherosclerosis (%) 80 71% 60% 60 37% 40 17% 20 0 <20 20-29 30-39 40-49 ≥50 32 Year Old Female Age (years) Tuzcu Circ 2001 103:2075-10
CV Risk Factors in Childhood and Carotid IMT in Adults Risk factors measured at ages 12-18yrs No. of risk factors 0 1 2 3 or 4 Mean maximum carotid P<0.001 P<0.001 0.88 IMT (mm) 0.80 0.72 0.64 0.56 0.48 Men Women Raitakari et al JAMA 2003;290;2277-2283
Framingham Heart Study :Lifetime Risk Men Women 0.7 69% 0.7 ≥2 Major RFs Adjusted Cumulative Incidence 1 Major RF 0.6 0.6 ≥ Elevated RF ≥ Not Elevated RF All Optimal RFs 50% 50% 0.5 0.5 46% 0.4 0.4 39% 36% 0.3 0.3 27% 0.2 0.2 0.1 0.1 8% 5% 0 0 60 70 90 60 70 90 50 80 50 80 Attained Age Lloyd-Jones Circ. 2006; 113: 791-798
LDL Cholesterol and Coronary Heart Disease among Black Subjects by PCSK9 142X or PCSK9 679X Allele No Nonsense 12 Mutation Coronary Heart Disease (%) 50 th Percentile (n=3278) 30 P=0.008 Frequency (%) 20 8 88% 10 0 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 PCSK9 142X 4 or PCSK9 679X 28% (N=85) 30 20 0 No Yes 10 Use Genetics to evaluate long term exposure PCSK9 142X or PCSK9 679X 0 0 Compound interest from early management 50 100 150 200 250 300 Cohen NEJM 2006; 354:1264-72 LDL Cholesterol in Black Subjects (mg/dl )
Effect of Lifetime CV RF Exposure Study sample: 102,773 persons (age 27 - 100 years) enrolled in one of 14 prospective cohort or case-control studies LDL-C genetic score: 46 polymorphisms associated primarily with lower LDL-C at genome-wide level of significance SBP genetic score: 33 polymorphisms associated with lower SBP at genome-wide level of significance Genetic scores used as both the instrument of randomization and the instrument of exposure B. Ference (Plymouth, US), FP 3163 ESC 2016
Combined Effect of LDL-C and SBP on Cardiovascular Events N = 14,368 Major Vascular Events B. Ference (Plymouth, US), FP 3163
Effect of 1 mmol/L lower LDL-C & 10 mmHg lower SBP on Major Cardiovascular Events 0 0.25 0.75 0.50 1.00 SBP and LDL-C have independent, multiplicative and cumulative effects on CVD risk B. Ference (Plymouth, US), FP 3163
Hazards of Smoking and Benefits of Smoking Cessation 113,752 w and 88,496 m aged ≥25y in US NHIS Jha N Engl J Med 2013; 368: 341-50
Lifetime Atherosclerosis Management Treat to Lower Levels Treat multiple Risk Factors Start Earlier
CVD Prediction and Prevention Knowledge Communication Empowerment
ESC CV Prevention Guidelines 2012 Disenfranchises the Young, especially Women! European Heart Journal 2012; 33: 1635-1701
Short Term v. Lifetime Risk in USA Non-smoking men <45yrs All women <65yrs <10% 10yr CHD Risk Marma Circ 2009;120:384-390 56% of US adults (87,000,000) have low (<10%) 10yr and high lifetime (≥39%) risk Marma Circ Cardiothoracic Qual Outcomes 2010;3:8-14
New Cholesterol Guidelines to a Population-Based Sample 56 million people Mostly Elderly Men! Pencina NEJM 2014; 370: 1422-31
JBS3 Lifetime Risk Calculator • Understandable measures of risk • Personalised opportunities to benefit Heart March 2014 and www.jbs3risk.com
Impact of Heart Age Tool on Modifiable CVRFs 3153 subjects (47% male), Mean Age 46yrs, 12m FU 2 1.0 8 4 2.0 2.0 P<0.001 P<0.001 P<0.001 P<0.001 P<0.001 P<0.001 0.8 1 3 6 1.5 1.5 Systolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) 0.6 Total cholesterol (mg/dl) 4 2 1.0 1.0 0 Current smoking (%^) 0.4 Glucose (mg/dl) Heart Age (yrs) 1 2 0.5 0.5 Weight (kg) 0.2 -1 0.0 0 0 0.0 0.0 -2 -0.2 -2 -1 -0.5 -0.5 -0.4 -3 -2 -4 -1.0 -1.0 -0.6 -4 -0.8 -3 -6 -1.5 -1.5 -1.0 -5 -8 -4 -2.0 -2.0 Control FR Lopez-Gonzalez European Journal of Preventive Cardiology 2015: 22; 389 – 396 HA
Primary Prevention of CVD with Mediteranean Diet 7447 persons with High CV Risk (55-80yrs) 57% women Total Mortality CV Events Years Years Estruch N Engl J Med 2013; 368: 1279-90
Changes in Fruit, Vegetable and Whole Grains Intake * Significantly different from control group (p<0.05) Healthy shifts in diet among generally well populations is likely to require a range of sustained approaches and multiple forms of communication in a process measured in decades rather than months”. Jenkins J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017; 69(9): 1103-12
Lifetime CVD Risk Management Total starts: 2,115,568 Total completes: 882,260 Launched on Feb 14th 2015 Starts 2,115,568 Completes 882,260
Heart Age 2 - Starts: 449,289 / Completes: 232,262 Age Features TC W e i g h t From 26.09.2016 – 10.02.2017
Digital Health: Empowerment ?
CV RF lowering and Dementia Risk? What’s Good for the Heart is Good for the Brain!
Mid LifeCV RFs and Dementia Risk Factors CV composite Score 2.5 8845 HMO patients 2.0 Age 40-43 yrs Hazard Factor 1.5 1.0 0.5 0 1 2 3 4 Whitmer Neurology 2005; 64: 277-281
Multidomain Treatment and Cognitive Decline: FINGER Trial Ngandu Lancet 2015; 385: 2255-2263
Statins and IMT in FH Children 208 FH children (8-18 yrs) 2 yrs with Pravastatin 20-40mg Placebo (n=104) Pravastatin (n=104) 15 Mean D IMT (mm) 10 5 0 -5 -10 -15 CCA Bulb CA Mean carotid P=0.06 P=0.3 P=0.2 P=0.019 Weigman JACC 2004
ALSPAC: Vascular Risk Factors at 9-11 yrs v. BMI 120 5 Blood pressure (mm Hg) Cholesterol (mmol/L) 4 Systolic Non-HDL Cholesterol 100 3 80 2 Diastolic 60 1 HDL Cholesterol 15 20 25 30 15 20 25 30 BMI (Kg/m 2 ) BMI (Kg/m 2 )
BMI during adolescence and CV mortality Twig G et al, NEJM 2016;374:2430-40
Revolution in the Delivery of Medicine Early Management / Digital Systems Wellness Illness Ageing
McConachie et al July 2013
Trends in Calories from Beverages National tax of 1% per oz of drink $14.9 billion State tax Florida $928 million Alabama $221 million 72% approval for health promotion 2008 NYC poll Brownell NEJM 2009;361:1599-1605
CVD Prevention: Never too early! Early intervention for lifetime gain. Novel treatment approaches Better communication, especially with the young Empowerment including use of innovative technology Political / legislative interventions Doctors need to play a major role in all of these!
Final Thought… “ It should be the function of medicine to have people die young as late as possible ” Ernest L. Wynder M.D.
Recommend
More recommend