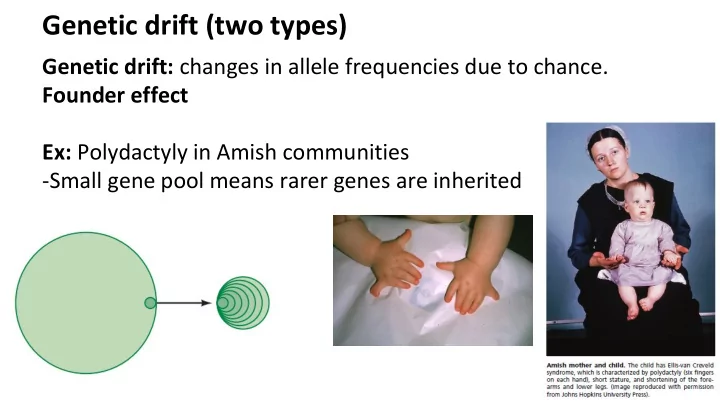

Genetic drift (two types) Genetic drift: changes in allele frequencies due to chance. Founder effect Ex: Polydactyly in Amish communities -Small gene pool means rarer genes are inherited 1
Genetic drift (two types) Genetic bottleneck: population shrinks to only a few people. Ex: Pingelap islanders are mostly colorblind. 2
Gene flow (migration) Gene flow: Exchange of genes between populations. -AKA migration Ex: Low occurrence of hominin speciation in the past million years explained by migration. 3
Natural selection -Acts on variation produced and redistributed by mutations, recombination, genetic drift, and gene flow. -Differential reproductive success relative to the environment. 4
Anthropology example: Sickle-cell anemia -Lethal, genetically inherited blood disease. -The phenotype of a mutated hemoglobin allele -Collapses red blood cells into sickles 5
Sickle-cell trait: Natural selection in humans 6
Anthropology example: Sickle-cell anemia Expect: Selection against sickle-cell allele. Instead: 30% some regional populations are carriers. 7
Anthropology example: Sickle-cell anemia Correlation between geographic locations with a malarial pressure and high frequencies of SCT 8
Anthropology example: Sickle-cell anemia Geographic distribution: Mediterranean, Arabian peninsula, Southeast Asia, West Africa. 9
Anthropology example: Sickle-cell anemia 10
Macroevolution Classification Kingdom: Animalia Phyla: Chordata Class: Mammalia Order: Primate Family: Hominidae Genus: Homo Species: sapiens 11
Classifying biology Question: Based on physical traits alone, which is the most similar? -Classification based on evolutionary relationships 12
Homologies Homologies: similarities between groups due to common descent. Ex: birds, bats, mice, crocs all have four limbs Contrast with analogies : similarities due to common function 13
Two types of homologies Ancestral traits: similarities in many taxonomic groups inherited from a remote ancestor. Derived traits: modified from the ancestral conditions. 14
Schools of classification Evolutionary systematics: hypothesizes about ancestor-descendant relationships over time -Make phylogenetic trees 15
Schools of classification Cladistics: use shared derived traits to identify new species Clades: lineages sharing a common ancestor. 16
Recommend
More recommend