
EVA An Expert System for Vases of the Antiquity Martina Trognitz Deutsches Arch¨ aologisches Institut, Berlin 22 October 2013 M. Trognitz (DAI) EVA 1 / 31
What is EVA? EVA is an expert system for computer aided classification and dating of ceramics. It represents the application of natural language processing methods for an archaeological problem. It was the subject of my master thesis at the University of Heidelberg, in the department of Computational Linguistics. M. Trognitz (DAI) EVA 2 / 31
Outline 1 Motivation 2 The problem 3 What is an expert system? How it works Properties 4 Implementation Before implementation System architecture The knowledge base Description texts 5 Discussion M. Trognitz (DAI) EVA 3 / 31
Motivation Motivation Combination of computational linguistics and archaeology Fill the gap between the number of human experts and amount of unclassified ceramic EVA could provide a second opinion and be used as a learning tool M. Trognitz (DAI) EVA 4 / 31
The problem Outline 1 Motivation 2 The problem 3 What is an expert system? How it works Properties 4 Implementation Before implementation System architecture The knowledge base Description texts 5 Discussion M. Trognitz (DAI) EVA 5 / 31
The problem The problem Ceramic is a common find at excavations. Form and decoration depend on various factors and change in the course of time: cultural environment source taste and fashion technical achievements Hence ceramic is used to date archeological find deposits. It serves as a type fossil. M. Trognitz (DAI) EVA 6 / 31
The problem Problem An ancient Greek vase is a difficult object for the non-expert to come to terms with. Faced with rows of apparently undifferentiated black, red and buff pots, he or she is at a loss as to where to begin. Tom Rasmussen & Nigel Spivey M. Trognitz (DAI) EVA 7 / 31
The problem Problem An ancient Greek vase is a difficult object for the non-expert to come to terms with. Faced with rows of apparently undifferentiated black, red and buff pots, he or she is at a loss as to where to begin. Tom Rasmussen & Nigel Spivey Solution Store the knowledge of an expert into an expert system to classify and date ceramic. M. Trognitz (DAI) EVA 7 / 31
What is an expert system? Outline 1 Motivation 2 The problem 3 What is an expert system? How it works Properties 4 Implementation Before implementation System architecture The knowledge base Description texts 5 Discussion M. Trognitz (DAI) EVA 8 / 31
What is an expert system? What is an expert system? It is a program capable of solving problems similarly as human experts would do. It uses knowledge and inference methods to solve problems. It can solve complex problems normally requiring enourmous human expertise. Edward Feigenbaum “Father of expert systems” M. Trognitz (DAI) EVA 9 / 31
What is an expert system? Special subject of artificial intelligence Early systems were developed in the sixties (DENDRAL) They are used comercially since the eighties Can be used in a wide range of subjects (MYCIN, PROSPECTOR, XCON/R1) M. Trognitz (DAI) EVA 10 / 31
What is an expert system? Special subject of artificial intelligence Early systems were developed in the sixties (DENDRAL) They are used comercially since the eighties Can be used in a wide range of subjects (MYCIN, PROSPECTOR, XCON/R1) Remark An expert system only works well in a well-defined special field, the knowledge domain . M. Trognitz (DAI) EVA 10 / 31
What is an expert system? How it works How it works expert system facts & informations user interface knowledge base expertise user inference engine M. Trognitz (DAI) EVA 11 / 31
What is an expert system? How it works Functionality of the inference engine inference engine deductions facts agenda working memory knowledge base M. Trognitz (DAI) EVA 12 / 31
What is an expert system? Properties Properties of expert systems high perfomance, results compete with those of human experts proper response time robust understandable flexible M. Trognitz (DAI) EVA 13 / 31
What is an expert system? Properties Properties of expert systems high perfomance, results compete with those of human experts proper response time robust understandable flexible Remark The knowledge is explicitly disconnected from the processig part of the program. M. Trognitz (DAI) EVA 13 / 31
Implementation Outline 1 Motivation 2 The problem 3 What is an expert system? How it works Properties 4 Implementation Before implementation System architecture The knowledge base Description texts 5 Discussion M. Trognitz (DAI) EVA 14 / 31
Implementation Before implementation Before implementation Size of knowledge domain? “Ancient vases” is reduced to: attic protogeometric and geometric Knowledge base? sort of a rule-based system based on a decision tree Inference engine and knowledge base depend on each other The system is implemented with Python M. Trognitz (DAI) EVA 15 / 31
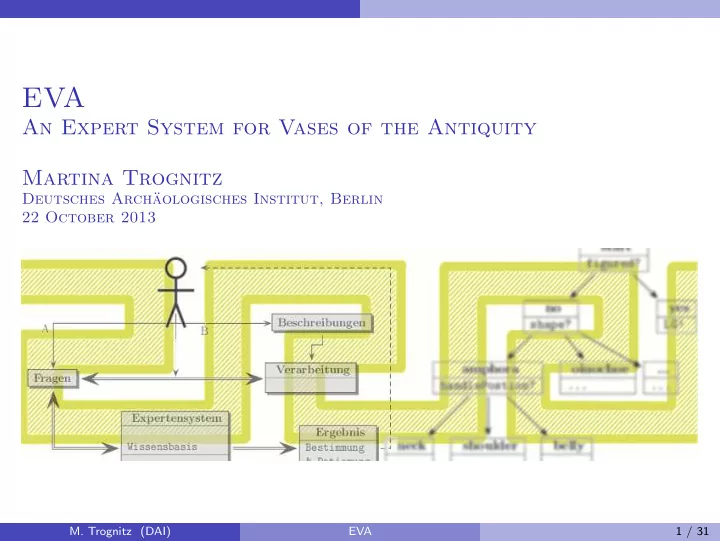
Implementation System architecture System architecture desriptions user B A processing questions expert system results knowledge base classification & dating inference engine M. Trognitz (DAI) EVA 16 / 31
Implementation The knowledge base The knowledge base The knowledge base is the heart of the system A restricted, well-defined knowledge domain is mapped to a knowledge base The knowledge representation depends on: area of application scope source of knowledge functionality of the inference engine A knowledge engineer transfers the knowledge from an expert to the knowledge base of the expert system. M. Trognitz (DAI) EVA 17 / 31
Implementation The knowledge base Why a decision tree? A specific vase can be described with a specific set of characteristics. EG I: figured:no; shape:amphora; handlePosition:neck; handleForm:band; body:ovoid; motifs:band of slanting lines MG II: figured:no; shape:amphora; handlePosition:neck; handleForm:band; body:ovoid; motifs:hatched meander, zigzag, dogtooth IF a specific set of characteristics is given THEN you get a specific vase. M. Trognitz (DAI) EVA 18 / 31
Implementation The knowledge base Decision tree in EVA start figured? no yes shape? LG! amphora oinochoe ... handlePostion? ... ... neck shoulder belly ... ... ... M. Trognitz (DAI) EVA 19 / 31
Implementation The knowledge base tree.py The decision tree is built in the module tree.py Each node in the tree consists of a value, a question related to the value, a link to the parent node and a list of child nodes. no yes shape? LG! amphora oinochoe ... handlePostion? ... ... M. Trognitz (DAI) EVA 20 / 31
Implementation The knowledge base Knowledge base details The knowledge base is stored in a separate text file root - figured? : yes - LG! root - figured? : no - shape? : amphora - handlePosition? : neck - ... root - figured? : no - shape? : amphora - handlePosition? : shoulder - The full question that is displayed to the user is stored in dictionaries.py M. Trognitz (DAI) EVA 21 / 31
Implementation Description texts Description texts descriptions user B A processing questions expert system result knowledge base classification & dating inference engine M. Trognitz (DAI) EVA 22 / 31
Implementation Description texts Description texts descriptions user B A processing questions expert system result knowledge base classification & dating inference engine M. Trognitz (DAI) EVA 22 / 31
Implementation Description texts This is a small oinochoe. The handle is outlined and has a wavy line. The rim is decorated with three horizontal lines. On the neck a horizontal row of dots, a horizontal panel with a lozenge chain and another row of dots can be seen. The shoulder is decorated with a dotted snake and some sparse dots. On the belly are linked dots. All ornaments are interspersed by encircling bands. The lower part of the CVA Oxford 4 (GB, 24) p. vase is covered by a thin layer of clay. 12, plate 30 1-3 M. Trognitz (DAI) EVA 23 / 31
Implementation Description texts This is a small oinochoe. The handle is outlined and has a wavy line. The rim is decorated with three horizontal lines. On the neck a horizontal row of dots, a horizontal panel with a lozenge chain and another row of dots can be seen. The shoulder is decorated with a dotted snake and some sparse dots. On the belly are linked dots. All ornaments are interspersed by encircling bands. The lower part of the CVA Oxford 4 (GB, 24) p. vase is covered by a thin layer of clay. 12, plate 30 1-3 M. Trognitz (DAI) EVA 23 / 31
Implementation Description texts Some aspects of natural language texts The form and structure of the texts depend on: personal style language skills knowledge of the subject Some informations may be missing M. Trognitz (DAI) EVA 24 / 31
Implementation Description texts Information extraction Question At which part of the body are the handles attached? M. Trognitz (DAI) EVA 25 / 31
Recommend
More recommend