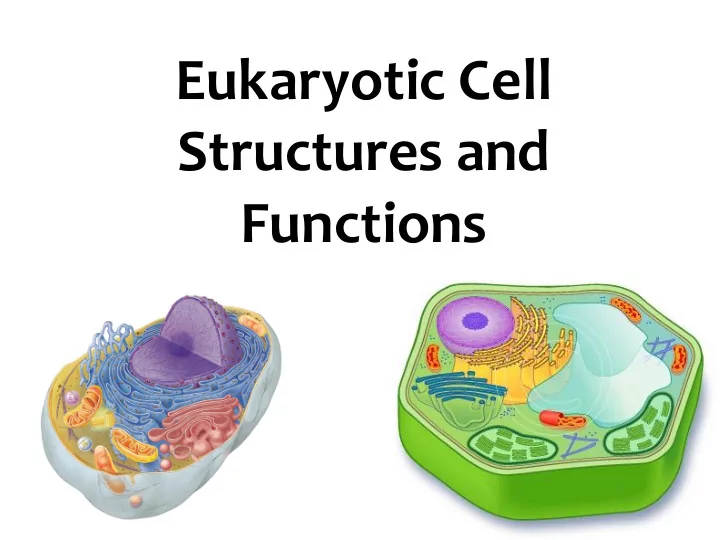

Eukaryotic Cell Structures and Functions
General Animal Cell Structure
General Plant Cell Structure
Plant Cells Animal Cells
Cell Structures
Plasma Membrane • Surrounds the cell, “selectively” permeable • Composed of a phospholipid bilayer (2 layers) and embedded proteins • Controls the passage of cell materials into and out of the cell
Cytoplasm • Primarily composed of water, salts and organic molecules • Suspends cell organelles inside the cell
Cytoskeleton • Internal support system for the cell • Assists in the movement of organelles within the cell • Composed of microfilaments and microtubules (contractile proteins)
Nucleus • Surrounded by a nuclear envelope with nuclear pores • Contains genetic information (DNA) which exists as chromatin in a non-dividing cell • Controls all cell activities
Nucleolus • Located within the nucleus • Produces parts of ribosomes
Nucleus, Nucleolus and Nuclear Pores
Mitochondrion • Produces cellular energy in the form of ATP molecules through a process called cellular respiration • During the process of cellular respiration, glucose is metabolized in the presence of oxygen to produce ATP
Ribosome • Site of protein synthesis • Ribosomes link amino acids together to form proteins during gene expression • All cell types contain ribosomes
Vesicle • Membrane-bound pouch that transports cell materials between organelles and throughout the cell
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) • Assists in the synthesis and transport of cell materials • Two types: rough (with ribosomes) and smooth (without ribosomes)
Rough and Smooth ER • Rough ER has ribosomes which give this structure a textured appearance, functions in synthesizing proteins • Smooth ER contains enzymes that function to synthesize lipids and hormones
Golgi Bodies • Consists of flattened stacks of membranes • Collects, packages and modifies cell materials to be used within the cell or exported out of the cell
Lysosome • Contain strong hydrolytic enzymes • Break down old cell parts and cell wastes
Centrioles • Composed of microtubules, used during cell division to move and separate chromosomes • Found only in animal cells
Vacuole • Specialized structure that primarily stores water in plants cells, sometimes waste storage
Chloroplast • Site of photosynthesis where light energy is converted into chemical energy (glucose) • Found in plant cells and photosynthetic protists (e.g. algae, Euglena)
Cell Wall • Exterior structure and support for cells, located surrounding the plasma membrane • Plants, bacteria and fungi all have cells with cells walls • Cell wall composition: – Plants – cellulose and pectin – Fungi – chitin – Bacteria - petidoglycan
Cell Movement • Some cells have structures that assist in movement – Cilia – numerous little hairs, cover cell surface – Flagella – whip-like structure that propels cells – Pseudopods – cytoplasmic extensions that help some cells move and obtain food (e.g. amoebas)
Recommend
More recommend