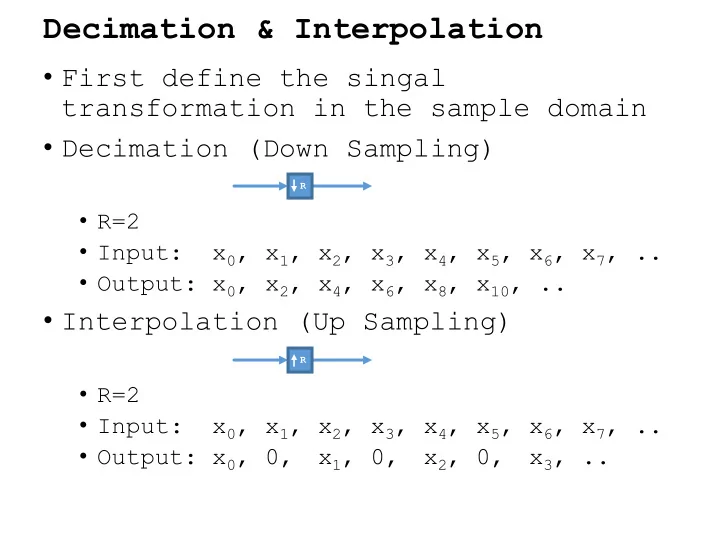

Decimation & Interpolation • First define the singal transformation in the sample domain • Decimation (Down Sampling) R • R=2 • Input: x 0 , x 1 , x 2 , x 3 , x 4 , x 5 , x 6 , x 7 , .. • Output: x 0 , x 2 , x 4 , x 6 , x 8 , x 10 , .. • Interpolation (Up Sampling) R • R=2 • Input: x 0 , x 1 , x 2 , x 3 , x 4 , x 5 , x 6 , x 7 , .. • Output: x 0 , 0, x 1 , 0, x 2 , 0, x 3 , ..
Decimation & Interpolation • Mathematical representation in the sample domain for ratio R: • Decimation: R x dec [n] = x[ R∙n ] • Interpolation: R x int [n] = x[n/R], for integer n/2 0, otherwise
Decimation & Interpolation • Mathematical representation in the normalized freq domain for ratio R. • Assuming real sample domain signals. • F goes from 0 to 1. • Decimation: R X dec (F) = X(F/R) + X(F/R + 1/R) + ... X(F/R + (R-1)/R) • Interpolation: R X int (F) = X(R*F mod 1)) ***Doesn’t account for scaling factors***
Example Spectrums • R=4 • Decimation • Interpolation
Filtering • Decimation • Filter before resampling. • Interpolation • Filter after resampling
Types of interpolation filters • Nearest • h R = [ones(R)], h 4 = [1 1 1 1] • R=4 • Input: x 0 , x 1 , x 2 , x 3 , x 4 , x 5 , x 6 , x 7 , .. • Output: x 0 ,0,0,0,x 1 ,0,0,0,x 2 ,0,0,0,x 3 , .. • 1 ,1,1,1 x 0 • 1,1,1,1 x 1 • 1,1,1, 1 x 1 • 1,1, 1,1 x 1 • 1, 1,1,1 x 1 • 1,1,1, 1 x 2 • Filter: x 0 ,x 1 ,x 1 ,x 1 ,x 1 ,x 2 ,..
Types of interpolation filters • linear • h R = [ones(R)*ones(R)]/R, • h 4 = [1 2 3 4 3 2 1]/R • R=4 • Input: x 0 , x 1 , x 2 , x 3 , x 4 , x 5 , x 6 , x 7 , .. • Output: x 0 ,0,0,0,x 1 ,0,0,0,x 2 ,0,0,0,x 3 , .. • [1 2 3 4 3 2 1]/4 (4x 0 +0x 1 )/4 • [1 2 3 4 3 2 1]/4 (3x 0 +1x 1 )/4 • [1 2 3 4 3 2 1]/4 (2x 0 +2x 1 )/4 • [1 2 3 4 3 2 1]/4 (1x 0 +3x 1 )/4 • [1 2 3 4 3 2 1]/4 (0x 0 +4x 1 )/4
Types of interpolation filters • Linear (first order expansion) • Alternative approach x(0) | | | x(1) • Expansion about a point half way between the two points. x int = x(1/2) + (x(1)- x(0))∙[ -.375 -.125 .125 .375] x int = (x(1)+x(0))/2 + (x(1)- x(0))∙[ -.375 -.125 .125 .375] x int = x(1)(1/2 + [-.375 -.125 .125 .375]) + x(0)(1/2 - [-.375 -.125 .125 .375]) • This filter looks like this ... [.125 .375 .625 .875 .875 .625 .375 .125]
Types of interpolation filters • Second Order Expansion • Alternative approach x(0) | | | x(1) | | | x(2) • Expansion about x(1). • Approximate x(1) = x(1) • Approximate x’(1) = (x(2) -x(0))/2 • Approximate (1/2)x’’(1) = (x(2) -2x(1)-x(1))/2 • Evaluate at points • n = [-.375 -.125 .125 .375] • n 2 = [-.375 2 -.125 2 .125 2 .375 2 ] • This filter looks like this ... [-0.1172 -0.0547 0.0703 0.2578 0.8594 0.9844 0.9844 0.8594 0.2578 0.0703 -0.0547 -0.1172]
Ideal Interpolation Filter • Ideally, the filter would retain the first image without any roll off and completely reject the images. • This is a sinc(n/R) filter.
Frequency Responses
sinc windowing
Recommend
More recommend