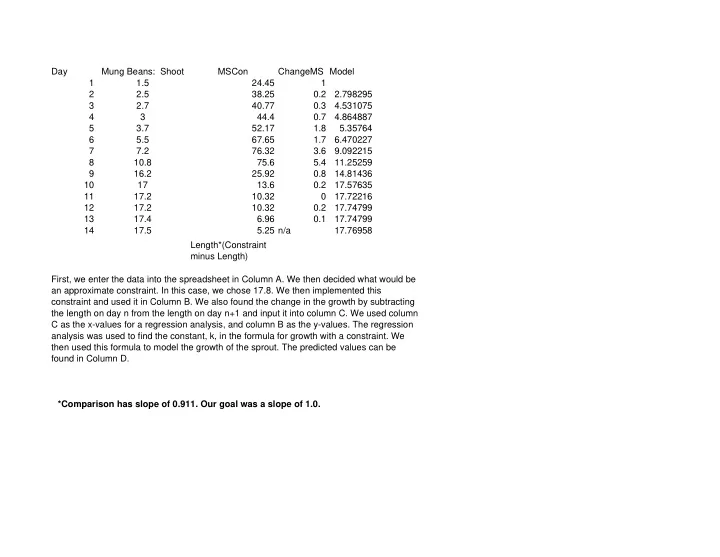

Day Mung Beans: Shoot MSCon ChangeMS Model 1 1.5 24.45 1 2 2.5 38.25 0.2 2.798295 3 2.7 40.77 0.3 4.531075 4 3 44.4 0.7 4.864887 5 3.7 52.17 1.8 5.35764 6 5.5 67.65 1.7 6.470227 7 7.2 76.32 3.6 9.092215 8 10.8 75.6 5.4 11.25259 9 16.2 25.92 0.8 14.81436 10 17 13.6 0.2 17.57635 11 17.2 10.32 0 17.72216 12 17.2 10.32 0.2 17.74799 13 17.4 6.96 0.1 17.74799 14 17.5 5.25 n/a 17.76958 Length*(Constraint minus Length) First, we enter the data into the spreadsheet in Column A. We then decided what would be an approximate constraint. In this case, we chose 17.8. We then implemented this constraint and used it in Column B. We also found the change in the growth by subtracting the length on day n from the length on day n+1 and input it into column C. We used column C as the x-values for a regression analysis, and column B as the y-values. The regression analysis was used to find the constant, k, in the formula for growth with a constraint. We then used this formula to model the growth of the sprout. The predicted values can be found in Column D. *Comparison has slope of 0.911. Our goal was a slope of 1.0.
Shoot Growth of the Mung Bean 20 Length of Shoot (cm) 15 10 5 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 Day Mung Bean Shoot Comparison y = 0.911x + 1.701 20 Predicted Length (cm) 15 10 5 0 0 5 10 15 20 Actual Length (cm)
SUMMARY OUTPUT Regression Statistics Multiple R 0.823321 R Square 0.677857 Adjusted R 0.648571 Standard E 0.951396 Observatio 13 ANOVA df SS MS F ignificance F Regression 1 20.95099 20.95099 23.14632 0.000544 Residual 11 9.956698 0.905154 Total 12 30.90769 Coefficientstandard Erro t Stat P-value Lower 95%Upper 95% Lower 95.0% Upper 95.0% Intercept -0.757737 0.490368 -1.545243 0.150555 -1.837029 0.321555 -1.837029 0.321555 X Variable 0.053111 0.011039 4.811062 0.000544 0.028813 0.077408 0.028813 0.077408
%
Recommend
More recommend